The finance director of Blod Co, Uma Thorton, has requested that your firm type the financial statements in the formto be presented to shareholders at the forthcoming company general meeting. Uma has also commented that theprevious auditors did not use a
题目
The finance director of Blod Co, Uma Thorton, has requested that your firm type the financial statements in the form
to be presented to shareholders at the forthcoming company general meeting. Uma has also commented that the
previous auditors did not use a liability disclaimer in their audit report, and would like more information about the use
of liability disclaimer paragraphs.
Required:
(b) Discuss the ethical issues raised by the request for your firm to type the financial statements of Blod Co.
(3 marks)
相似考题
更多“The finance director of Blod Co, Uma Thorton, has requested that your firm type the financial statements in the formto be presented to shareholders at the forthcoming company general meeting. Uma has also commented that theprevious auditors did not use a ”相关问题
-
第1题:
5 You are an audit manager in Fox & Steeple, a firm of Chartered Certified Accountants, responsible for allocating staff
to the following three audits of financial statements for the year ending 31 December 2006:
(a) Blythe Co is a new audit client. This private company is a local manufacturer and distributor of sportswear. The
company’s finance director, Peter, sees little value in the audit and put it out to tender last year as a cost-cutting
exercise. In accordance with the requirements of the invitation to tender your firm indicated that there would not
be an interim audit.
(b) Huggins Co, a long-standing client, operates a national supermarket chain. Your firm provided Huggins Co with
corporate financial advice on obtaining a listing on a recognised stock exchange in 2005. Senior management
expects a thorough examination of the company’s computerised systems, and are also seeking assurance that
the annual report will not attract adverse criticism.
(c) Gray Co has been an audit client since 1999 after your firm advised management on a successful buyout. Gray
provides communication services and software solutions. Your firm provides Gray with technical advice on
financial reporting and tax services. Most recently you have been asked to conduct due diligence reviews on
potential acquisitions.
Required:
For these assignments, compare and contrast:
(i) the threats to independence;
(ii) the other professional and practical matters that arise; and
(iii) the implications for allocating staff.
(15 marks)
正确答案:
5 FOX & STEEPLE – THREE AUDIT ASSIGNMENTS
(i) Threats to independence
Self-interest
Tutorial note: This threat arises when a firm or a member of the audit team could benefit from a financial interest in, or
other self-interest conflict with, an assurance client.
■ A self-interest threat could potentially arise in respect of any (or all) of these assignments as, regardless of any fee
restrictions (e.g. per IFAC’s ‘Code of Ethics for Professional Accountants’), the auditor is remunerated by clients for
services provided.
■ This threat is likely to be greater for Huggins Co (larger/listed) and Gray Co (requires other services) than for Blythe Co
(audit a statutory necessity).
■ The self-interest threat may be greatest for Huggins Co. As a company listed on a recognised stock exchange it may
give prestige and credibility to Fox & Steeple (though this may be reciprocated). Fox & Steeple could be pressurised into
taking evasive action to avoid the loss of a listed client (e.g. concurring with an inappropriate accounting treatment).
Self-review
Tutorial note: This arises when, for example, any product or judgment of a previous engagement needs to be re-evaluated
in reaching conclusions on the audit engagement.
■ This threat is also likely to be greater for Huggins and Gray where Fox & Steeple is providing other (non-audit) services.
■ A self-review threat may be created by Fox & Steeple providing Huggins with a ‘thorough examination’ of its computerised
systems if it involves an extension of the procedures required to conduct an audit in accordance with International
Standards on Auditing (ISAs).
■ Appropriate safeguards must be put in place if Fox & Steeple assists Huggins in the performance of internal audit
activities. In particular, Fox & Steeple’s personnel must not act (or appear to act) in a capacity equivalent to a member
of Huggins’ management (e.g. reporting, in a management role, to those charged with governance).
■ Fox & Steeple may provide Gray with accounting and bookkeeping services, as Gray is not a listed entity, provided that
any self-review threat created is reduced to an acceptable level. In particular, in giving technical advice on financial
reporting, Fox & Steeple must take care not to make managerial decisions such as determining or changing journal
entries without obtaining Gray’s approval.
■ Taxation services comprise a broad range of services, including compliance, planning, provision of formal taxation
opinions and assistance in the resolution of tax disputes. Such assignments are generally not seen to create threats to
independence.
Tutorial note: It is assumed that the provision of tax services is permitted in the jurisdiction (i.e. that Fox and Steeple
are not providing such services if prohibited).
■ The due diligence reviews for Gray may create a self-review threat (e.g. on the fair valuation of net assets acquired).
However, safeguards may be available to reduce these threats to an acceptable level.
■ If staff involved in providing other services are also assigned to the audit, their work should be reviewed by more senior
staff not involved in the provision of the other services (to the extent that the other service is relevant to the audit).
■ The reporting lines of any staff involved in the audit of Huggins and the provision of other services for Huggins should
be different. (Similarly for Gray.)
Familiarity
Tutorial note: This arises when, by virtue of a close relationship with an audit client (or its management or employees) an
audit firm (or a member of the audit team) becomes too sympathetic to the client’s interests.
■ Long association of a senior member of an audit team with an audit client may create a familiarity threat. This threat
is likely to be greatest for Huggins, a long-standing client. It may also be significant for Gray as Fox & Steeple have had
dealings with this client for seven years now.
■ As Blythe is a new audit client this particular threat does not appear to be relevant.
■ Senior personnel should be rotated off the Huggins and Gray audit teams. If this is not possible (for either client), an
additional professional accountant who was not a member of the audit team should be required to independently review
the work done by the senior personnel.
■ The familiarity threat of using the same lead engagement partner on an audit over a prolonged period is particularly
relevant to Huggins, which is now a listed entity. IFAC’s ‘Code of Ethics for Professional Accountants’ requires that the
lead engagement partner should be rotated after a pre-defined period, normally no more than seven years. Although it
might be time for the lead engagement partner of Huggins to be changed, the current lead engagement partner may
continue to serve for the 2006 audit.
Tutorial note: Two additional years are permitted when an existing client becomes listed, since it may not be in the
client’s best interests to have an immediate rotation of engagement partner.
Intimidation
Tutorial note: This arises when a member of the audit team may be deterred from acting objectively and exercising
professional skepticism by threat (actual or perceived), from the audit client.
■ This threat is most likely to come from Blythe as auditors are threatened with a tendering process to keep fees down.
■ Peter may have already applied pressure to reduce inappropriately the extent of audit work performed in order to reduce
fees, by stipulating that there should not be an interim audit.
■ The audit senior allocated to Blythe will need to be experienced in standing up to client management personnel such as
Peter.
Tutorial note: ‘Correct’ classification under ‘ethical’, ‘other professional’, ‘practical’ or ‘staff implications’ is not as important
as identifying the matters.
(ii) Other professional and practical matters
Tutorial note: ‘Other professional’ includes quality control.
■ The experience of staff allocated to each assignment should be commensurate with the assessment of associated risk.
For example, there may be a risk that insufficient audit evidence is obtained within the budget for the audit of Blythe.
Huggins, as a listed client, carries a high reputational risk.
■ Sufficient appropriate staff should be allocated to each audit to ensure adequate quality control (in particular in the
direction, supervision, review of each assignment). It may be appropriate for a second partner to be assigned to carry
out a ‘hot review’ (before the auditor’s report is signed) of:
– Blythe, because it is the first audit of a new client; and
– Huggins, as it is listed.
■ Existing clients (Huggins and Gray) may already have some expectation regarding who should be assigned to their
audits. There is no reason why there should not be some continuity of staff providing appropriate safeguards are put in
place (e.g. to overcome any familiarity threat).
■ Senior staff assigned to Blythe should be alerted to the need to exercise a high degree of professional skepticism (in the
light of Peter’s attitude towards the audit).
■ New staff assigned to Huggins and Gray would perhaps be less likely to assume unquestioned honesty than staff
previously involved with these audits.
Logistics (practical)
■ All three assignments have the same financial year end, therefore there will be an element of ‘competition’ for the staff
to be assigned to the year-end visits and final audit assignments. As a listed company, Huggins is likely to have the
tightest reporting deadline and so have a ‘priority’ for staff.
■ Blythe is a local and private company. Staff involved in the year-end visit (e.g. to attend the physical inventory count)
should also be involved in the final audit. As this is a new client, staff assigned to this audit should get involved at every
stage to increase their knowledge and understanding of the business.
■ Huggins is a national operation and may require numerous staff to attend year-end procedures. It would not be expected
that all staff assigned to year-end visits should all be involved in the final audit.
Time/fee/staff budgets
■ Time budgets will need to be prepared for each assignment to determine manpower requirements (and to schedule audit
work).
(iii) Implications for allocating staff
■ Fox & Steeple should allocate staff so that those providing other services to Huggins and Gray (that may create a selfreview
threat) do not participate in the audit engagement.
Competence and due care (Qualifications/Specialisation)
■ All audit assignments will require competent staff.
■ Huggins will require staff with an in-depth knowledge of their computerised system.
■ Gray will require senior audit staff to be experienced in financial reporting matters specific to communications and
software solutions (e.g. in revenue recognition issues and accounting for internally-generated intangible assets).
■ Specialists providing tax services and undertaking the due diligence reviews for Gray may not be required to have any
involvement in the audit assignment. -
第2题:
5 You are the audit manager for three clients of Bertie & Co, a firm of Chartered Certified Accountants. The financial
year end for each client is 30 September 2007.
You are reviewing the audit senior’s proposed audit reports for two clients, Alpha Co and Deema Co.
Alpha Co, a listed company, permanently closed several factories in May 2007, with all costs of closure finalised and
paid in August 2007. The factories all produced the same item, which contributed 10% of Alpha Co’s total revenue
for the year ended 30 September 2007 (2006 – 23%). The closure has been discussed accurately and fully in the
chairman’s statement and Directors’ Report. However, the closure is not mentioned in the notes to the financial
statements, nor separately disclosed on the financial statements.
The audit senior has proposed an unmodified audit opinion for Alpha Co as the matter has been fully addressed in
the chairman’s statement and Directors’ Report.
