11 The following information is available for Orset, a sole trader who does not keep full accounting records:$Inventory 1 July 2004 138,60030 June 2005 149,100Purchases for year ended 30 June 2005 716,100Orset makes a standard gross profit of 30 per cent
题目
11 The following information is available for Orset, a sole trader who does not keep full accounting records:
$
Inventory 1 July 2004 138,600
30 June 2005 149,100
Purchases for year ended 30 June 2005 716,100
Orset makes a standard gross profit of 30 per cent on sales.
Based on these figures, what is Orset’s sales figure for the year ended 30 June 2005?
A $2,352,000
B $1,038,000
C $917,280
D $1,008,000
相似考题
更多“11 The following information is available for Orset, a sole trader who does not keep full accounting records:$Inventory 1 July 2004 138,60030 June 2005 149,100Purchases for year ended 30 June 2005 716,100Orset makes a standard gross profit of 30 per cent ”相关问题
-
第1题:
24 Sigma’s bank statement shows an overdrawn balance of $38,600 at 30 June 2005. A check against the company’s cash book revealed the following differences:
1 Bank charges of $200 have not been entered in the cash book.
2 Lodgements recorded on 30 June 2005 but credited by the bank on 2 July $14,700.
3 Cheque payments entered in cash book but not presented for payment at 30 June 2005 $27,800.
4 A cheque payment to a supplier of $4,200 charged to the account in June 2005 recorded in the cash book as a receipt.
Based on this information, what was the cash book balance BEFORE any adjustments?
A $43,100 overdrawn
B $16,900 overdrawn
C $60,300 overdrawn
D $34,100 overdrawn
正确答案:A
-
第2题:
(b) Ambush loaned $200,000 to Bromwich on 1 December 2003. The effective and stated interest rate for this
loan was 8 per cent. Interest is payable by Bromwich at the end of each year and the loan is repayable on
30 November 2007. At 30 November 2005, the directors of Ambush have heard that Bromwich is in financial
difficulties and is undergoing a financial reorganisation. The directors feel that it is likely that they will only
receive $100,000 on 30 November 2007 and no future interest payment. Interest for the year ended
30 November 2005 had been received. The financial year end of Ambush is 30 November 2005.
Required:
(i) Outline the requirements of IAS 39 as regards the impairment of financial assets. (6 marks)
正确答案:
(b) (i) IAS 39 requires an entity to assess at each balance sheet date whether there is any objective evidence that financial
assets are impaired and whether the impairment impacts on future cash flows. Objective evidence that financial assets
are impaired includes the significant financial difficulty of the issuer or obligor and whether it becomes probable that the
borrower will enter bankruptcy or other financial reorganisation.
For investments in equity instruments that are classified as available for sale, a significant and prolonged decline in the
fair value below its cost is also objective evidence of impairment.
If any objective evidence of impairment exists, the entity recognises any associated impairment loss in profit or loss.
Only losses that have been incurred from past events can be reported as impairment losses. Therefore, losses expected
from future events, no matter how likely, are not recognised. A loss is incurred only if both of the following two
conditions are met:
(i) there is objective evidence of impairment as a result of one or more events that occurred after the initial recognition
of the asset (a ‘loss event’), and
(ii) the loss event has an impact on the estimated future cash flows of the financial asset or group of financial assets
that can be reliably estimated
The impairment requirements apply to all types of financial assets. The only category of financial asset that is not subject
to testing for impairment is a financial asset held at fair value through profit or loss, since any decline in value for such
assets are recognised immediately in profit or loss.
For loans and receivables and held-to-maturity investments, impaired assets are measured at the present value of the
estimated future cash flows discounted using the original effective interest rate of the financial assets. Any difference
between the carrying amount and the new value of the impaired asset is an impairment loss.
For investments in unquoted equity instruments that cannot be reliably measured at fair value, impaired assets are
measured at the present value of the estimated future cash flows discounted using the current market rate of return for
a similar financial asset. Any difference between the previous carrying amount and the new measurement of theimpaired asset is recognised as an impairment loss in profit or loss. -
第3题:
(c) Wader is reviewing the accounting treatment of its buildings. The company uses the ‘revaluation model’ for its
buildings. The buildings had originally cost $10 million on 1 June 2005 and had a useful economic life of
20 years. They are being depreciated on a straight line basis to a nil residual value. The buildings were revalued
downwards on 31 May 2006 to $8 million which was the buildings’ recoverable amount. At 31 May 2007 the
value of the buildings had risen to $11 million which is to be included in the financial statements. The company
is unsure how to treat the above events. (7 marks)
Required:
Discuss the accounting treatments of the above items in the financial statements for the year ended 31 May
2007.
Note: a discount rate of 5% should be used where necessary. Candidates should show suitable calculations where
necessary.
正确答案: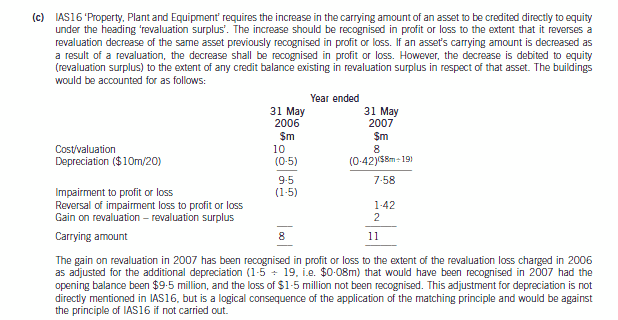
-
第4题:
17 A business income statement for the year ended 31 December 2004 showed a net profit of $83,600. It was later
found that $18,000 paid for the purchase of a motor van had been debited to motor expenses account. It is the
company’s policy to depreciate motor vans at 25 per cent per year, with a full year’s charge in the year of acquisition.
What would the net profit be after adjusting for this error?
A $106,100
B $70,100
C $97,100
D $101,600
正确答案:C
83,600 + 18,000 – 4,500 = 97,100 -
第5题:
2 The draft financial statements of Rampion, a limited liability company, for the year ended 31 December 2005
included the following figures:
$
Profit 684,000
Closing inventory 116,800
Trade receivables 248,000
Allowance for receivables 10,000
No adjustments have yet been made for the following matters:
(1) The company’s inventory count was carried out on 3 January 2006 leading to the figure shown above. Sales
between the close of business on 31 December 2005 and the inventory count totalled $36,000. There were no
deliveries from suppliers in that period. The company fixes selling prices to produce a 40% gross profit on sales.
The $36,000 sales were included in the sales records in January 2006.
(2) $10,000 of goods supplied on sale or return terms in December 2005 have been included as sales and
receivables. They had cost $6,000. On 10 January 2006 the customer returned the goods in good condition.
(3) Goods included in inventory at cost $18,000 were sold in January 2006 for $13,500. Selling expenses were
$500.
(4) $8,000 of trade receivables are to be written off.
(5) The allowance for receivables is to be adjusted to the equivalent of 5% of the trade receivables after allowing for
the above matters, based on past experience.
Required:
(a) Prepare a statement showing the effect of the adjustments on the company’s net profit for the year ended
31 December 2005. (5 marks)
正确答案:
-
第6题:
(b) The marketing director of CTC has suggested the introduction of a new toy ‘Nellie the Elephant’ for which the
following estimated information is available:
1. Sales volumes and selling prices per unit
Year ending, 31 May 2009 2010 2011
Sales units (000) 80 180 100
Selling price per unit ($) 50 50 50
2. Nellie will generate a contribution to sales ratio of 50% throughout the three year period.
3. Product specific fixed overheads during the year ending 31 May 2009 are estimated to be $1·6 million. It
is anticipated that these fixed overheads would decrease by 10% per annum during each of the years ending
31 May 2010 and 31 May 2011.
4. Capital investment amounting to $3·9 million would be required in June 2008. The investment would have
no residual value at 31 May 2011.
5. Additional working capital of $500,000 would be required in June 2008. A further $200,000 would be
required on 31 May 2009. These amounts would be recovered in full at the end of the three year period.
6. The cost of capital is expected to be 12% per annum.
Assume all cash flows (other than where stated) arise at the end of the year.