In October 2007 a legal claim was filed against Deema Co, a retailer of toys. The claim is from a customer who slipped
on a greasy step outside one of the retail outlets. The matter has been fully disclosed as a material contingent liability
in the notes to the financial statements, and audit working papers provide sufficient evidence that no provision is
necessary as Deema Co’s lawyers have stated in writing that the likelihood of the claim succeeding is only possible.
The amount of the claim is fixed and is adequately covered by cash resources.
The audit senior proposes that the audit opinion for Deema Co should not be qualified, but that an emphasis of matter
paragraph should be included after the audit opinion to highlight the situation.
Hugh Co was incorporated in October 2006, using a bank loan for finance. Revenue for the first year of trading is
$750,000, and there are hopes of rapid growth in the next few years. The business retails luxury hand made wooden
toys, currently in a single retail outlet. The two directors (who also own all of the shares in Hugh Co) are aware that
due to the small size of the company, the financial statements do not have to be subject to annual external audit, but
they are unsure whether there would be any benefit in a voluntary audit of the first year financial statements. The
directors are also aware that a review of the financial statements could be performed as an alternative to a full audit.
Hugh Co currently employs a part-time, part-qualified accountant, Monty Parkes, who has prepared a year end
balance sheet and income statement, and who produces summary management accounts every three months.
Required:
(a) Evaluate whether the audit senior’s proposed audit report is appropriate, and where you disagree with the
proposed report, recommend the amendment necessary to the audit report of:
(i) Alpha Co; (6 marks)
正确答案:
5 BERTIE & CO
(a) (i) Alpha Co
The factory closures constitute a discontinued operation per IFRS 5 Non-Current Assets Held for Sale and Discontinued
Operations, due to the discontinuance of a separate major component of the business. It is a major component due to
the 10% contribution to revenue in the year to 30 September 2007 and 23% contribution in 2006. It is a separate
business component of the company due to the factories having made only one item, indicating a separate income
generating unit.
Under IFRS 5 there must be separate disclosure on the face of the income statement of the post tax results of the
discontinued operation, and of any profit or loss resulting from the closures. The revenue and costs of the discontinued
operation should be separately disclosed either on the face of the income statement or in the notes to the financial
statements. Cash flows relating to the discontinued operation should also be separately disclosed per IAS 7 Cash Flow
Statements.
In addition, as Alpha Co is a listed company, IFRS 8 Operating Segments requires separate segmental disclosure of
discontinued operations.
Failure to disclose the above information in the financial statements is a material breach of International Accounting
Standards. The audit opinion should therefore be qualified on the grounds of disagreement on disclosure (IFRS 5,
IAS 7 and IFRS 8). The matter is material, but not pervasive, and therefore an ‘except for’ opinion should be issued.
The opinion paragraph should clearly state the reason for the disagreement, and an indication of the financial
significance of the matter.
The audit opinion relates only to the financial statements which have been audited, and the contents of the other
information (chairman’s statement and Directors’ Report) are irrelevant when deciding if the financial statements show
a true and fair view, or are fairly presented.
Tutorial note: there is no indication in the question scenario that Alpha Co is in financial or operational difficulty
therefore no marks are awarded for irrelevant discussion of going concern issues and the resultant impact on the audit
opinion. -
第3题:
You are the manager responsible for performing hot reviews on audit files where there is a potential disagreement
between your firm and the client regarding a material issue. You are reviewing the going concern section of the audit
file of Dexter Co, a client with considerable cash flow difficulties, and other, less significant operational indicators of
going concern problems. The working papers indicate that Dexter Co is currently trying to raise finance to fund
operating cash flows, and state that if the finance is not received, there is significant doubt over the going concern
status of the company. The working papers conclude that the going concern assumption is appropriate, but it is
recommended that the financial statements should contain a note explaining the cash flow problems faced by the
company, along with a description of the finance being sought, and an evaluation of the going concern status of the
company. The directors do not wish to include the note in the financial statements.
Required:
(b) Consider and comment on the possible reasons why the directors of Dexter Co are reluctant to provide the
note to the financial statements. (5 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Directors reluctance to disclose
The directors are likely to have several reasons behind their reluctance to disclose the note as recommended by the audit
manager. The first is that the disclosure of Dexter Co’s poor cash flow position and perilous going concern status may reflect
badly on the directors themselves. The company’s shareholders and other stakeholders will be displeased to see the company
in such a poor position, and the directors will be held accountable for the problems. Of course it may not be the case that
the directors have exercised poor management of the company – the problems could be caused by external influences outside
the control of the directors. However, it is natural that the directors will not want to highlight the situation in order to protect
their own position.
Secondly, the note could itself trigger further financial distress for the company. Dexter Co is trying to raise finance, and it is
probable that the availability of further finance will be detrimentally affected by the disclosure of the company’s financial
problems. In particular, if the cash flow difficulties are highlighted, providers of finance will consider the company too risky
an investment, and are not likely to make funds available for fear of non-repayment. Existing lenders may seek repayment of
their funds in fear that the company may be unable in the future to meet repayments.
In addition, the disclosures could cause operational problems, for example, suppliers may curtail trading relationships as they
become concerned that they will not be paid, or customers may be deterred from purchasing from the company if they feel
that there is no long-term future for the business. Unfortunately the mere disclosure of financial problems can be self-fulfilling,
and cause such further problems for the company that it is pushed into non-going concern status.
The directors may also be concerned that if staff were to hear of this they may worry about the future of the company and
seek alternative employment, which could lead in turn to the loss of key members of staff. This would be detrimental to the
business and trigger further operational problems.
Finally, the reluctance to disclose may be caused by an entirely different reason. The directors could genuinely feel that the
cash flow and operational problems faced by the company do not constitute factors affecting the going concern status. They
may be confident that although a final decision has not been made regarding financing, the finance is likely to be forthcoming,
and therefore there is no long-term material uncertainty over the future of the company. However audit working papers
conclude that there is a significant level of doubt over the going concern status of Dexter Co, and therefore it seems that the
directors may be over optimistic if they feel that there is no significant doubt to be disclosed in the financial statements. -
第4题:
You are an audit manager responsible for providing hot reviews on selected audit clients within your firm of Chartered
Certified Accountants. You are currently reviewing the audit working papers for Pulp Co, a long standing audit client,
for the year ended 31 January 2008. The draft statement of financial position (balance sheet) of Pulp Co shows total
assets of $12 million (2007 – $11·5 million).The audit senior has made the following comment in a summary of
issues for your review:
‘Pulp Co’s statement of financial position (balance sheet) shows a receivable classified as a current asset with a value
of $25,000. The only audit evidence we have requested and obtained is a management representation stating the
following:
(1) that the amount is owed to Pulp Co from Jarvis Co,
(2) that Jarvis Co is controlled by Pulp Co’s chairman, Peter Sheffield, and
(3) that the balance is likely to be received six months after Pulp Co’s year end.
The receivable was also outstanding at the last year end when an identical management representation was provided,
and our working papers noted that because the balance was immaterial no further work was considered necessary.
No disclosure has been made in the financial statements regarding the balance. Jarvis Co is not audited by our firm
and we have verified that Pulp Co does not own any shares in Jarvis Co.’
Required:
(b) In relation to the receivable recognised on the statement of financial position (balance sheet) of Pulp Co as
at 31 January 2008:
(i) Comment on the matters you should consider. (5 marks)
正确答案:
(b) (i) Matters to consider
Materiality
The receivable represents only 0·2% (25,000/12 million x 100) of total assets so is immaterial in monetary terms.
However, the details of the transaction could make it material by nature.
The amount is outstanding from a company under the control of Pulp Co’s chairman. Readers of the financial statements
would be interested to know the details of this transaction, which currently is not disclosed. Elements of the transaction
could be subject to bias, specifically the repayment terms, which appear to be beyond normal commercial credit terms.
Paul Sheffield may have used his influence over the two companies to ‘engineer’ the transaction. Disclosure is necessary
due to the nature of the transaction, the monetary value is irrelevant.
A further matter to consider is whether this is a one-off transaction, or indicative of further transactions between the two
companies.
Relevant accounting standard
The definitions in IAS 24 must be carefully considered to establish whether this actually constitutes a related party
transaction. The standard specifically states that two entities are not necessarily related parties just because they have
a director or other member of key management in common. The audit senior states that Jarvis Co is controlled by Peter
Sheffield, who is also the chairman of Pulp Co. It seems that Peter Sheffield is in a position of control/significant influence
over the two companies (though this would have to be clarified through further audit procedures), and thus the two
companies are likely to be perceived as related.
IAS 24 requires full disclosure of the following in respect of related party transactions:
– the nature of the related party relationship,
– the amount of the transaction,
– the amount of any balances outstanding including terms and conditions, details of security offered, and the nature
of consideration to be provided in settlement,
– any allowances for receivables and associated expense.
There is currently a breach of IAS 24 as no disclosure has been made in the notes to the financial statements. If not
amended, the audit opinion on the financial statements should be qualified with an ‘except for’ disagreement. In
addition, if practicable, the auditor’s report should include the information that would have been included in the financial
statements had the requirements of IAS 24 been adhered to.
Valuation and classification of the receivable
A receivable should only be recognised if it will give rise to future economic benefit, i.e. a future cash inflow. It appears
that the receivable is long outstanding – if the amount is unlikely to be recovered then it should be written off as a bad
debt and the associated expense recognised. It is possible that assets and profits are overstated.
Although a representation has been received indicating that the amount will be paid to Pulp Co, the auditor should be
sceptical of this claim given that the same representation was given last year, and the amount was not subsequently
recovered. The $25,000 could be recoverable in the long term, in which case the receivable should be reclassified as
a non-current asset. The amount advanced to Jarvis Co could effectively be an investment rather than a short term
receivable. Correct classification on the statement of financial position (balance sheet) is crucial for the financial
statements to properly show the liquidity position of the company at the year end.
Tutorial note: Digressions into management imposing a limitation in scope by withholding evidence are irrelevant in this
case, as the scenario states that the only evidence that the auditors have asked for is a management representation.
There is no indication in the scenario that the auditors have asked for, and been refused any evidence. -
第5题:
Your firm has been recommended to us by DINOSOUR TOY CO,LTD()we have done business for many fears.A、which
B、with whom
C、whom
D、with which
参考答案:B
-
第6题:
(a) Contrast the role of internal and external auditors. (8 marks)
(b) Conoy Co designs and manufactures luxury motor vehicles. The company employs 2,500 staff and consistently makes a net profit of between 10% and 15% of sales. Conoy Co is not listed; its shares are held by 15 individuals, most of them from the same family. The maximum shareholding is 15% of the share capital.
The executive directors are drawn mainly from the shareholders. There are no non-executive directors because the company legislation in Conoy Co’s jurisdiction does not require any. The executive directors are very successful in running Conoy Co, partly from their training in production and management techniques, and partly from their ‘hands-on’ approach providing motivation to employees.
The board are considering a significant expansion of the company. However, the company’s bankers are
concerned with the standard of financial reporting as the financial director (FD) has recently left Conoy Co. The board are delaying provision of additional financial information until a new FD is appointed.
Conoy Co does have an internal audit department, although the chief internal auditor frequently comments that the board of Conoy Co do not understand his reports or provide sufficient support for his department or the internal control systems within Conoy Co. The board of Conoy Co concur with this view. Anders & Co, the external auditors have also expressed concern in this area and the fact that the internal audit department focuses work on control systems, not financial reporting. Anders & Co are appointed by and report to the board of Conoy Co.
The board of Conoy Co are considering a proposal from the chief internal auditor to establish an audit committee.
The committee would consist of one executive director, the chief internal auditor as well as three new appointees.
One appointee would have a non-executive seat on the board of directors.
Required:
Discuss the benefits to Conoy Co of forming an audit committee. (12 marks)
正确答案:
(a)Roleofinternalandexternalauditors–differencesObjectivesThemainobjectiveofinternalauditistoimproveacompany’soperations,primarilyintermsofvalidatingtheefficiencyandeffectivenessoftheinternalcontrolsystemsofacompany.Themainobjectiveoftheexternalauditoristoexpressanopiniononthetruthandfairnessofthefinancialstatements,andotherjurisdictionspecificrequirementssuchasconfirmingthatthefinancialstatementscomplywiththereportingrequirementsincludedinlegislation.ReportingInternalauditreportsarenormallyaddressedtotheboardofdirectors,orotherpeoplechargedwithgovernancesuchastheauditcommittee.Thosereportsarenotpubliclyavailable,beingconfidentialbetweentheinternalauditorandtherecipient.Externalauditreportsareprovidedtotheshareholdersofacompany.Thereportisattachedtotheannualfinancialstatementsofthecompanyandisthereforepubliclyavailabletotheshareholdersandanyreaderofthefinancialstatements.ScopeofworkTheworkoftheinternalauditornormallyrelatestotheoperationsoftheorganisation,includingthetransactionprocessingsystemsandthesystemstoproducetheannualfinancialstatements.Theinternalauditormayalsoprovideotherreportstomanagement,suchasvalueformoneyauditswhichexternalauditorsrarelybecomeinvolvedwith.Theworkoftheexternalauditorrelatesonlytothefinancialstatementsoftheorganisation.However,theinternalcontrolsystemsoftheorganisationwillbetestedastheseprovideevidenceonthecompletenessandaccuracyofthefinancialstatements.RelationshipwithcompanyInmostorganisations,theinternalauditorisanemployeeoftheorganisation,whichmayhaveanimpactontheauditor’sindependence.However,insomeorganisationstheinternalauditfunctionisoutsourced.Theexternalauditorisappointedbytheshareholdersofanorganisation,providingsomedegreeofindependencefromthecompanyandmanagement.(b)BenefitsofauditcommitteeinConoyCoAssistancewithfinancialreporting(nofinanceexpertise)TheexecutivedirectorsofConoyCodonotappeartohaveanyspecificfinancialskills–asthefinancialdirectorhasrecentlyleftthecompanyandhasnotyetbeenreplaced.ThismaymeanthatfinancialreportinginConoyCoislimitedorthattheothernon-financialdirectorsspendasignificantamountoftimekeepinguptodateonfinancialreportingissues.AnauditcommitteewillassistConoyCobyprovidingspecialistknowledgeoffinancialreportingonatemporarybasis–atleastoneofthenewappointeesshouldhaverelevantandrecentfinancialreportingexperienceundercodesofcorporategovernance.ThiswillallowtheexecutivedirectorstofocusonrunningConoyCo.EnhanceinternalcontrolsystemsTheboardofConoyCodonotnecessarilyunderstandtheworkoftheinternalauditor,ortheneedforcontrolsystems.ThismeansthatinternalcontrolwithinConoyComaybeinadequateorthatemployeesmaynotrecognisetheimportanceofinternalcontrolsystemswithinanorganisation.TheauditcommitteecanraiseawarenessoftheneedforgoodinternalcontrolsystemssimplybybeingpresentinConoyCoandbyeducatingtheboardontheneedforsoundcontrols.Improvingtheinternalcontrol‘climate’willensuretheneedforinternalcontrolsisunderstoodandreducecontrolerrors.RelianceonexternalauditorsConoyCo’sinternalauditorscurrentlyreporttotheboardofConoyCo.Aspreviouslynoted,thelackoffinancialandcontrolexpertiseontheboardwillmeanthatexternalauditorreportsandadvicewillnotnecessarilybeunderstood–andtheboardmayrelytoomuchonexternalauditorsIfConoyCoreporttoanauditcommitteethiswilldecreasethedependenceoftheboardontheexternalauditors.Theauditcommitteecantaketimetounderstandtheexternalauditor’scomments,andthenviathenon-executivedirector,ensurethattheboardtakeactiononthosecomments.AppointmentofexternalauditorsAtpresent,theboardofConoyCoappointtheexternalauditors.Thisraisesissuesofindependenceastheboardmaybecometoofamiliarwiththeexternalauditorsandsoappointonthisfriendshipratherthanmerit.Ifanauditcommitteeisestablished,thenthiscommitteecanrecommendtheappointmentoftheexternalauditors.Thecommitteewillhavethetimeandexpertisetoreviewthequalityofserviceprovidedbytheexternalauditors,removingtheindependenceissue.Corporategovernancerequirements–bestpracticeConoyCodonotneedtofollowcorporategovernancerequirements(thecompanyisnotlisted).However,notfollowingthoserequirementsmaystarttohaveadverseeffectsonConoy.Forexample,ConoyCo’sbankisalreadyconcernedaboutthelackoftransparencyinreporting.EstablishinganauditcommitteewillshowthattheboardofConoyCoarecommittedtomaintainingappropriateinternalsystemsinthecompanyandprovidingthestandardofreportingexpectedbylargecompanies.Obtainingthenewbankloanshouldalsobeeasierasthebankwillbesatisfiedwithfinancialreportingstandards.Givennonon-executives–independentadvicetoboardCurrentlyConoyCodoesnothaveanynon-executivedirectors.Thismeansthatthedecisionsoftheexecutivedirectorsarenotbeingchallengedbyotherdirectorsindependentofthecompanyandwithlittleornofinancialinterestinthecompany.Theappointmentofanauditcommitteewithonenon-executivedirectorontheboardofConoyCowillstarttoprovidesomenon-executiveinputtoboardmeetings.Whilenotsufficientintermsofcorporategovernancerequirements(aboutequalnumbersofexecutiveandnon-executivedirectorsareexpected)itdoesshowtheboardofConoyCoareattemptingtoestablishappropriategovernancesystems.AdviceonriskmanagementFinally,thereareothergeneralareaswhereConoyCowouldbenefitfromanauditcommittee.Forexample,lackofcorporategovernancestructuresprobablymeansConoyCodoesnothaveariskmanagementcommittee.Theauditcommitteecanalsoprovideadviceonriskmanagement,helpingtodecreasetheriskexposureofthecompany. -
第7题:
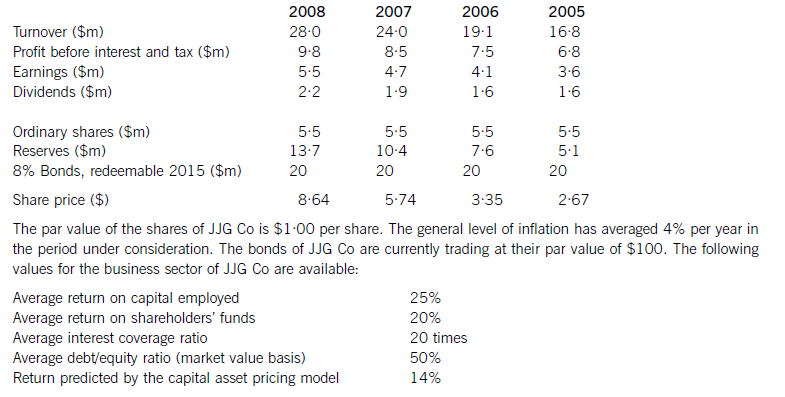
JJG Co is planning to raise $15 million of new finance for a major expansion of existing business and is considering a rights issue, a placing or an issue of bonds. The corporate objectives of JJG Co, as stated in its Annual Report, are to maximise the wealth of its shareholders and to achieve continuous growth in earnings per share. Recent financial information on JJG Co is as follows:
Required:
(a) Evaluate the financial performance of JJG Co, and analyse and discuss the extent to which the company has achieved its stated corporate objectives of:
(i) maximising the wealth of its shareholders;
(ii) achieving continuous growth in earnings per share.