Required:
(i) Determine whether the new product is viable purely on financial grounds. (4 marks)
正确答案:
-
第7题:
3 You are the manager responsible for the audit of Albreda Co, a limited liability company, and its subsidiaries. The
group mainly operates a chain of national restaurants and provides vending and other catering services to corporate
clients. All restaurants offer ‘eat-in’, ‘take-away’ and ‘home delivery’ services. The draft consolidated financial
statements for the year ended 30 September 2005 show revenue of $42·2 million (2004 – $41·8 million), profit
before taxation of $1·8 million (2004 – $2·2 million) and total assets of $30·7 million (2004 – $23·4 million).
The following issues arising during the final audit have been noted on a schedule of points for your attention:
(a) In September 2005 the management board announced plans to cease offering ‘home delivery’ services from the
end of the month. These sales amounted to $0·6 million for the year to 30 September 2005 (2004 – $0·8
million). A provision of $0·2 million has been made as at 30 September 2005 for the compensation of redundant
employees (mainly drivers). Delivery vehicles have been classified as non-current assets held for sale as at 30
September 2005 and measured at fair value less costs to sell, $0·8 million (carrying amount,
$0·5 million). (8 marks)
Required:
For each of the above issues:
(i) comment on the matters that you should consider; and
(ii) state the audit evidence that you should expect to find,
in undertaking your review of the audit working papers and financial statements of Albreda Co for the year ended
30 September 2005.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three issues.
正确答案:3 ALBREDA CO
(a) Cessation of ‘home delivery’ service
(i) Matters
■ $0·6 million represents 1·4% of reported revenue (prior year 1·9%) and is therefore material.
Tutorial note: However, it is clearly not of such significance that it should raise any doubts whatsoever regarding
the going concern assumption. (On the contrary, as revenue from this service has declined since last year.)
■ The home delivery service is not a component of Albreda and its cessation does not classify as a discontinued
operation (IFRS 5 ‘Non-current Assets Held for Sale and Discontinued Operations’).
? It is not a cash-generating unit because home delivery revenues are not independent of other revenues
generated by the restaurant kitchens.
? 1·4% of revenue is not a ‘major line of business’.
? Home delivery does not cover a separate geographical area (but many areas around the numerous
restaurants).
■ The redundancy provision of $0·2 million represents 11·1% of profit before tax (10% before allowing for the
provision) and is therefore material. However, it represents only 0·6% of total assets and is therefore immaterial
to the balance sheet.
■ As the provision is a liability it should have been tested primarily for understatement (completeness).
■ The delivery vehicles should be classified as held for sale if their carrying amount will be recovered principally
through a sale transaction rather than through continuing use. For this to be the case the following IFRS 5 criteria
must be met:
? the vehicles must be available for immediate sale in their present condition; and
? their sale must be highly probable.
Tutorial note: Highly probable = management commitment to a plan + initiation of plan to locate buyer(s) +
active marketing + completion expected in a year.
■ However, even if the classification as held for sale is appropriate the measurement basis is incorrect.
■ Non-current assets classified as held for sale should be carried at the lower of carrying amount and fair value less
costs to sell.
■ It is incorrect that the vehicles are being measured at fair value less costs to sell which is $0·3 million in excess
of the carrying amount. This amounts to a revaluation. Wherever the credit entry is (equity or income statement)
it should be reversed. $0·3 million represents just less than 1% of assets (16·7% of profit if the credit is to the
income statement).
■ Comparison of fair value less costs to sell against carrying amount should have been made on an item by item
basis (and not on their totals).
(ii) Audit evidence
■ Copy of board minute documenting management’s decision to cease home deliveries (and any press
releases/internal memoranda to staff).
■ An analysis of revenue (e.g. extracted from management accounts) showing the amount attributed to home delivery
sales.
■ Redundancy terms for drivers as set out in their contracts of employment.
■ A ‘proof in total’ for the reasonableness/completeness of the redundancy provision (e.g. number of drivers × sum
of years employed × payment per year of service).
■ A schedule of depreciated cost of delivery vehicles extracted from the non-current asset register.
■ Checking of fair values on a sample basis to second hand market prices (as published/advertised in used vehicle
guides).
■ After-date net sale proceeds from sale of vehicles and comparison of proceeds against estimated fair values.
■ Physical inspection of condition of unsold vehicles.
■ Separate disclosure of the held for sale assets on the face of the balance sheet or in the notes.
■ Assets classified as held for sale (and other disposals) shown in the reconciliation of carrying amount at the
beginning and end of the period.
■ Additional descriptions in the notes of:
? the non-current assets; and
? the facts and circumstances leading to the sale/disposal (i.e. cessation of home delivery service). -
第8题:
5 You are an audit manager in Dedza, a firm of Chartered Certified Accountants. Recently, you have been assigned
specific responsibility for undertaking annual reviews of existing clients. The following situations have arisen in
connection with three client companies:
(a) Dedza was appointed auditor and tax advisor to Kora Co, a limited liability company, last year and has recently
issued an unmodified opinion on the financial statements for the year ended 30 June 2005. To your surprise,
the tax authority has just launched an investigation into the affairs of Kora on suspicion of underdeclaring income.
(7 marks)
Required:
Identify and comment on the ethical and other professional issues raised by each of these matters and state what
action, if any, Dedza should now take.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three situations.
正确答案:
5 DEDZA CO
(a) Tax investigation
■ Kora is a relatively new client. Before accepting the assignment(s) Dedza should have carried out customer due
diligence (CDD). Dedza should therefore have a sufficient knowledge and understanding of Kora to be aware of any
suspicions that the tax authority might have.
■ As the investigation has come as a surprise it is possible that, for example:
– the tax authority’s suspicions are unfounded;
– Dedza has failed to recognise suspicious circumstances.
Tutorial note: In either case, Dedza should seek clarification on the period of suspicion and review relevant procedures.
■ Dedza should review any communication from the predecessor auditor obtained in response to its ‘professional inquiry’
(for any professional reasons why the appointment should not have been accepted).
■ A quality control for new audits is that the audit opinion should be subject to a second partner review before it is issued.
It should be considered now whether or not such a review took place. If it did, then it should be sufficiently well
documented to evidence that the review was thorough and not a mere formality.
■ Criminal property includes the proceeds of tax evasion. If Kora is found to be guilty of under-declaring income that is a
money laundering offence.
■ Dedza’s reputational risk will be increased if implicated because it knew (or ought to have known) about Kora’s activities.
(Dedza may also be liable if found to have been negligent in failing to detect any material misstatement arising in the
2004/05 financial statements as a result.)
■ Kora’s audit working paper files and tax returns should be reviewed for any suspicion of fraud being committed by Kora
or error overlooked by Dedza. Tax advisory work should have been undertaken and/or reviewed by a manager/partner
not involved in the audit work.
■ As tax advisor, Dedza could soon be making disclosures of misstatements to the tax authority on behalf of Kora. Dedza
should encourage Kora to make necessary disclosure voluntarily.
■ Dedza will not be in breach of its duty of confidentiality to Kora if Kora gives Dedza permission to disclose information
to the tax authority (or Dedza is legally required to do so).
■ If Dedza finds reasonable grounds to know or suspect that potential disclosures to the tax authority relate to criminal
conduct, then a suspicious transaction report (STR) should be made to the financial intelligence unit (FIU) also.
Tutorial note: Though not the main issue credit will be awarded for other ethical issues such as the potential selfinterest/
self-review threat arising from the provision of other services. -
第9题:
(b) You are the audit manager of Johnston Co, a private company. The draft consolidated financial statements for
the year ended 31 March 2006 show profit before taxation of $10·5 million (2005 – $9·4 million) and total
assets of $55·2 million (2005 – $50·7 million).
Your firm was appointed auditor of Tiltman Co when Johnston Co acquired all the shares of Tiltman Co in March
2006. Tiltman’s draft financial statements for the year ended 31 March 2006 show profit before taxation of
$0·7 million (2005 – $1·7 million) and total assets of $16·1 million (2005 – $16·6 million). The auditor’s
report on the financial statements for the year ended 31 March 2005 was unmodified.