Note: up to 7 marks are available for financial analysis.(12 marks)
(b) If the new finance is raised via a rights issue at $7·50 per share and the major expansion of business has
not yet begun, calculate and comment on the effect of the rights issue on:
(i) the share price of JJG Co;
(ii) the earnings per share of the company; and
(iii) the debt/equity ratio. (6 marks)
(c) Analyse and discuss the relative merits of a rights issue, a placing and an issue of bonds as ways of raising the finance for the expansion. (7 marks)
正确答案:
AchievementofcorporateobjectivesJJGCohasshareholderwealthmaximisationasanobjective.Thewealthofshareholdersisincreasedbydividendsreceivedandcapitalgainsonsharesowned.Totalshareholderreturncomparesthesumofthedividendreceivedandthecapitalgainwiththeopeningshareprice.TheshareholdersofJJGCohadareturnof58%in2008,comparedwithareturnpredictedbythecapitalassetpricingmodelof14%.Thelowestreturnshareholdershavereceivedwas21%andthehighestreturnwas82%.Onthisbasis,theshareholdersofthecompanyhaveexperiencedasignificantincreaseinwealth.Itisdebatablewhetherthishasbeenasaresultoftheactionsofthecompany,however.Sharepricesmayincreaseirrespectiveoftheactionsanddecisionsofmanagers,orevendespitethem.Infact,lookingatthedividendpersharehistoryofthecompany,therewasoneyear(2006)wheredividendswereconstant,eventhoughearningspershareincreased.Itisalsodifficulttoknowwhenwealthhasbeenmaximised.Anotherobjectiveofthecompanywastoachieveacontinuousincreaseinearningspershare.Analysisshowsthatearningspershareincreasedeveryyear,withanaverageincreaseof14·9%.Thisobjectiveappearstohavebeenachieved.CommentonfinancialperformanceReturnoncapitalemployed(ROCE)hasbeengrowingtowardsthesectoraverageof25%onayear-by-yearbasisfrom22%in2005.Thissteadygrowthintheprimaryaccountingratiocanbecontrastedwithirregulargrowthinturnover,thereasonsforwhichareunknown.Returnonshareholders’fundshasbeenconsistentlyhigherthantheaverageforthesector.ThismaybeduemoretothecapitalstructureofJJGCothantogoodperformancebythecompany,however,inthesensethatshareholders’fundsaresmalleronabookvaluebasisthanthelong-termdebtcapital.Ineverypreviousyearbut2008thegearingofthecompanywashigherthanthesectoraverage.(b)CalculationoftheoreticalexrightspershareCurrentshareprice=$8·64pershareCurrentnumberofshares=5·5millionsharesFinancetoberaised=$15mRightsissueprice=$7·50pershareNumberofsharesissued=15m/7·50=2millionsharesTheoreticalexrightspricepershare=((5·5mx8·64)+(2mx7·50))/7·5m=$8·34pershareThesharepricewouldfallfrom$8·64to$8·34pershareHowever,therewouldbenoeffectonshareholderwealthEffectofrightsissueonearningspershareCurrentEPS=100centspershareRevisedEPS=100x5·5m/7·5m=73centspershareTheEPSwouldfallfrom100centspershareto73centspershareHowever,asmentionedearlier,therewouldbenoeffectonshareholderwealthEffectofrightsissueonthedebt/equityratioCurrentdebt/equityratio=100x20/47·5=42%Revisedmarketvalueofequity=7·5mx8·34=$62·55millionReviseddebt/equityratio=100x20/62·55=32%Thedebt/equityratiowouldfallfrom42%to32%,whichiswellbelowthesectoraveragevalueandwouldsignalareductioninfinancialrisk(c)Thecurrentdebt/equityratioofJJGCois42%(20/47·5).Althoughthisislessthanthesectoraveragevalueof50%,itismoreusefulfromafinancialriskperspectivetolookattheextenttowhichinterestpaymentsarecoveredbyprofits.Theinterestonthebondissueis$1·6million(8%of$20m),givinganinterestcoverageratioof6·1times.IfJJGCohasoverdraftfinance,theinterestcoverageratiowillbelowerthanthis,butthereisinsufficientinformationtodetermineifanoverdraftexists.Theinterestcoverageratioisnotonlybelowthesectoraverage,itisalsolowenoughtobeacauseforconcern.Whiletheratioshowsanupwardtrendovertheperiodunderconsideration,itstillindicatesthatanissueoffurtherdebtwouldbeunwise.Aplacing,oranyissueofnewsharessuchasarightsissueorapublicoffer,woulddecreasegearing.Iftheexpansionofbusinessresultsinanincreaseinprofitbeforeinterestandtax,theinterestcoverageratiowillincreaseandfinancialriskwillfall.GiventhecurrentfinancialpositionofJJGCo,adecreaseinfinancialriskiscertainlypreferabletoanincrease.Aplacingwilldiluteownershipandcontrol,providingthenewequityissueistakenupbynewinstitutionalshareholders,whilearightsissuewillnotdiluteownershipandcontrol,providingexistingshareholderstakeuptheirrights.Abondissuedoesnothaveownershipandcontrolimplications,althoughrestrictiveornegativecovenantsinbondissuedocumentscanlimittheactionsofacompanyanditsmanagers.Allthreefinancingchoicesarelong-termsourcesoffinanceandsoareappropriateforalong-terminvestmentsuchastheproposedexpansionofexistingbusiness.Equityissuessuchasaplacingandarightsissuedonotrequiresecurity.Noinformationisprovidedonthenon-currentassetsofJJGCo,butitislikelythattheexistingbondissueissecured.Ifanewbondissuewasbeingconsidered,JJGCowouldneedtoconsiderwhetherithadsufficientnon-currentassetstoofferassecurity,althoughitislikelythatnewnon-currentassetswouldbeboughtaspartofthebusinessexpansion. -
第8题:
Moonstar Co is a property development company which is planning to undertake a $200 million commercial property development. Moonstar Co has had some difficulties over the last few years, with some developments not generating the expected returns and the company has at times struggled to pay its finance costs. As a result Moonstar Co’s credit rating has been lowered, affecting the terms it can obtain for bank finance. Although Moonstar Co is listed on its local stock exchange, 75% of the share capital is held by members of the family who founded the company. The family members who are shareholders do not wish to subscribe for a rights issue and are unwilling to dilute their control over the company by authorising a new issue of equity shares. Moonstar Co’s board is therefore considering other methods of financing the development, which the directors believe will generate higher returns than other recent investments, as the country where Moonstar Co is based appears to be emerging from recession.
Securitisation proposals
One of the non-executive directors of Moonstar Co has proposed that it should raise funds by means of a securitisation process, transferring the rights to the rental income from the commercial property development to a special purpose vehicle. Her proposals assume that the leases will generate an income of 11% per annum to Moonstar Co over a ten-year period. She proposes that Moonstar Co should use 90% of the value of the investment for a collateralised loan obligation which should be structured as follows:
– 60% of the collateral value to support a tranche of A-rated floating rate loan notes offering investors LIBOR plus 150 basis points
– 15% of the collateral value to support a tranche of B-rated fixed rate loan notes offering investors 12%
– 15% of the collateral value to support a tranche of C-rated fixed rate loan notes offering investors 13%
– 10% of the collateral value to support a tranche as subordinated certificates, with the return being the excess of receipts over payments from the securitisation process
The non-executive director believes that there will be sufficient demand for all tranches of the loan notes from investors. Investors will expect that the income stream from the development to be low risk, as they will expect the property market to improve with the recession coming to an end and enough potential lessees to be attracted by the new development.
The non-executive director predicts that there would be annual costs of $200,000 in administering the loan. She acknowledges that there would be interest rate risks associated with the proposal, and proposes a fixed for variable interest rate swap on the A-rated floating rate notes, exchanging LIBOR for 9·5%.
However the finance director believes that the prediction of the income from the development that the non-executive director has made is over-optimistic. He believes that it is most likely that the total value of the rental income will be 5% lower than the non-executive director has forecast. He believes that there is some risk that the returns could be so low as to jeopardise the income for the C-rated fixed rate loan note holders.
Islamic finance
Moonstar Co’s chief executive has wondered whether Sukuk finance would be a better way of funding the development than the securitisation.
Moonstar Co’s chairman has pointed out that a major bank in the country where Moonstar Co is located has begun to offer a range of Islamic financial products. The chairman has suggested that a Mudaraba contract would be the most appropriate method of providing the funds required for the investment.
Required:
(a) Calculate the amounts in $ which each of the tranches can expect to receive from the securitisation arrangement proposed by the non-executive director and discuss how the variability in rental income affects the returns from the securitisation. (11 marks)
(b) Discuss the benefits and risks for Moonstar Co associated with the securitisation arrangement that the non-executive director has proposed. (6 marks)
(c) (i) Discuss the suitability of Sukuk finance to fund the investment, including an assessment of its appeal to potential investors. (4 marks)
(ii) Discuss whether a Mudaraba contract would be an appropriate method of financing the investment and discuss why the bank may have concerns about providing finance by this method. (4 marks)
正确答案:(a) An annual cash flow account compares the estimated cash flows receivable from the property against the liabilities within the securitisation process. The swap introduces leverage into the arrangement.
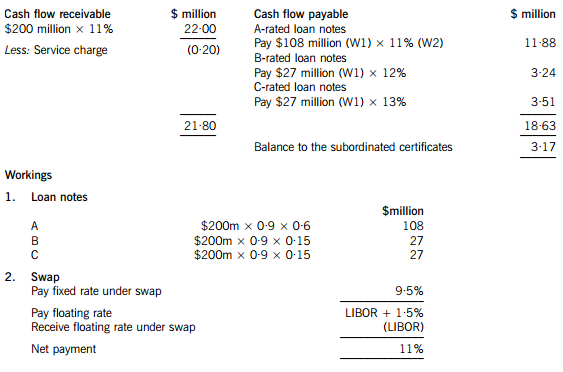
The holders of the certificates are expected to receive $3·17million on $18 million, giving them a return of 17·6%. If the cash flows are 5% lower than the non-executive director has predicted, annual revenue received will fall to $20·90 million, reducing the balance available for the subordinated certificates to $2·07 million, giving a return of 11·5% on the subordinated certificates, which is below the returns offered on the B and C-rated loan notes. The point at which the holders of the certificates will receive nothing and below which the holders of the C-rated loan notes will not receive their full income will be an annual income of $18·83 million (a return of 9·4%), which is 14·4% less than the income that the non-executive director has forecast.
(b) Benefits
The finance costs of the securitisation may be lower than the finance costs of ordinary loan capital. The cash flows from the commercial property development may be regarded as lower risk than Moonstar Co’s other revenue streams. This will impact upon the rates that Moonstar Co is able to offer borrowers.
The securitisation matches the assets of the future cash flows to the liabilities to loan note holders. The non-executive director is assuming a steady stream of lease income over the next 10 years, with the development probably being close to being fully occupied over that period.
The securitisation means that Moonstar Co is no longer concerned with the risk that the level of earnings from the properties will be insufficient to pay the finance costs. Risks have effectively been transferred to the loan note holders.
Risks
Not all of the tranches may appeal to investors. The risk-return relationship on the subordinated certificates does not look very appealing, with the return quite likely to be below what is received on the C-rated loan notes. Even the C-rated loan note holders may question the relationship between the risk and return if there is continued uncertainty in the property sector.
If Moonstar Co seeks funding from other sources for other developments, transferring out a lower risk income stream means that the residual risks associated with the rest of Moonstar Co’s portfolio will be higher. This may affect the availability and terms of other borrowing.
It appears that the size of the securitisation should be large enough for the costs to be bearable. However Moonstar Co may face unforeseen costs, possibly unexpected management or legal expenses.
(c) (i) Sukuk finance could be appropriate for the securitisation of the leasing portfolio. An asset-backed Sukuk would be the same kind of arrangement as the securitisation, where assets are transferred to a special purpose vehicle and the returns and repayments are directly financed by the income from the assets. The Sukuk holders would bear the risks and returns of the relationship.
The other type of Sukuk would be more like a sale and leaseback of the development. Here the Sukuk holders would be guaranteed a rental, so it would seem less appropriate for Moonstar Co if there is significant uncertainty about the returns from the development.
The main issue with the asset-backed Sukuk finance is whether it would be as appealing as certainly the A-tranche of the securitisation arrangement which the non-executive director has proposed. The safer income that the securitisation offers A-tranche investors may be more appealing to investors than a marginally better return from the Sukuk. There will also be costs involved in establishing and gaining approval for the Sukuk, although these costs may be less than for the securitisation arrangement described above.
(ii) A Mudaraba contract would involve the bank providing capital for Moonstar Co to invest in the development. Moonstar Co would manage the investment which the capital funded. Profits from the investment would be shared with the bank, but losses would be solely borne by the bank. A Mudaraba contract is essentially an equity partnership, so Moonstar Co might not face the threat to its credit rating which it would if it obtained ordinary loan finance for the development. A Mudaraba contract would also represent a diversification of sources of finance. It would not require the commitment to pay interest that loan finance would involve.
Moonstar Co would maintain control over the running of the project. A Mudaraba contract would offer a method of obtaining equity funding without the dilution of control which an issue of shares to external shareholders would bring. This is likely to make it appealing to Moonstar Co’s directors, given their desire to maintain a dominant influence over the business.
The bank would be concerned about the uncertainties regarding the rental income from the development. Although the lack of involvement by the bank might appeal to Moonstar Co's directors, the bank might not find it so attractive. The bank might be concerned about information asymmetry – that Moonstar Co’s management might be reluctant to supply the bank with the information it needs to judge how well its investment is performing.
-
第9题:
You are the audit manager of Chestnut & Co and are reviewing the key issues identified in the files of two audit clients.
Palm Industries Co (Palm)
Palm’s year end was 31 March 2015 and the draft financial statements show revenue of $28·2 million, receivables of $5·6 million and profit before tax of $4·8 million. The fieldwork stage for this audit has been completed.
A customer of Palm owed an amount of $350,000 at the year end. Testing of receivables in April highlighted that no amounts had been paid to Palm from this customer as they were disputing the quality of certain goods received from Palm. The finance director is confident the issue will be resolved and no allowance for receivables was made with regards to this balance.
Ash Trading Co (Ash)
Ash is a new client of Chestnut & Co, its year end was 31 January 2015 and the firm was only appointed auditors in February 2015, as the previous auditors were suddenly unable to undertake the audit. The fieldwork stage for this audit is currently ongoing.
The inventory count at Ash’s warehouse was undertaken on 31 January 2015 and was overseen by the company’s internal audit department. Neither Chestnut & Co nor the previous auditors attended the count. Detailed inventory records were maintained but it was not possible to undertake another full inventory count subsequent to the year end.
The draft financial statements show a profit before tax of $2·4 million, revenue of $10·1 million and inventory of $510,000.
Required:
For each of the two issues:
(i) Discuss the issue, including an assessment of whether it is material;
(ii) Recommend ONE procedure the audit team should undertake to try to resolve the issue; and
(iii) Describe the impact on the audit report if the issue remains UNRESOLVED.
Notes:
1 The total marks will be split equally between each of the two issues.
2 Audit report extracts are NOT required.
正确答案:Audit reports
Palm Industries Co (Palm)
(i) A customer of Palm’s owing $350,000 at the year end has not made any post year-end payments as they are disputing the quality of goods received. No allowance for receivables has been made against this balance. As the balance is being disputed, there is a risk of incorrect valuation as some or all of the receivable balance is overstated, as it may not be paid.
This $350,000 receivables balance represents 1·2% (0·35/28·2m) of revenue, 6·3% (0·35/5·6m) of receivables and 7·3% (0·35/4·8m) of profit before tax; hence this is a material issue.
(ii) A procedure to adopt includes:
– Review whether any payments have subsequently been made by this customer since the audit fieldwork was completed.
– Discuss with management whether the issue of quality of goods sold to the customer has been resolved, or whether it is still in dispute.
– Review the latest customer correspondence with regards to an assessment of the likelihood of the customer making payment.
(iii) If management refuses to provide against this receivable, the audit report will need to be modified. As receivables are overstated and the error is material but not pervasive a qualified opinion would be necessary.
A basis for qualified opinion paragraph would be needed and would include an explanation of the material misstatement in relation to the valuation of receivables and the effect on the financial statements. The opinion paragraph would be qualified ‘except for’.
Ash Trading Co (Ash)
(i) Chestnut & Co was only appointed as auditors subsequent to Ash’s year end and hence did not attend the year-end inventory count. Therefore, they have not been able to gather sufficient and appropriate audit evidence with regards to the completeness and existence of inventory.
Inventory is a material amount as it represents 21·3% (0·51/2·4m) of profit before tax and 5% (0·51/10·1m) of revenue; hence this is a material issue.
(ii) A procedure to adopt includes:
– Review the internal audit reports of the inventory count to identify the level of adjustments to the records to assess the reasonableness of relying on the inventory records.
– Undertake a sample check of inventory in the warehouse and compare to the inventory records and then from inventory records to the warehouse, to assess the reasonableness of the inventory records maintained by Ash.
(iii) The auditors will need to modify the audit report as they are unable to obtain sufficient appropriate evidence in relation to inventory which is a material but not pervasive balance. Therefore a qualified opinion will be required.
A basis for qualified opinion paragraph will be required to explain the limitation in relation to the lack of evidence over inventory. The opinion paragraph will be qualified ‘except for’.
-
第10题:
Your firm has been recommended to us by AMK company, () we have done business for many years.
- A、with whom
- B、with who
- C、whom
- D、who
正确答案:A -
第11题:
You work as an Exchange Administrator for TechWorld Inc.The company has a Windows 2008 Active Directory-based contains an Exchange Server 2010 organization.The CIO has requested you to ensure that all emails with JPEG at that they are not allowed into the users’ mailboxes.You decide to use the Exchange Management Shell.Which of t you use to accomplish the task?()
- A、Add-AttachmentFilterEntry -Name image/jpeg -Type FileName
- B、Add-AttachmentFilterEntry -Name *.exe -Type FileName
- C、Add-AttachmentFilterEntry -Name image/jpeg -Type ContentType
- D、Add-AttachmentFilterEntry -Name ".jpeg -Type ContentType
正确答案:C -
第12题:
单选题Your firm has been recommended to us by AMK company, () we have done business for many years.Awith whom
Bwith who
Cwhom
Dwho
正确答案: C解析: 暂无解析 -
第13题:
3 You are an audit manager in Webb & Co, a firm of Chartered Certified Accountants. Your audit client, Mulligan Co,
designs and manufactures wooden tables and chairs. The business has expanded rapidly in the last two years, since
the arrival of Patrick Tiler, an experienced sales and marketing manager.
The directors want to secure a loan of $3 million in order to expand operations, following the design of a completely
new range of wooden garden furniture. The directors have approached LCT Bank for the loan. The bank’s lending
criteria stipulate the following:
‘Loan applications must be accompanied by a detailed business plan, including an analysis of how the finance will
be used. LCT Bank need to see that the finance requested is adequate for the proposed business purpose. The
business plan must be supported by an assurance opinion on the adequacy of the requested finance.’
The $3 million finance raised will be used as follows:
$000
Construction of new factory 1,250
Purchase of new machinery 1,000
Initial supply of timber raw material 250
Advertising and marketing of new product 500
Your firm has agreed to review the business plan and to provide an assurance opinion on the completeness of the
finance request. A meeting will be held tomorrow to discuss this assignment.
Required:
(a) Identify and explain the matters relating to the assurance assignment that should be discussed at the meeting
with Mulligan Co. (8 marks)
正确答案:
3 MULLIGAN CO
(a) Matters to be discussed would include the following:
The exact content of the business plan which could include:
– Description of past business performance and key products
– Discussion of the new product
– Evidence of the marketability of the new product
– Cash flow projections
– Capital expenditure forecasts
– Key business assumptions.
The form. of the assurance report that is required – in an assurance engagement the nature and wording of the expected
opinion should be discussed. Webb & Co should clarify that an opinion of ‘negative assurance’ will be required, and whether
this will meet the bank’s lending criteria.
The intended recipient of the report – Webb & Co need to clarify the name and address of the recipient at LCT Bank. For the
limitation of professional liability, it should be clarified that LCT Bank will be the only recipient, and that the assurance opinion
is being used only as part of the bank’s overall lending decision.