You are currently reviewing two matters that have been left for your attention on the audit working paper files for
the year ended 31 March 2006:
(i) In December 2004 Tiltman installed a new computer system that properly quantified an overvaluation of
inventory amounting to $2·7 million. This is being written off over three years.
(ii) In May 2006, Tiltman’s head office was relocated to Johnston’s premises as part of a restructuring.
Provisions for the resulting redundancies and non-cancellable lease payments amounting to $2·3 million
have been made in the financial statements of Tiltman for the year ended 31 March 2006.
Required:
Identify and comment on the implications of these two matters for your auditor’s reports on the financial
statements of Johnston Co and Tiltman Co for the year ended 31 March 2006. (10 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Tiltman Co
Tiltman’s total assets at 31 March 2006 represent 29% (16·1/55·2 × 100) of Johnston’s total assets. The subsidiary is
therefore material to Johnston’s consolidated financial statements.
Tutorial note: Tiltman’s profit for the year is not relevant as the acquisition took place just before the year end and will
therefore have no impact on the consolidated income statement. Calculations of the effect on consolidated profit before
taxation are therefore inappropriate and will not be awarded marks.
(i) Inventory overvaluation
This should have been written off to the income statement in the year to 31 March 2005 and not spread over three
years (contrary to IAS 2 ‘Inventories’).
At 31 March 2006 inventory is overvalued by $0·9m. This represents all Tiltmans’s profit for the year and 5·6% of
total assets and is material. At 31 March 2005 inventory was materially overvalued by $1·8m ($1·7m reported profit
should have been a $0·1m loss).
Tutorial note: 1/3 of the overvaluation was written off in the prior period (i.e. year to 31 March 2005) instead of $2·7m.
That the prior period’s auditor’s report was unmodified means that the previous auditor concurred with an incorrect
accounting treatment (or otherwise gave an inappropriate audit opinion).
As the matter is material a prior period adjustment is required (IAS 8 ‘Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting
Estimates and Errors’). $1·8m should be written off against opening reserves (i.e. restated as at 1 April 2005).
(ii) Restructuring provision
$2·3m expense has been charged to Tiltman’s profit and loss in arriving at a draft profit of $0·7m. This is very material.
(The provision represents 14·3% of Tiltman’s total assets and is material to the balance sheet date also.)
The provision for redundancies and onerous contracts should not have been made for the year ended 31 March 2006
unless there was a constructive obligation at the balance sheet date (IAS 37 ‘Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and
Contingent Assets’). So, unless the main features of the restructuring plan had been announced to those affected (i.e.
redundancy notifications issued to employees), the provision should be reversed. However, it should then be disclosed
as a non-adjusting post balance sheet event (IAS 10 ‘Events After the Balance Sheet Date’).
Given the short time (less than one month) between acquisition and the balance sheet it is very possible that a
constructive obligation does not arise at the balance sheet date. The relocation in May was only part of a restructuring
(and could be the first evidence that Johnston’s management has started to implement a restructuring plan).
There is a risk that goodwill on consolidation of Tiltman may be overstated in Johnston’s consolidated financial
statements. To avoid the $2·3 expense having a significant effect on post-acquisition profit (which may be negligible
due to the short time between acquisition and year end), Johnston may have recognised it as a liability in the
determination of goodwill on acquisition.
However, the execution of Tiltman’s restructuring plan, though made for the year ended 31 March 2006, was conditional
upon its acquisition by Johnston. It does not therefore represent, immediately before the business combination, a
present obligation of Johnston. Nor is it a contingent liability of Johnston immediately before the combination. Therefore
Johnston cannot recognise a liability for Tiltman’s restructuring plans as part of allocating the cost of the combination
(IFRS 3 ‘Business Combinations’).
Tiltman’s auditor’s report
The following adjustments are required to the financial statements:
■ restructuring provision, $2·3m, eliminated;
■ adequate disclosure of relocation as a non-adjusting post balance sheet event;
■ current period inventory written down by $0·9m;
■ prior period inventory (and reserves) written down by $1·8m.
Profit for the year to 31 March 2006 should be $3·9m ($0·7 + $0·9 + $2·3).
If all these adjustments are made the auditor’s report should be unmodified. Otherwise, the auditor’s report should be
qualified ‘except for’ on grounds of disagreement. If none of the adjustments are made, the qualification should still be
‘except for’ as the matters are not pervasive.
Johnston’s auditor’s report
If Tiltman’s auditor’s report is unmodified (because the required adjustments are made) the auditor’s report of Johnston
should be similarly unmodified. As Tiltman is wholly-owned by Johnston there should be no problem getting the
adjustments made.
If no adjustments were made in Tiltman’s financial statements, adjustments could be made on consolidation, if
necessary, to avoid modification of the auditor’s report on Johnston’s financial statements.
The effect of these adjustments on Tiltman’s net assets is an increase of $1·4m. Goodwill arising on consolidation (if
any) would be reduced by $1·4m. The reduction in consolidated total assets required ($0·9m + $1·4m) is therefore
the same as the reduction in consolidated total liabilities (i.e. $2·3m). $2·3m is material (4·2% consolidated total
assets). If Tiltman’s financial statements are not adjusted and no adjustments are made on consolidation, the
consolidated financial position (balance sheet) should be qualified ‘except for’. The results of operations (i.e. profit for
the period) should be unqualified (if permitted in the jurisdiction in which Johnston reports).
Adjustment in respect of the inventory valuation may not be required as Johnston should have consolidated inventory
at fair value on acquisition. In this case, consolidated total liabilities should be reduced by $2·3m and goodwill arising
on consolidation (if any) reduced by $2·3m.
Tutorial note: The effect of any possible goodwill impairment has been ignored as the subsidiary has only just been
acquired and the balance sheet date is very close to the date of acquisition. -
第10题:
(b) You are an audit manager in a firm of Chartered Certified Accountants currently assigned to the audit of Cleeves
Co for the year ended 30 September 2006. During the year Cleeves acquired a 100% interest in Howard Co.
Howard is material to Cleeves and audited by another firm, Parr & Co. You have just received Parr’s draft
auditor’s report for the year ended 30 September 2006. The wording is that of an unmodified report except for
the opinion paragraph which is as follows:
Audit opinion
As more fully explained in notes 11 and 15 impairment losses on non-current assets have not been
recognised in profit or loss as the directors are unable to quantify the amounts.
In our opinion, provision should be made for these as required by International Accounting Standard 36
(Impairment). If the provision had been so recognised the effect would have been to increase the loss before
and after tax for the year and to reduce the value of tangible and intangible non-current assets. However,
as the directors are unable to quantify the amounts we are unable to indicate the financial effect of such
omissions.
In view of the failure to provide for the impairments referred to above, in our opinion the financial statements
do not present fairly in all material respects the financial position of Howard Co as of 30 September 2006
and of its loss and its cash flows for the year then ended in accordance with International Financial Reporting
Standards.
Your review of the prior year auditor’s report shows that the 2005 audit opinion was worded identically.
Required:
(i) Critically appraise the appropriateness of the audit opinion given by Parr & Co on the financial
statements of Howard Co, for the years ended 30 September 2006 and 2005. (7 marks)
正确答案:(b) (i) Appropriateness of audit opinion given
Tutorial note: The answer points suggested by the marking scheme are listed in roughly the order in which they might
be extracted from the information presented in the question. The suggested answer groups together some of these
points under headings to give the analysis of the situation a possible structure.
Heading
■ The opinion paragraph is not properly headed. It does not state the form. of the opinion that has been given nor
the grounds for qualification.
■ The opinion ‘the financial statements do not give a true and fair view’ is an ‘adverse’ opinion.
■ That ‘provision should be made’, but has not, is a matter of disagreement that should be clearly stated as noncompliance
with IAS 36. The title of IAS 36 Impairment of Assets should be given in full.
■ The opinion should be headed ‘Disagreement on Accounting Policies – Inappropriate Accounting Method – Adverse
Opinion’.
1 ISA 250 does not specify with whom agreement should be reached but presumably with those charged with corporate governance (e.g audit committee or
2 other supervisory board).