Limiting liability – Webb & Co may want to receive in writing a statement that the report is for information purposes only, and
does not give rise to any responsibility, liability, duty or obligation from the firm to the lender.
Deadlines – it should be discussed when the bank need the report. This in turn will be influenced by when Mulligan Co needs
the requested $3 million finance. The bank may need a considerable period of time to assess the request, review the report,
and ensure that their lending criteria have been fully met prior to advancing the finance.
Availability of evidence – Mulligan Co should be made aware that in order to express an opinion on the finance request, they
must be prepared to provide all the necessary paperwork to assist the assurance provider. Evidence is likely to include
discussions with key management, and written representations of discussions may be required.
Professional regulation – Webb & Co should discuss the kind of procedures that will be undertaken, and confirm that they
will be complying with relevant professional guidance, for example:
– ISAE 3000 Assurance Engagements other than Audits or Reviews of Historical Financial Information
– ISAE 3400 The Examination of Prospective Financial Information
Engagement administration – any points not yet discussed in detail when deciding to take the assurance engagement should
be finalised at the meeting. These points could include the following:
– Fees – the total fee and billing arrangements must be agreed before any work is carried out
– Personnel – Webb & Co should identify the key personnel who will be involved in the assignment
– Complaints procedures – should be briefly outlined (the complaints procedures in an assurance engagement may differ
from an audit assignment)
– Engagement letter – if not already signed by both Webb & Co and Mulligan Co, the engagement letter should be
discussed and signed at the meeting before any assignment work is conducted.
Tutorial note: the scenario states that Webb & Co have already decided to take the assurance assignment for their existing
client, therefore the answer to this requirement should not focus on client or engagement acceptance procedures. -
第14题:
4 You are a senior manager in Becker & Co, a firm of Chartered Certified Accountants offering audit and assurance
services mainly to large, privately owned companies. The firm has suffered from increased competition, due to two
new firms of accountants setting up in the same town. Several audit clients have moved to the new firms, leading to
loss of revenue, and an over staffed audit department. Bob McEnroe, one of the partners of Becker & Co, has asked
you to consider how the firm could react to this situation. Several possibilities have been raised for your consideration:
1. Murray Co, a manufacturer of electronic equipment, is one of Becker & Co’s audit clients. You are aware that the
company has recently designed a new product, which market research indicates is likely to be very successful.
The development of the product has been a huge drain on cash resources. The managing director of Murray Co
has written to the audit engagement partner to see if Becker & Co would be interested in making an investment
in the new product. It has been suggested that Becker & Co could provide finance for the completion of the
development and the marketing of the product. The finance would be in the form. of convertible debentures.
Alternatively, a joint venture company in which control is shared between Murray Co and Becker & Co could be
established to manufacture, market and distribute the new product.
2. Becker & Co is considering expanding the provision of non-audit services. Ingrid Sharapova, a senior manager in
Becker & Co, has suggested that the firm could offer a recruitment advisory service to clients, specialising in the
recruitment of finance professionals. Becker & Co would charge a fee for this service based on the salary of the
employee recruited. Ingrid Sharapova worked as a recruitment consultant for a year before deciding to train as
an accountant.
3. Several audit clients are experiencing staff shortages, and it has been suggested that temporary staff assignments
could be offered. It is envisaged that a number of audit managers or seniors could be seconded to clients for
periods not exceeding six months, after which time they would return to Becker & Co.
Required:
Identify and explain the ethical and practice management implications in respect of:
(a) A business arrangement with Murray Co. (7 marks)
正确答案:
4 Becker & Co
(a) Joint business arrangement
The business opportunity in respect of Murray Co could be lucrative if the market research is to be believed.
However, IFAC’s Code of Ethics for Professional Accountants states that a mutual business arrangement is likely to give rise
to self-interest and intimidation threats to independence and objectivity. The audit firm must be and be seen to be independent
of the audit client, which clearly cannot be the case if the audit firm and the client are seen to be working together for a
mutual financial gain.
In the scenario, two options are available. Firstly, Becker & Co could provide the audit client with finance to complete the
development and take the product to market. There is a general prohibition on audit firms providing finance to their audit
clients. This would create a clear financial self-interest threat as the audit firm would be receiving a return on investment from
their client. The Code states that if a firm makes a loan (or guarantees a loan) to a client, the self-interest threat created would
be so significant that no safeguard could reduce the threat to an acceptable level.
The provision of finance using convertible debentures raises a further ethical problem, because if the debentures are ultimately
converted to equity, the audit firm would then hold equity shares in their audit client. This is a severe financial self-interest,
which safeguards are unlikely to be able to reduce to an acceptable level.
The finance should not be advanced to Murray Co while the company remains an audit client of Becker & Co.
The second option is for a joint venture company to be established. This would be perceived as a significant mutual business
interest as Becker & Co and Murray Co would be investing together, sharing control and sharing a return on investment in
the form. of dividends. IFAC’s Code of Ethics states that unless the relationship between the two parties is clearly insignificant,
the financial interest is immaterial, and the audit firm is unable to exercise significant influence, then no safeguards could
reduce the threat to an acceptable level. In this case Becker & Co may not enter into the joint venture arrangement while
Murray Co is still an audit client.
The audit practice may consider that investing in the new electronic product is a commercial strategy that it wishes to pursue,
either through loan finance or using a joint venture arrangement. In this case the firm should resign as auditor with immediate
effect in order to eliminate any ethical problem with the business arrangement. The partners should carefully consider if the
potential return on investment will more than compensate for the lost audit fee from Murray Co.
The partners should also reflect on whether they want to diversify to such an extent – this investment is unlikely to be in an
area where any of the audit partners have much knowledge or expertise. A thorough commercial evaluation and business risk
analysis must be performed on the new product to ensure that it is a sound business decision for the firm to invest.
The audit partners should also consider how much time they would need to spend on this business development, if they
decided to resign as auditors and to go ahead with the investment. Such a new and important project could mean that they
take their focus off the key business i.e. the audit practice. They should consider if it would be better to spend their time trying
to compete effectively with the two new firms of accountants, trying to retain key clients, and to attract new accounting and
audit clients rather than diversify into something completely different. -
第15题:
(c) Maxwell Co is audited by Lead & Co, a firm of Chartered Certified Accountants. Leo Sabat has enquired as to
whether your firm would be prepared to conduct a joint audit in cooperation with Lead & Co, on the future
financial statements of Maxwell Co if the acquisition goes ahead. Leo Sabat thinks that this would enable your
firm to improve group audit efficiency, without losing the cumulative experience that Lead & Co has built up while
acting as auditor to Maxwell Co.
Required:
Define ‘joint audit’, and assess the advantages and disadvantages of the audit of Maxwell Co being conducted
on a ‘joint basis’. (7 marks)
正确答案:
(c) A joint audit is when two or more audit firms are jointly responsible for giving the audit opinion. This is very common in a
group situation where the principal auditor is appointed jointly with the auditor of a subsidiary to provide a joint opinion on
the subsidiary’s financial statements. There are several advantages and disadvantages in a joint audit being performed.
Advantages
It can be beneficial in terms of audit efficiency for a joint audit to be conducted, especially in the case of a new subsidiary.
In this case, Lead & Co will have built up an understanding of Maxwell Co’s business, systems and controls, and financial
statement issues. It will be time efficient for the two firms of auditors to work together in order for Chien & Co to build up
knowledge of the new subsidiary. This is a key issue, as Chien & Co need to acquire a thorough understanding of the
subsidiary in order to assess any risks inherent in the company which could impact on the overall assessment of risk within
the group. Lead & Co will be able to provide a good insight into the company, and advise Chien & Co of the key risk areas
they have previously identified.
On the practical side, it seems that Maxwell Co is a significant addition to the group, as it is expected to increase operating
facilities by 40%. If Chien & Co were appointed as sole auditors to Maxwell Co it may be difficult for the audit firm to provide
adequate resources to conduct the audit at the same time as auditing the other group companies. A joint audit will allow
sufficient resources to be allocated to the audit of Maxwell Co, assuring the quality of the opinion provided.
If there is a tight deadline, as is common with the audit of subsidiaries, which should be completed before the group audit
commences, then having access to two firms’ resources should enable the audit to be completed in good time.
The audit should also benefit from an improvement in quality. The two audit firms may have different points of view, and
would be able to discuss contentious issues throughout the audit process. In particular, the newly appointed audit team will
have a ‘fresh pair of eyes’ and be able to offer new insight to matters identified. It should be easier to challenge management
and therefore ensure that the auditors’ position is taken seriously.
Tutorial note: Candidates may have referred to the recent debate over whether joint audits increase competition in the
profession. In particular, joint audits have been proposed as a way for ‘mid tier’ audit firms to break into the market of
auditing large companies and groups, which at the moment is monopolised by the ‘Big 4’. Although this does not answer
the specific question set, credit will be awarded for demonstration of awareness of this topical issue.
Disadvantages
For the client, it is likely to be more expensive to engage two audit firms than to have the audit opinion provided by one firm.
From a cost/benefit point of view there is clearly no point in paying twice for one opinion to be provided. Despite the audit
workload being shared, both firms will have a high cost for being involved in the audit in terms of senior manager and partner
time. These costs will be passed on to the client within the audit fee.
The two audit firms may use very different audit approaches and terminology. This could make it difficult for the audit firms
to work closely together, negating some of the efficiency and cost benefits discussed above. Problems could arise in deciding
which firm’s method to use, for example, to calculate materiality, design and pick samples for audit procedures, or evaluate
controls within the accounting system. It may be impossible to reconcile two different methods and one firm’s methods may
end up dominating the audit process, which then eliminates the benefit of a joint audit being conducted. It could be time
consuming to develop a ‘joint’ audit approach, based on elements of each of the two firms’ methodologies, time which
obviously would not have been spent if a single firm was providing the audit.
There may be problems for the two audit firms to work together harmoniously. Lead & Co may feel that ultimately they will
be replaced by Chien & Co as audit provider, and therefore could be unwilling to offer assistance and help.
Potentially, problems could arise in terms of liability. In the event of litigation, because both firms have provided the audit
opinion, it follows that the firms would be jointly liable. The firms could blame each other for any negligence which was
discovered, making the litigation process more complex than if a single audit firm had provided the opinion. However, it could
be argued that joint liability is not necessarily a drawback, as the firms should both be covered by professional indemnity
insurance. -
第16题:
5 You are the manager responsible for the audit of Blod Co, a listed company, for the year ended 31 March 2008. Your
firm was appointed as auditors of Blod Co in September 2007. The audit work has been completed, and you are
reviewing the working papers in order to draft a report to those charged with governance. The statement of financial
position (balance sheet) shows total assets of $78 million (2007 – $66 million). The main business activity of Blod
Co is the manufacture of farm machinery.
During the audit of property, plant and equipment it was discovered that controls over capital expenditure transactions
had deteriorated during the year. Authorisation had not been gained for the purchase of office equipment with a cost
of $225,000. No material errors in the financial statements were revealed by audit procedures performed on property,
plant and equipment.
An internally generated brand name has been included in the statement of financial position (balance sheet) at a fair
value of $10 million. Audit working papers show that the matter was discussed with the financial controller, who
stated that the $10 million represents the present value of future cash flows estimated to be generated by the brand
name. The member of the audit team who completed the work programme on intangible assets has noted that this
treatment appears to be in breach of IAS 38 Intangible Assets, and that the management refuses to derecognise the
asset.
Problems were experienced in the audit of inventories. Due to an oversight by the internal auditors of Blod Co, the
external audit team did not receive a copy of inventory counting procedures prior to attending the count. This caused
a delay at the beginning of the inventory count, when the audit team had to quickly familiarise themselves with the
procedures. In addition, on the final audit, when the audit senior requested documentation to support the final
inventory valuation, it took two weeks for the information to be received because the accountant who had prepared
the schedules had mislaid them.
Required:
(a) (i) Identify the main purpose of including ‘findings from the audit’ (management letter points) in a report
to those charged with governance. (2 marks)
正确答案:
5 Blod Co
(a) (i) A report to those charged with governance is produced to communicate matters relating to the external audit to those
who are ultimately responsible for the financial statements. ISA 260 Communication of Audit Matters With Those
Charged With Governance requires the auditor to communicate many matters, including independence and other ethical
issues, the audit approach and scope, the details of management representations, and the findings of the audit. The
findings of the audit are commonly referred to as management letter points. By communicating these matters, the auditor
is confident that there is written documentation outlining all significant matters raised during the audit process, and that
such matters have been formally notified to the highest level of management of the client. For the management, the
report should ensure that they fully understand the scope and results of the audit service which has been provided, and
is likely to provide constructive comments to help them to fulfil their duties in relation to the financial statements and
accounting systems and controls more effectively. The report should also include, where relevant, any actions that
management has indicated they will take in relation to recommendations made by the auditors. -
第17题:
Your IT director has decided to allow employees to use their laptops at home as well as in the office. You have deployed the Junos Pulse client to allow access to the offices 802.1X-enabled wired network. Your company also has the Junos Pulse Secure Access Service deployed. You want the Junos Pulse client to automatically launch the appropriate access method depending on each users location.Which three are supported to determine the users location?()
A. MAC address
B. DNS server
C. DHCP server
D. resolve address
E. endpoint address
参考答案:B, D, E
-
第18题:
One of your audit clients is Tye Co a company providing petrol, aviation fuel and similar oil based products to the government of the country it is based in. Although the company is not listed on any stock exchange, it does follow best practice regarding corporate governance regulations. The audit work for this year is complete, apart from the matter referred to below.
As part of Tye Co’s service contract with the government, it is required to hold an emergency inventory reserve of 6,000 barrels of aviation fuel. The inventory is to be used if the supply of aviation fuel is interrupted due to unforeseen events such as natural disaster or terrorist activity.
This fuel has in the past been valued at its cost price of $15 a barrel. The current value of aviation fuel is $120 a barrel. Although the audit work is complete, as noted above, the directors of Tye Co have now decided to show the ‘real’ value of this closing inventory in the financial statements by valuing closing inventory of fuel at market value, which does not comply with relevant accounting standards. The draft financial statements of Tye Co currently show a profit of approximately $500,000 with net assets of $170 million.
Required:
(a) List the audit procedures and actions that you should now take in respect of the above matter. (6 marks)
(b) For the purposes of this section assume from part (a) that the directors have agreed to value inventory at
$15/barrel.
Having investigated the matter in part (a) above, the directors present you with an amended set of financial
statements showing the emergency reserve stated not at 6,000 barrels, but reported as 60,000 barrels. The final financial statements now show a profit following the inclusion of another 54,000 barrels of oil in inventory. When queried about the change from 6,000 to 60,000 barrels of inventory, the finance director stated that this change was made to meet expected amendments to emergency reserve requirements to be published in about six months time. The inventory will be purchased this year, and no liability will be shown in the financial statements for this future purchase. The finance director also pointed out that part of Tye Co’s contract with the government requires Tye Co to disclose an annual profit and that a review of bank loans is due in three months. Finally the finance director stated that if your audit firm qualifies the financial statements in respect of the increase in inventory, they will not be recommended for re-appointment at the annual general meeting. The finance director refuses to amend the financial statements to remove this ‘fictitious’ inventory.
Required:
(i) State the external auditor’s responsibilities regarding the detection of fraud; (4 marks)
(ii) Discuss to which groups the auditors of Tye Co could report the ‘fictitious’ aviation fuel inventory;
(6 marks)
(iii) Discuss the safeguards that the auditors of Tye Co can use in an attempt to overcome the intimidation
threat from the directors of Tye Co. (4 marks)
正确答案:
(a)Valuationofaviationinventory–ReviewGAAPtoensurethattherearenoexceptionsforaviationfuelorinventoryheldforemergencypurposeswhichwouldsuggestamarketvaluationshouldbeused.–Calculatethedifferenceinvaluation.Theerrorininventoryvaluationis$105*6,000barrelsor$630k,whichisamaterialamountcomparedtoprofit.–Reviewprioryearworkingpaperstodeterminewhetherasimilarsituationoccurredlastyearandascertaintheoutcomeatthatstage.–Discussthematterwiththedirectorstoobtainreasonswhytheybelievethatmarketvalueshouldbeusedfortheinventorythisyear.–Warnthedirectorsthatinyouropinion,aviationfuelshouldbevaluedatthelowerofcostornetrealisablevalue(thatis$15/barrel)andthatusingmarketvaluewillresultinamodificationtotheauditreport.–Ifthedirectorsnowamendthefinancialstatementstoshowinventoryvaluedatcost,thenconsidermentioningtheissueintheweaknessletteranddonotmodifytheauditreportinrespectofthismatter.–Ifthedirectorswillnotamendthefinancialstatements,quantifytheeffectofthedisagreementinthevaluationmethod–thesumof$630,000ismaterialtothefinancialstatementsasTyeCo’sincomestatementfigureisdecreasedfromasmalllosstoalossof$130,000althoughnetassetsdecreasebyonlyabout0·3%.–ObtainamanagementrepresentationletterfromthedirectorsofTyeCoconfirmingthatmarketvalueistobeusedfortheemergencyinventoryofaviationfuel.–Ifthedirectorswillnotamendthefinancialstatements,drafttherelevantsectionsoftheauditreport,showingaqualificationonthegroundsofdisagreementwiththeaccountingpolicyforvaluationofinventory.(b)(i)ExternalauditorresponsibilitiesregardingdetectionoffraudOverallresponsibilityofauditorTheexternalauditorisprimarilyresponsiblefortheauditopiniononthefinancialstatementsfollowingtheinternationalauditingstandards(ISAs).ISA240(Redrafted)TheAuditor’sResponsibilitiesRelatingtoFraudinanAuditofFinancialStatementsisrelevanttoauditworkregardingfraud.Themainfocusofauditworkisthereforetoensurethatthefinancialstatementsshowatrueandfairview.Thedetectionoffraudisthereforenotthemainfocusoftheexternalauditor’swork.Anauditorisresponsibleforobtainingreasonableassurancethatthefinancialstatementsasawholearefreefrommaterialmisstatement,whethercausedbyfraudorerror.Theauditorisresponsibleformaintaininganattitudeofprofessionalscepticismthroughouttheaudit,consideringthepotentialformanagementoverrideofcontrolsandrecognisingthefactthatauditproceduresthatareeffectivefordetectingerrormaynotbeeffectivefordetectingfraud.MaterialityISA240statesthattheauditorshouldreduceauditrisktoanacceptablylowlevel.Therefore,inreachingtheauditopinionandperformingauditwork,theexternalauditortakesintoaccounttheconceptofmateriality.Inotherwords,theexternalauditorisnotresponsibleforcheckingallthetransactions.Auditproceduresareplannedtohaveareasonablelikelihoodofidentifyingmaterialfraud.DiscussionamongtheauditteamAdiscussionisrequiredamongtheengagementteamplacingparticularemphasisonhowandwheretheentity’sfinancialstatementsmaybesusceptibletomaterialmisstatementduetofaud,includinghowfraudmightoccur.IdentificationoffraudInsituationswheretheexternalauditordoesdetectfraud,thentheauditorwillneedtoconsidertheimplicationsfortheentireaudit.Inotherwords,theexternalauditorhasaresponsibilitytoextendtestingintootherareasbecausetheriskofprovidinganincorrectauditopinionwillhaveincreased.(ii)GroupstoreportfraudtoReporttoauditcommitteeDisclosethesituationtotheauditcommitteeastheyarechargedwithmaintainingahighstandardofgovernanceinthecompany.Thecommitteeshouldbeabletodiscussthesituationwiththedirectorsandrecommendthattheytakeappropriateactione.g.amendthefinancialstatements.ReporttogovernmentAsTyeCoisactingunderagovernmentcontract,andtheover-statementofinventorywillmeanTyeCobreachesthatcontract(thereportedprofitbecomingaloss),thentheauditormayhavetoreportthesituationdirectlytothegovernment.TheauditorofTyeConeedstoreviewthecontracttoconfirmthereportingrequiredunderthatcontract.ReporttomembersIfthefinancialstatementsdonotshowatrueandfairviewthentheauditorneedstoreportthisfacttothemembersofTyeCo.Theauditreportwillbequalifiedwithanexceptfororadverseopinion(dependingonmateriality)andinformationconcerningthereasonforthedisagreementgiven.Inthiscasetheauditorislikelytostatefactuallytheproblemofinventoryquantitiesbeingincorrect,ratherthanstatingorimplyingthatthedirectorsareinvolvedinfraud.ReporttoprofessionalbodyIftheauditorisuncertainastothecorrectcourseofaction,advicemaybeobtainedfromtheauditor’sprofessionalbody.Dependingontheadvicereceived,theauditormaysimplyreporttothemembersintheauditreport,althoughresignationandtheconveningofageneralmeetingisanotherreportingoption.(iii)Intimidationthreat–safeguardsInresponsetotheimpliedthreatofdismissaliftheauditreportismodifiedregardingthepotentialfraud/error,thefollowingsafeguardsareavailabletotheauditor.DiscusswithauditcommitteeThesituationcanbediscussedwiththeauditcommittee.Astheauditcommitteeshouldcomprisenon-executivedirectors,theywillbeabletodiscussthesituationwiththefinancedirectorandpointoutclearlytheauditor’sopinion.Theycanalsoremindthedirectorsasawholethattheappointmentoftheauditorrestswiththemembersontherecommendationoftheauditcommittee.Iftherecommendationoftheauditcommitteeisrejectedbytheboard,goodcorporategovernancerequiresdisclosureofthereasonforrejection.ObtainsecondpartnerreviewTheengagementpartnercanaskasecondpartnertoreviewtheworkingpapersandotherevidencerelatingtotheissueofpossiblefraud.Whilethisactiondoesnotresolvetheissue,itdoesprovideadditionalassurancethatthefindingsandactionsoftheengagementpartnerarevalid.ResignationIfthematterisserious,thentheauditorcanconsiderresignationratherthannotbeingre-appointed.Resignationhastheadditionalsafeguardthattheauditorcannormallyrequirethedirectorstoconveneageneralmeetingtoconsiderthecircumstancesoftheresignation. -
第19题:
You are the audit supervisor of Maple & Co and are currently planning the audit of an existing client, Sycamore Science Co (Sycamore), whose year end was 30 April 2015. Sycamore is a pharmaceutical company, which manufactures and supplies a wide range of medical supplies. The draft financial statements show revenue of $35·6 million and profit before tax of $5·9 million.