20
6D–INTBA
Paper 3.1INT
Content
■ It is appropriate that the opinion paragraph should refer to the note(s) in the financial statements where the matter
giving rise to the modification is more fully explained. However, this is not an excuse for the audit opinion being
‘light’ on detail. For example, the reason for impairment could be summarised in the auditor’s report.
■ The effects have not been quantified, but they should be quantifiable. The maximum possible loss would be the
carrying amount of the non-current assets identified as impaired.
■ It is not clear why the directors have been ‘unable to quantify the amounts’. Since impairments should be
quantifiable any ‘inability’ suggest a limitation in scope of the audit, in which case the opinion should be disclaimed
(or ‘except for’) on grounds of lack of evidence rather than disagreement.
■ The wording is confusing. ‘Failure to provide’ suggests disagreement. However, there must be sufficient evidence
to support any disagreement. Although the directors cannot quantify the amounts it seems the auditors must have
been able to (estimate at least) in order to form. an opinion that the amounts involved are sufficiently material to
warrant a qualification.
■ The first paragraph refers to ‘non-current assets’. The second paragraph specifies ‘tangible and intangible assets’.
There is no explanation why or how both tangible and intangible assets are impaired.
■ The first paragraph refers to ‘profit or loss’ and the second and third paragraphs to ‘loss’. It may be clearer if the
first paragraph were to refer to recognition in the income statement.
■ It is not clear why the failure to recognise impairment warrants an adverse opinion rather than ‘except for’. The
effects of non-compliance with IAS 36 are to overstate the carrying amount(s) of non-current assets (that can be
specified) and to understate the loss. The matter does not appear to be pervasive and so an adverse opinion looks
unsuitable as the financial statements as a whole are not incomplete or misleading. A loss is already being reported
so it is not that a reported profit would be turned into a loss (which is sometimes judged to be ‘pervasive’).
Prior year
■ As the 2005 auditor’s report, as previously issued, included an adverse opinion and the matter that gave rise to
the modification:
– is unresolved; and
– results in a modification of the 2006 auditor’s report,
the 2006 auditor’s report should also be modified regarding the corresponding figures (ISA 710 Comparatives).
■ The 2006 auditor’s report does not refer to the prior period modification nor highlight that the matter resulting in
the current period modification is not new. For example, the report could say ‘As previously reported and as more
fully explained in notes ….’ and state ‘increase the loss by $x (2005 – $y)’. -
第11题:
The following trial balance relates to Sandown at 30 September 2009:
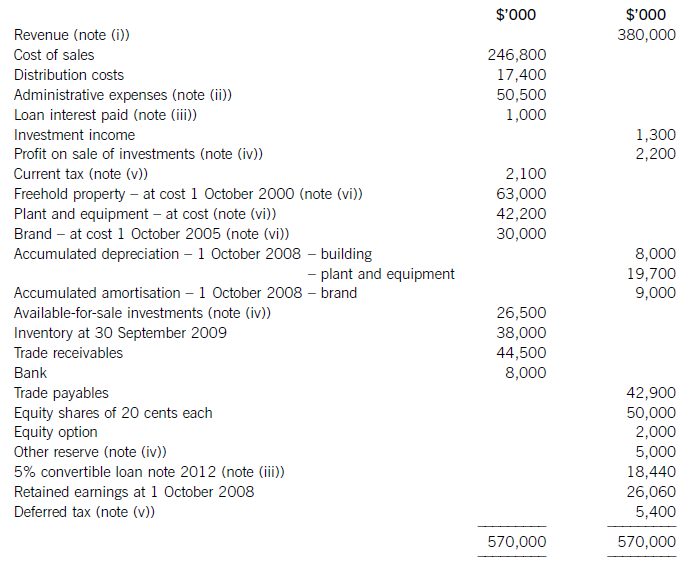
The following notes are relevant:
(i) Sandown’s revenue includes $16 million for goods sold to Pending on 1 October 2008. The terms of the sale are that Sandown will incur ongoing service and support costs of $1·2 million per annum for three years after the sale. Sandown normally makes a gross profit of 40% on such servicing and support work. Ignore the time value of money.
(ii) Administrative expenses include an equity dividend of 4·8 cents per share paid during the year.
(iii) The 5% convertible loan note was issued for proceeds of $20 million on 1 October 2007. It has an effective interest rate of 8% due to the value of its conversion option.
(iv) During the year Sandown sold an available-for-sale investment for $11 million. At the date of sale it had a
carrying amount of $8·8 million and had originally cost $7 million. Sandown has recorded the disposal of the
investment. The remaining available-for-sale investments (the $26·5 million in the trial balance) have a fair value of $29 million at 30 September 2009. The other reserve in the trial balance represents the net increase in the value of the available-for-sale investments as at 1 October 2008. Ignore deferred tax on these transactions.
(v) The balance on current tax represents the under/over provision of the tax liability for the year ended 30 September 2008. The directors have estimated the provision for income tax for the year ended 30 September 2009 at $16·2 million. At 30 September 2009 the carrying amounts of Sandown’s net assets were $13 million in excess of their tax base. The income tax rate of Sandown is 30%.
(vi) Non-current assets:
The freehold property has a land element of $13 million. The building element is being depreciated on a
straight-line basis.
Plant and equipment is depreciated at 40% per annum using the reducing balance method.
Sandown’s brand in the trial balance relates to a product line that received bad publicity during the year which led to falling sales revenues. An impairment review was conducted on 1 April 2009 which concluded that, based on estimated future sales, the brand had a value in use of $12 million and a remaining life of only three years.
However, on the same date as the impairment review, Sandown received an offer to purchase the brand for
$15 million. Prior to the impairment review, it was being depreciated using the straight-line method over a
10-year life.
No depreciation/amortisation has yet been charged on any non-current asset for the year ended 30 September
2009. Depreciation, amortisation and impairment charges are all charged to cost of sales.
Required:
(a) Prepare the statement of comprehensive income for Sandown for the year ended 30 September 2009.
(13 marks)
(b) Prepare the statement of financial position of Sandown as at 30 September 2009. (12 marks)
Notes to the financial statements are not required.
A statement of changes in equity is not required.
正确答案:
(i)IAS18Revenuerequiresthatwheresalesrevenueincludesanamountforaftersalesservicingandsupportcoststhenaproportionoftherevenueshouldbedeferred.Theamountdeferredshouldcoverthecostandareasonableprofit(inthiscaseagrossprofitof40%)ontheservices.Astheservicingandsupportisforthreeyearsandthedateofthesalewas1October2008,revenuerelatingtotwoyears’servicingandsupportprovisionmustbedeferred:($1·2millionx2/0·6)=$4million.Thisisshownas$2millioninbothcurrentandnon-currentliabilities. -
第12题:
The Jewish New Year most probably comes between ______.
A. July and September
B. October and December
C. January and March
D. April and June
正确答案:A51.答案为A 此号题为理解题。文章告读者犹太人庆祝新年是在夏季结束的时候。根据常识.我们可以推断山夏末应大约在7~9月份之间,故A正确。
-
第13题:
4 Ryder, a public limited company, is reviewing certain events which have occurred since its year end of 31 October
2005. The financial statements were authorised on 12 December 2005. The following events are relevant to the
financial statements for the year ended 31 October 2005:
(i) Ryder has a good record of ordinary dividend payments and has adopted a recent strategy of increasing its
dividend per share annually. For the last three years the dividend per share has increased by 5% per annum.
On 20 November 2005, the board of directors proposed a dividend of 10c per share for the year ended
31 October 2005. The shareholders are expected to approve it at a meeting on 10 January 2006, and a
dividend amount of $20 million will be paid on 20 February 2006 having been provided for in the financial
statements at 31 October 2005. The directors feel that a provision should be made because a ‘valid expectation’
has been created through the company’s dividend record. (3 marks)
(ii) Ryder disposed of a wholly owned subsidiary, Krup, a public limited company, on 10 December 2005 and made
a loss of $9 million on the transaction in the group financial statements. As at 31 October 2005, Ryder had no
intention of selling the subsidiary which was material to the group. The directors of Ryder have stated that there
were no significant events which have occurred since 31 October 2005 which could have resulted in a reduction
in the value of Krup. The carrying value of the net assets and purchased goodwill of Krup at 31 October 2005
were $20 million and $12 million respectively. Krup had made a loss of $2 million in the period 1 November
2005 to 10 December 2005. (5 marks)
(iii) Ryder acquired a wholly owned subsidiary, Metalic, a public limited company, on 21 January 2004. The
consideration payable in respect of the acquisition of Metalic was 2 million ordinary shares of $1 of Ryder plus
a further 300,000 ordinary shares if the profit of Metalic exceeded $6 million for the year ended 31 October
2005. The profit for the year of Metalic was $7 million and the ordinary shares were issued on 12 November
2005. The annual profits of Metalic had averaged $7 million over the last few years and, therefore, Ryder had
included an estimate of the contingent consideration in the cost of the acquisition at 21 January 2004. The fair
value used for the ordinary shares of Ryder at this date including the contingent consideration was $10 per share.
The fair value of the ordinary shares on 12 November 2005 was $11 per share. Ryder also made a one for four
bonus issue on 13 November 2005 which was applicable to the contingent shares issued. The directors are
unsure of the impact of the above on earnings per share and the accounting for the acquisition. (7 marks)
(iv) The company acquired a property on 1 November 2004 which it intended to sell. The property was obtained
as a result of a default on a loan agreement by a third party and was valued at $20 million on that date for
accounting purposes which exactly offset the defaulted loan. The property is in a state of disrepair and Ryder
intends to complete the repairs before it sells the property. The repairs were completed on 30 November 2005.
The property was sold after costs for $27 million on 9 December 2005. The property was classified as ‘held for
sale’ at the year end under IFRS5 ‘Non-current Assets Held for Sale and Discontinued Operations’ but shown at
the net sale proceeds of $27 million. Property is depreciated at 5% per annum on the straight-line basis and no
depreciation has been charged in the year. (5 marks)
(v) The company granted share appreciation rights (SARs) to its employees on 1 November 2003 based on ten
million shares. The SARs provide employees at the date the rights are exercised with the right to receive cash
equal to the appreciation in the company’s share price since the grant date. The rights vested on 31 October
2005 and payment was made on schedule on 1 December 2005. The fair value of the SARs per share at
31 October 2004 was $6, at 31 October 2005 was $8 and at 1 December 2005 was $9. The company has
recognised a liability for the SARs as at 31 October 2004 based upon IFRS2 ‘Share-based Payment’ but the
liability was stated at the same amount at 31 October 2005. (5 marks)
Required:
Discuss the accounting treatment of the above events in the financial statements of the Ryder Group for the year
ended 31 October 2005, taking into account the implications of events occurring after the balance sheet date.
(The mark allocations are set out after each paragraph above.)
(25 marks)
正确答案:
4 (i) Proposed dividend
The dividend was proposed after the balance sheet date and the company, therefore, did not have a liability at the balance
sheet date. No provision for the dividend should be recognised. The approval by the directors and the shareholders are
enough to create a valid expectation that the payment will be made and give rise to an obligation. However, this occurred
after the current year end and, therefore, will be charged against the profits for the year ending 31 October 2006.
The existence of a good record of dividend payments and an established dividend policy does not create a valid expectation
or an obligation. However, the proposed dividend will be disclosed in the notes to the financial statements as the directors
approved it prior to the authorisation of the financial statements.
(ii) Disposal of subsidiary
It would appear that the loss on the sale of the subsidiary provides evidence that the value of the consolidated net assets of
the subsidiary was impaired at the year end as there has been no significant event since 31 October 2005 which would have
caused the reduction in the value of the subsidiary. The disposal loss provides evidence of the impairment and, therefore,
the value of the net assets and goodwill should be reduced by the loss of $9 million plus the loss ($2 million) to the date of
the disposal, i.e. $11 million. The sale provides evidence of a condition that must have existed at the balance sheet date
(IAS10). This amount will be charged to the income statement and written off goodwill of $12 million, leaving a balance of
$1 million on that account. The subsidiary’s assets are impaired because the carrying values are not recoverable. The net
assets and goodwill of Krup would form. a separate income generating unit as the subsidiary is being disposed of before the
financial statements are authorised. The recoverable amount will be the sale proceeds at the date of sale and represents the
value-in-use to the group. The impairment loss is effectively taking account of the ultimate loss on sale at an earlier point in
time. IFRS5, ‘Non-current assets held for sale and discontinued operations’, will not apply as the company had no intention
of selling the subsidiary at the year end. IAS10 would require disclosure of the disposal of the subsidiary as a non-adjusting
event after the balance sheet date.
(iii) Issue of ordinary shares
IAS33 ‘Earnings per share’ states that if there is a bonus issue after the year end but before the date of the approval of the
financial statements, then the earnings per share figure should be based on the new number of shares issued. Additionally
a company should disclose details of all material ordinary share transactions or potential transactions entered into after the
balance sheet date other than the bonus issue or similar events (IAS10/IAS33). The principle is that if there has been a
change in the number of shares in issue without a change in the resources of the company, then the earnings per share
calculation should be based on the new number of shares even though the number of shares used in the earnings per share
calculation will be inconsistent with the number shown in the balance sheet. The conditions relating to the share issue
(contingent) have been met by the end of the period. Although the shares were issued after the balance sheet date, the issue
of the shares was no longer contingent at 31 October 2005, and therefore the relevant shares will be included in the
computation of both basic and diluted EPS. Thus, in this case both the bonus issue and the contingent consideration issue
should be taken into account in the earnings per share calculation and disclosure made to that effect. Any subsequent change
in the estimate of the contingent consideration will be adjusted in the period when the revision is made in accordance with
IAS8.
Additionally IFRS3 ‘Business Combinations’ requires the fair value of all types of consideration to be reflected in the cost of
the acquisition. The contingent consideration should be included in the cost of the business combination at the acquisition
date if the adjustment is probable and can be measured reliably. In the case of Metalic, the contingent consideration has
been paid in the post-balance sheet period and the value of such consideration can be determined ($11 per share). Thus
an accurate calculation of the goodwill arising on the acquisition of Metalic can be made in the period to 31 October 2005.
Prior to the issue of the shares on 12 November 2005, a value of $10 per share would have been used to value the
contingent consideration. The payment of the contingent consideration was probable because the average profits of Metalic
averaged over $7 million for several years. At 31 October 2005 the value of the contingent shares would be included in a
separate category of equity until they were issued on 12 November 2005 when they would be transferred to the share capital
and share premium account. Goodwill will increase by 300,000 x ($11 – $10) i.e. $300,000.
(iv) Property
IFRS5 (paragraph 7) states that for a non-current asset to be classified as held for sale, the asset must be available for
immediate sale in its present condition subject to the usual selling terms, and its sale must be highly probable. The delay in
this case in the selling of the property would indicate that at 31 October 2005 the property was not available for sale. The
property was not to be made available for sale until the repairs were completed and thus could not have been available for
sale at the year end. If the criteria are met after the year end (in this case on 30 November 2005), then the non-current
asset should not be classified as held for sale in the previous financial statements. However, disclosure of the event should
be made if it meets the criteria before the financial statements are authorised (IFRS5 paragraph 12). Thus in this case,
disclosure should be made.
The property on the application of IFRS5 should have been carried at the lower of its carrying amount and fair value less
costs to sell. However, the company has simply used fair value less costs to sell as the basis of valuation and shown the
property at $27 million in the financial statements.
The carrying amount of the property would have been $20 million less depreciation $1 million, i.e. $19 million. Because
the property is not held for sale under IFRS5, then its classification in the balance sheet will change and the property will be
valued at $19 million. Thus the gain of $7 million on the wrong application of IFRS5 will be deducted from reserves, and
the property included in property, plant and equipment. Total equity will therefore be reduced by $8 million.
(v) Share appreciation rights
IFRS2 ‘Share-based payment’ (paragraph 30) requires a company to re-measure the fair value of a liability to pay cash-settled
share based payment transactions at each reporting date and the settlement date, until the liability is settled. An example of
such a transaction is share appreciation rights. Thus the company should recognise a liability of ($8 x 10 million shares),
i.e. $80 million at 31 October 2005, the vesting date. The liability recognised at 31 October 2005 was in fact based on the
share price at the previous year end and would have been shown at ($6 x 1/2) x 10 million shares, i.e. $30 million. This
liability at 31 October 2005 had not been changed since the previous year end by the company. The SARs vest over a twoyear
period and thus at 31 October 2004 there would be a weighting of the eventual cost by 1 year/2 years. Therefore, an
additional liability and expense of $50 million should be accounted for in the financial statements at 31 October 2005. The
SARs would be settled on 1 December 2005 at $9 x 10 million shares, i.e. $90 million. The increase in the value of the
SARs since the year end would not be accrued in the financial statements but charged to profit or loss in the year ended31 October 2006. -
第14题:
(ii) Explain the accounting treatment under IAS39 of the loan to Bromwich in the financial statements of
Ambush for the year ended 30 November 2005. (4 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) There is objective evidence of impairment because of the financial difficulties and reorganisation of Bromwich. The
impairment loss on the loan will be calculated by discounting the estimated future cash flows. The future cash flows
will be $100,000 on 30 November 2007. This will be discounted at an effective interest rate of 8% to give a present
value of $85,733. The loan will, therefore, be impaired by ($200,000 – $85,733) i.e. $114,267.
(Note: IAS 39 requires accrual of interest on impaired loans at the original effective interest rate. In the year to
30 November 2006 interest of 8% of $85,733 i.e. $6,859 would be accrued.)
-
第15题:
8 P and Q are in partnership, sharing profits in the ratio 2:1. On 1 July 2004 they admitted P’s son R as a partner. P
guaranteed that R’s profit share would not be less than $25,000 for the six months to 31 December 2004. The profitsharing
arrangements after R’s admission were P 50%, Q 30%, R 20%. The profit for the year ended 31 December
2004 is $240,000, accruing evenly over the year.
What should P’s final profit share be for the year ended 31 December 2004?
A $140,000
B $139,000
C $114,000
D $139,375
正确答案:B
80,000 + 60,000 – 1,000 = 139,000 -
第16题:
2 The draft financial statements of Choctaw, a limited liability company, for the year ended 31 December 2004 showed
a profit of $86,400. The trial balance did not balance, and a suspense account with a credit balance of $3,310 was
included in the balance sheet.
In subsequent checking the following errors were found:
(a) Depreciation of motor vehicles at 25 per cent was calculated for the year ended 31 December 2004 on the
reducing balance basis, and should have been calculated on the straight-line basis at 25 per cent.
Relevant figures:
Cost of motor vehicles $120,000, net book value at 1 January 2004, $88,000
(b) Rent received from subletting part of the office accommodation $1,200 had been put into the petty cash box.
No receivable balance had been recognised when the rent fell due and no entries had been made in the petty
cash book or elsewhere for it. The petty cash float in the trial balance is the amount according to the records,
which is $1,200 less than the actual balance in the box.
(c) Bad debts totalling $8,400 are to be written off.
(d) The opening accrual on the motor repairs account of $3,400, representing repair bills due but not paid at
31 December 2003, had not been brought down at 1 January 2004.
(e) The cash discount totals for December 2004 had not been posted to the discount accounts in the nominal ledger.
The figures were:
$
Discount allowed 380
Discount received 290
After the necessary entries, the suspense account balanced.
Required:
Prepare journal entries, with narratives, to correct the errors found, and prepare a statement showing the
necessary adjustments to the profit.
(10 marks)
正确答案:
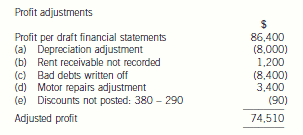
-
第17题:
(b) Comment (with relevant calculations) on the performance of the business of Quicklink Ltd and Celer
Transport during the year ended 31 May 2005 and, insofar as the information permits, its projected
performance for the year ending 31 May 2006. Your answer should specifically consider:
(i) Revenue generation per vehicle
(ii) Vehicle utilisation and delivery mix
(iii) Service quality. (14 marks)
正确答案: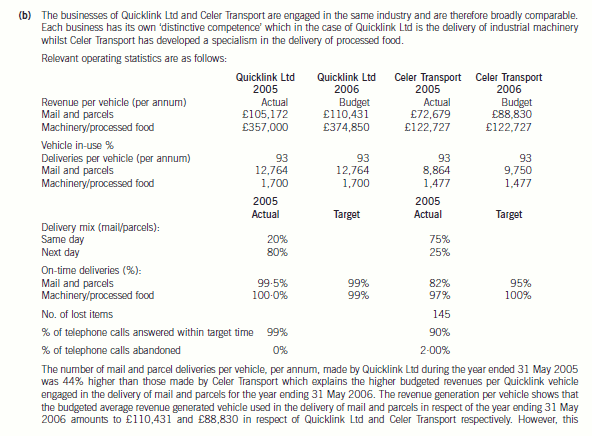
difference will reduce in the year ending 31 May 2006 due to the projected growth in sales volumes of the Celer Transport
business. The average mail/parcels delivery of mail/parcels per vehicle of the Quicklink Ltd part of the business is budgeted
at 12,764 which is still 30·91% higher than that of the Celer Transport business.
As far as specialist activities are concerned, Quicklink Ltd is budgeted to generate average revenues per vehicle amounting to
£374,850 whilst Celer Transport is budgeted to earn an average of £122,727 from each of the vehicles engaged in delivery
of processed food. It is noticeable that all contracts with major food producers were renewed on 1 June 2005 and it would
appear that there were no increases in the annual value of the contracts with major food producers. This might have been
the result of a strategic decision by the management of the combined entity in order to secure the future of this part of the
business which had been built up previously by the management of Celer Transport.
Each vehicle owned by Quicklink Ltd and Celer Transport is in use for 340 days during each year, which based on a
365 day year would give an in use % of 93%. This appears acceptable given the need for routine maintenance and repairs
due to wear and tear.
During the year ended 31 May 2005 the number of on-time deliveries of mail and parcel and industrial machinery deliveries
were 99·5% and 100% respectively. This compares with ratios of 82% and 97% in respect of mail and parcel and processed
food deliveries made by Celer Transport. In this critical area it is worth noting that Quicklink Ltd achieved their higher on-time
delivery target of 99% in respect of each activity whereas Celer Transport were unable to do so. Moreover, it is worth noting
that Celer Transport missed their target time for delivery of food products on 975 occasions throughout the year 31 May 2005
and this might well cause a high level of customer dissatisfaction and even result in lost business.
It is interesting to note that whilst the businesses operate in the same industry they have a rather different delivery mix in
terms of same day/next day demands by clients. Same day deliveries only comprise 20% of the business of Quicklink Ltd
whereas they comprise 75% of the business of Celer Transport. This may explain why the delivery performance of Celer
Transport with regard to mail and parcel deliveries was not as good as that of Quicklink Ltd.
The fact that 120 items of mail and 25 parcels were lost by the Celer Transport business is most disturbing and could prove
damaging as the safe delivery of such items is the very substance of the business and would almost certainly have resulted
in a loss of customer goodwill. This is an issue which must be addressed as a matter of urgency.
The introduction of the call management system by Quicklink Ltd on 1 June 2004 is now proving its worth with 99% of calls
answered within the target time of 20 seconds. This compares favourably with the Celer Transport business in which only
90% of a much smaller volume of calls were answered within a longer target time of 30 seconds. Future performance in this
area will improve if the call management system is applied to the Celer Transport business. In particular, it is likely that the
number of abandoned calls will be reduced and enhance the ‘image’ of the Celer Transport business.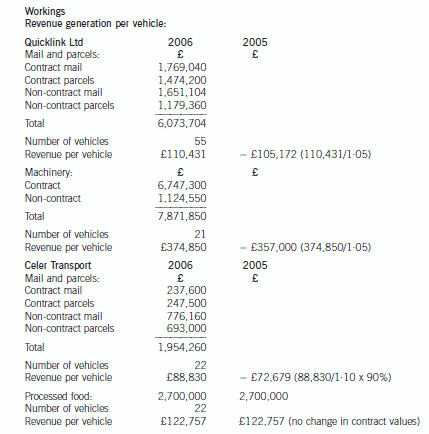

-
第18题:
(ii) Illustrate the benefit of revising the corporate structure by calculating the corporation tax (CT) payable
for the year ended 31 March 2006, on the assumptions that:
(1) no action is taken; and
(2) an amended structure as recommended in (i) above is implemented from 1 June 2005. (3 marks)
正确答案:
-
第19题:
(b) You are the audit manager of Jinack Co, a private limited liability company. You are currently reviewing two
matters that have been left for your attention on the audit working paper file for the year ended 30 September
2005:
(i) Jinack holds an extensive range of inventory and keeps perpetual inventory records. There was no full
physical inventory count at 30 September 2005 as a system of continuous stock checking is operated by
warehouse personnel under the supervision of an internal audit department.
A major systems failure in October 2005 caused the perpetual inventory records to be corrupted before the
year-end inventory position was determined. As data recovery procedures were found to be inadequate,
Jinack is reconstructing the year-end quantities through a physical count and ‘rollback’. The reconstruction
exercise is expected to be completed in January 2006. (6 marks)
Required:
Identify and comment on the implications of the above matters for the auditor’s report on the financial
statements of Jinack Co for the year ended 30 September 2005 and, where appropriate, the year ending
30 September 2006.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the matters.
正确答案:
(b) Implications for the auditor’s report
(i) Corruption of perpetual inventory records
■ The loss of data (of physical inventory quantities at the balance sheet date) gives rise to a limitation on scope.
Tutorial note: It is the records of the asset that have been destroyed – not the physical asset.
■ The systems failure in October 2005 is clearly a non-adjusting post balance sheet event (IAS 10). If it is material
(such that non-disclosure could influence the economic decisions of users) Jinack should disclose:
– the nature of the event (i.e. systems failure); and
– an estimate of its financial effect (i.e. the cost of disruption and reconstruction of data to the extent that it is
not covered by insurance).
Tutorial note: The event has no financial effect on the realisability of inventory, only on its measurement for the
purpose of reporting it in the financial statements.
■ If material this disclosure could be made in the context of explaining how inventory has been estimated at
30 September 2005 (see later). If such disclosure, that the auditor considers to be necessary, is not made, the
audit opinion should be qualified ‘except for’ disagreement (over lack of disclosure).
Tutorial note: Such qualifications are extremely rare since management should be persuaded to make necessary
disclosure in the notes to the financial statements rather than have users’ attention drawn to the matter through
a qualification of the audit opinion.
■ The limitation on scope of the auditor’s work has been imposed by circumstances. Jinack’s accounting records
(for inventory) are inadequate (non-existent) for the auditor to perform. tests on them.
■ An alternative procedure to obtain sufficient appropriate audit evidence of inventory quantities at a year end is
subsequent count and ‘rollback’. However, the extent of ‘roll back’ testing is limited as records are still under
reconstruction.
■ The auditor may be able to obtain sufficient evidence that there is no material misstatement through a combination
of procedures:
– testing management’s controls over counting inventory after the balance sheet date and recording inventory
movements (e.g. sales and goods received);
– reperforming the reconstruction for significant items on a sample basis;
– analytical procedures such as a review of profit margins by inventory category.
■ ‘An extensive range of inventory’ is clearly material. The matter (i.e. systems failure) is not however pervasive, as
only inventory is affected.
■ Unless the reconstruction is substantially completed (i.e. inventory items not accounted for are insignificant) the
auditor cannot determine what adjustment, if any, might be determined to be necessary. The auditor’s report
should then be modified, ‘except for’, limitation on scope.
■ However, if sufficient evidence is obtained the auditor’s report should be unmodified.
■ An ‘emphasis of matter’ paragraph would not be appropriate because this matter is not one of significant
uncertainty.
Tutorial note: An uncertainty in this context is a matter whose outcome depends on future actions or events not
under the direct control of Jinack.
2006
■ If the 2005 auditor’s report is qualified ‘except for’ on grounds of limitation on scope there are two possibilities for
the inventory figure as at 30 September 2005 determined on completion of the reconstruction exercise:
(1) it is not materially different from the inventory figure reported; or
(2) it is materially different.
■ In (1), with the limitation now removed, the need for qualification is removed and the 2006 auditor’s report would
be unmodified (in respect of this matter).
■ In (2) the opening position should be restated and the comparatives adjusted in accordance with IAS 8 ‘Accounting
Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates and Errors’. The 2006 auditor’s report would again be unmodified.
Tutorial note: If the error was not corrected in accordance with IAS 8 it would be a different matter and the
auditor’s report would be modified (‘except for’ qualification) disagreement on accounting treatment. -
第20题:
3 You are the manager responsible for the audit of Volcan, a long-established limited liability company. Volcan operates
a national supermarket chain of 23 stores, five of which are in the capital city, Urvina. All the stores are managed in
the same way with purchases being made through Volcan’s central buying department and product pricing, marketing,
advertising and human resources policies being decided centrally. The draft financial statements for the year ended
31 March 2005 show revenue of $303 million (2004 – $282 million), profit before taxation of $9·5 million (2004
– $7·3 million) and total assets of $178 million (2004 – $173 million).
The following issues arising during the final audit have been noted on a schedule of points for your attention:
(a) On 1 May 2005, Volcan announced its intention to downsize one of the stores in Urvina from a supermarket to
a ‘City Metro’ in response to a significant decline in the demand for supermarket-style. shopping in the capital.
The store will be closed throughout June, re-opening on 1 July 2005. Goodwill of $5·5 million was recognised
three years ago when this store, together with two others, was bought from a national competitor. It is Volcan’s
policy to write off goodwill over five years. (7 marks)
Required:
For each of the above issues:
(i) comment on the matters that you should consider; and
(ii) state the audit evidence that you should expect to find,
in undertaking your review of the audit working papers and financial statements of Volcan for the year ended
31 March 2005.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three issues.
正确答案:
3 VOLCAN
(a) Store impairment
(i) Matters
■ Materiality
? The cost of goodwill represents 3·1% of total assets and is therefore material.
? However, after three years the carrying amount of goodwill ($2·2m) represents only 1·2% of total assets –
and is therefore immaterial in the context of the balance sheet.
? The annual amortisation charge ($1·1m) represents 11·6% profit before tax (PBT) and is therefore also
material (to the income statement).
? The impact of writing off the whole of the carrying amount would be material to PBT (23%).
Tutorial note: The temporary closure of the supermarket does not constitute a discontinued operation under IFRS 5
‘Non-Current Assets Held for Sale and Discontinued Operations’.
■ Under IFRS 3 ‘Business Combinations’ Volcan should no longer be writing goodwill off over five years but
subjecting it to an annual impairment test.
■ The announcement is after the balance sheet date and is therefore a non-adjusting event (IAS 10 ‘Events After the
Balance Sheet Date’) insofar as no provision for restructuring (for example) can be made.
■ However, the event provides evidence of a possible impairment of the cash-generating unit which is this store and,
in particular, the value of goodwill assigned to it.
■ If the carrying amount of goodwill ($2·2m) can be allocated on a reasonable and consistent basis to this and the
other two stores (purchased at the same time) Volcan’s management should have applied an impairment test to
the goodwill of the downsized store (this is likely to show impairment).
■ If more than 22% of goodwill is attributable to the City Metro store – then its write-off would be material to PBT
(22% × $2·2m ÷ $9·5m = 5%).
■ If the carrying amount of goodwill cannot be so allocated; the impairment test should be applied to the
cash-generating unit that is the three stores (this may not necessarily show impairment).
■ Management should have considered whether the other four stores in Urvina (and elsewhere) are similarly
impaired.
■ Going concern is unlikely to be an issue unless all the supermarkets are located in cities facing a downward trend
in demand.
Tutorial note: Marks will be awarded for stating the rules for recognition of an impairment loss for a cash-generating
unit. However, as it is expected that the majority of candidates will not deal with this matter, the rules of IAS 36 are
not reproduced here.
(ii) Audit evidence
■ Board minutes approving the store’s ‘facelift’ and documenting the need to address the fall in demand for it as a
supermarket.
■ Recomputation of the carrying amount of goodwill (2/5 × $5·5m = $2·2m).
■ A schedule identifying all the assets that relate to the store under review and the carrying amounts thereof agreed
to the underlying accounting records (e.g. non-current asset register).
■ Recalculation of value in use and/or fair value less costs to sell of the cash-generating unit (i.e. the store that is to
become the City Metro, or the three stores bought together) as at 31 March 2005.
Tutorial note: If just one of these amounts exceeds carrying amount there will be no impairment loss. Also, as
there is a plan NOT to sell the store it is most likely that value in use should be used.
■ Agreement of cash flow projections (e.g. to approved budgets/forecast revenues and costs for a maximum of five
years, unless a longer period can be justified).
■ Written management representation relating to the assumptions used in the preparation of financial budgets.
■ Agreement that the pre-tax discount rate used reflects current market assessments of the time value of money (and
the risks specific to the store) and is reasonable. For example, by comparison with Volcan’s weighted average cost
of capital.
■ Inspection of the store (if this month it should be closed for refurbishment).
■ Revenue budgets and cash flow projections for:
– the two stores purchased at the same time;
– the other stores in Urvina; and
– the stores elsewhere.
Also actual after-date sales by store compared with budget. -
第21题:
3 You are the manager responsible for the audit of Seymour Co. The company offers information, proprietary foods and
medical innovations designed to improve the quality of life. (Proprietary foods are marketed under and protected by
registered names.) The draft consolidated financial statements for the year ended 30 September 2006 show revenue
of $74·4 million (2005 – $69·2 million), profit before taxation of $13·2 million (2005 – $15·8 million) and total
assets of $53·3 million (2005 – $40·5 million).
The following issues arising during the final audit have been noted on a schedule of points for your attention:
(a) In 2001, Seymour had been awarded a 20-year patent on a new drug, Tournose, that was also approved for
food use. The drug had been developed at a cost of $4 million which is being amortised over the life of the
patent. The patent cost $11,600. In September 2006 a competitor announced the successful completion of
preliminary trials on an alternative drug with the same beneficial properties as Tournose. The alternative drug is
expected to be readily available in two years time. (7 marks)
Required:
For each of the above issues:
(i) comment on the matters that you should consider; and
(ii) state the audit evidence that you should expect to find,
in undertaking your review of the audit working papers and financial statements of Seymour Co for the year ended
30 September 2006.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three issues.
正确答案:
■ A change in the estimated useful life should be accounted for as a change in accounting estimate in accordance
with IAS 8 Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates and Errors. For example, if the development
costs have little, if any, useful life after the introduction of the alternative drug (‘worst case’ scenario), the carrying
value ($3 million) should be written off over the current and remaining years, i.e. $1 million p.a. The increase in
amortisation/decrease in carrying value ($800,000) is material to PBT (6%) and total assets (1·5%).
■ Similarly a change in the expected pattern of consumption of the future economic benefits should be accounted for
as a change in accounting estimate (IAS 8). For example, it may be that the useful life is still to 2020 but that
the economic benefits may reduce significantly in two years time.
■ After adjusting the carrying amount to take account of the change in accounting estimate(s) management should
have tested it for impairment and any impairment loss recognised in profit or loss.
(ii) Audit evidence
■ $3 million carrying amount of development costs brought forward agreed to prior year working papers and financial
statements.
■ A copy of the press release announcing the competitor’s alternative drug.
■ Management’s projections of future cashflows from Tournose-related sales as evidence of the useful life of the
development costs and pattern of consumption.
■ Reperformance of management’s impairment test on the development costs: Recalculation of management’s
calculation of the carrying amount after revising estimates of useful life and/or consumption of benefits compared
with management’s calculation of value in use.
■ Sensitivity analysis on management’s key assumptions (e.g. estimates of useful life, discount rate).
■ Written management representation on the key assumptions concerning the future that have a significant risk of
causing material adjustment to the carrying amount of the development costs. (These assumptions should be
disclosed in accordance with IAS 1 Presentation of Financial Statements.) -
第22题:
We learn from the passage that the date of sowing cotton is usually______.
A) on June 15th
B) on July 15th
C) on July 1st
D) on July 20th
正确答案:C
答案:C
[试题分析]细节题。
[详细解答]第二段第一句告诉了我们正确答案:The aver age date of sowing is about July 1st.所以答案为C。
-
第23题:
(a) The following figures have been calculated from the financial statements (including comparatives) of Barstead for
the year ended 30 September 2009:
increase in profit after taxation 80%
increase in (basic) earnings per share 5%
increase in diluted earnings per share 2%
Required:
Explain why the three measures of earnings (profit) growth for the same company over the same period can
give apparently differing impressions. (4 marks)
(b) The profit after tax for Barstead for the year ended 30 September 2009 was $15 million. At 1 October 2008 the company had in issue 36 million equity shares and a $10 million 8% convertible loan note. The loan note will mature in 2010 and will be redeemed at par or converted to equity shares on the basis of 25 shares for each $100 of loan note at the loan-note holders’ option. On 1 January 2009 Barstead made a fully subscribed rights issue of one new share for every four shares held at a price of $2·80 each. The market price of the equity shares of Barstead immediately before the issue was $3·80. The earnings per share (EPS) reported for the year ended 30 September 2008 was 35 cents.
Barstead’s income tax rate is 25%.
Required:
Calculate the (basic) EPS figure for Barstead (including comparatives) and the diluted EPS (comparatives not required) that would be disclosed for the year ended 30 September 2009. (6 marks)
正确答案:
(a)Whilstprofitaftertax(anditsgrowth)isausefulmeasure,itmaynotgiveafairrepresentationofthetrueunderlyingearningsperformance.Inthisexample,userscouldinterpretthelargeannualincreaseinprofitaftertaxof80%asbeingindicativeofanunderlyingimprovementinprofitability(ratherthanwhatitreallyis:anincreaseinabsoluteprofit).Itispossible,evenprobable,that(someof)theprofitgrowthhasbeenachievedthroughtheacquisitionofothercompanies(acquisitivegrowth).Wherecompaniesareacquiredfromtheproceedsofanewissueofshares,orwheretheyhavebeenacquiredthroughshareexchanges,thiswillresultinagreaternumberofequitysharesoftheacquiringcompanybeinginissue.ThisiswhatappearstohavehappenedinthecaseofBarsteadastheimprovementindicatedbyitsearningspershare(EPS)isonly5%perannum.ThisexplainswhytheEPS(andthetrendofEPS)isconsideredamorereliableindicatorofperformancebecausetheadditionalprofitswhichcouldbeexpectedfromthegreaterresources(proceedsfromthesharesissued)ismatchedwiththeincreaseinthenumberofshares.Simplylookingatthegrowthinacompany’sprofitaftertaxdoesnottakeintoaccountanyincreasesintheresourcesusedtoearnthem.Anyincreaseingrowthfinancedbyborrowings(debt)wouldnothavethesameimpactonprofit(asbeingfinancedbyequityshares)becausethefinancecostsofthedebtwouldacttoreduceprofit.ThecalculationofadilutedEPStakesintoaccountanypotentialequitysharesinissue.Potentialordinarysharesarisefromfinancialinstruments(e.g.convertibleloannotesandoptions)thatmayentitletheirholderstoequitysharesinthefuture.ThedilutedEPSisusefulasitalertsexistingshareholderstothefactthatfutureEPSmaybereducedasaresultofsharecapitalchanges;inasenseitisawarningsign.InthiscasethelowerincreaseinthedilutedEPSisevidencethatthe(higher)increaseinthebasicEPShas,inpart,beenachievedthroughtheincreaseduseofdilutingfinancialinstruments.Thefinancecostoftheseinstrumentsislessthantheearningstheirproceedshavegeneratedleadingtoanincreaseincurrentprofits(andbasicEPS);however,inthefuturetheywillcausemoresharestobeissued.ThiscausesadilutionwherethefinancecostperpotentialnewshareislessthanthebasicEPS.