Sycamore’s previous finance director left the company in December 2014 after it was discovered that he had been claiming fraudulent expenses from the company for a significant period of time. A new finance director was appointed in January 2015 who was previously a financial controller of a bank, and she has expressed surprise that Maple & Co had not uncovered the fraud during last year’s audit.
During the year Sycamore has spent $1·8 million on developing several new products. These projects are at different stages of development and the draft financial statements show the full amount of $1·8 million within intangible assets. In order to fund this development, $2·0 million was borrowed from the bank and is due for repayment over a ten-year period. The bank has attached minimum profit targets as part of the loan covenants.
The new finance director has informed the audit partner that since the year end there has been an increased number of sales returns and that in the month of May over $0·5 million of goods sold in April were returned.
Maple & Co attended the year-end inventory count at Sycamore’s warehouse. The auditor present raised concerns that during the count there were movements of goods in and out the warehouse and this process did not seem well controlled.
During the year, a review of plant and equipment in the factory was undertaken and surplus plant was sold, resulting in a profit on disposal of $210,000.
Required:
(a) State Maples & Co’s responsibilities in relation to the prevention and detection of fraud and error. (4 marks)
(b) Describe SIX audit risks, and explain the auditor’s response to each risk, in planning the audit of Sycamore Science Co. (12 marks)
(c) Sycamore’s new finance director has read about review engagements and is interested in the possibility of Maple & Co undertaking these in the future. However, she is unsure how these engagements differ from an external audit and how much assurance would be gained from this type of engagement.
Required:
(i) Explain the purpose of review engagements and how these differ from external audits; and (2 marks)
(ii) Describe the level of assurance provided by external audits and review engagements. (2 marks)
正确答案:(a) Fraud responsibility
Maple & Co must conduct an audit in accordance with ISA 240 The Auditor’s Responsibilities Relating to Fraud in an Audit of Financial Statements and are responsible for obtaining reasonable assurance that the financial statements taken as a whole are free from material misstatement, whether caused by fraud or error.
In order to fulfil this responsibility, Maple & Co is required to identify and assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements due to fraud.
They need to obtain sufficient appropriate audit evidence regarding the assessed risks of material misstatement due to fraud, through designing and implementing appropriate responses. In addition, Maple & Co must respond appropriately to fraud or suspected fraud identified during the audit.
When obtaining reasonable assurance, Maple & Co is responsible for maintaining professional scepticism throughout the audit, considering the potential for management override of controls and recognising the fact that audit procedures which are effective in detecting error may not be effective in detecting fraud.
To ensure that the whole engagement team is aware of the risks and responsibilities for fraud and error, ISAs require that a discussion is held within the team. For members not present at the meeting, Sycamore’s audit engagement partner should determine which matters are to be communicated to them.
(b) Audit risks and auditors’ responses



(c) (i) Review engagements
Review engagements are often undertaken as an alternative to an audit, and involve a practitioner reviewing financial data, such as six-monthly figures. This would involve the practitioner undertaking procedures to state whether anything has come to their attention which causes the practitioner to believe that the financial data is not in accordance with the financial reporting framework.
A review engagement differs to an external audit in that the procedures undertaken are not nearly as comprehensive as those in an audit, with procedures such as analytical review and enquiry used extensively. In addition, the practitioner does not need to comply with ISAs as these only relate to external audits.
(ii) Levels of assurance
The level of assurance provided by audit and review engagements is as follows:
External audit – A high but not absolute level of assurance is provided, this is known as reasonable assurance. This provides comfort that the financial statements present fairly in all material respects (or are true and fair) and are free of material misstatements.
Review engagements – where an opinion is being provided, the practitioner gathers sufficient evidence to be satisfied that the subject matter is plausible; in this case negative assurance is given whereby the practitioner confirms that nothing has come to their attention which indicates that the subject matter contains material misstatements.
-
第20题:
You are an audit manager at Rockwell & Co, a firm of Chartered Certified Accountants. You are responsible for the audit of the Hopper Group, a listed audit client which supplies ingredients to the food and beverage industry worldwide.
The audit work for the year ended 30 June 2015 is nearly complete, and you are reviewing the draft audit report which has been prepared by the audit senior. During the year the Hopper Group purchased a new subsidiary company, Seurat Sweeteners Co, which has expertise in the research and design of sugar alternatives. The draft financial statements of the Hopper Group for the year ended 30 June 2015 recognise profit before tax of $495 million (2014 – $462 million) and total assets of $4,617 million (2014: $4,751 million). An extract from the draft audit report is shown below:
Basis of modified opinion (extract)
In their calculation of goodwill on the acquisition of the new subsidiary, the directors have failed to recognise consideration which is contingent upon meeting certain development targets. The directors believe that it is unlikely that these targets will be met by the subsidiary company and, therefore, have not recorded the contingent consideration in the cost of the acquisition. They have disclosed this contingent liability fully in the notes to the financial statements. We do not feel that the directors’ treatment of the contingent consideration is correct and, therefore, do not believe that the criteria of the relevant standard have been met. If this is the case, it would be appropriate to adjust the goodwill balance in the statement of financial position.
We believe that any required adjustment may materially affect the goodwill balance in the statement of financial position. Therefore, in our opinion, the financial statements do not give a true and fair view of the financial position of the Hopper Group and of the Hopper Group’s financial performance and cash flows for the year then ended in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards.
Emphasis of Matter Paragraph
We draw attention to the note to the financial statements which describes the uncertainty relating to the contingent consideration described above. The note provides further information necessary to understand the potential implications of the contingency.
Required:
(a) Critically appraise the draft audit report of the Hopper Group for the year ended 30 June 2015, prepared by the audit senior.
Note: You are NOT required to re-draft the extracts from the audit report. (10 marks)
(b) The audit of the new subsidiary, Seurat Sweeteners Co, was performed by a different firm of auditors, Fish Associates. During your review of the communication from Fish Associates, you note that they were unable to obtain sufficient appropriate evidence with regard to the breakdown of research expenses. The total of research costs expensed by Seurat Sweeteners Co during the year was $1·2 million. Fish Associates has issued a qualified audit opinion on the financial statements of Seurat Sweeteners Co due to this inability to obtain sufficient appropriate evidence.
Required:
Comment on the actions which Rockwell & Co should take as the auditor of the Hopper Group, and the implications for the auditor’s report on the Hopper Group financial statements. (6 marks)
(c) Discuss the quality control procedures which should be carried out by Rockwell & Co prior to the audit report on the Hopper Group being issued. (4 marks)
正确答案:(a) Critical appraisal of the draft audit report
Type of opinion
When an auditor issues an opinion expressing that the financial statements ‘do not give a true and fair view’, this represents an adverse opinion. The paragraph explaining the modification should, therefore, be titled ‘Basis of Adverse Opinion’ rather than simply ‘Basis of Modified Opinion’.
An adverse opinion means that the auditor considers the misstatement to be material and pervasive to the financial statements of the Hopper Group. According to ISA 705 Modifications to Opinions in the Independent Auditor’s Report, pervasive matters are those which affect a substantial proportion of the financial statements or fundamentally affect the users’ understanding of the financial statements. It is unlikely that the failure to recognise contingent consideration is pervasive; the main effect would be to understate goodwill and liabilities. This would not be considered a substantial proportion of the financial statements, neither would it be fundamental to understanding the Hopper Group’s performance and position.
However, there is also some uncertainty as to whether the matter is even material. If the matter is determined to be material but not pervasive, then a qualified opinion would be appropriate on the basis of a material misstatement. If the matter is not material, then no modification would be necessary to the audit opinion.
Wording of opinion/report
The auditor’s reference to ‘the acquisition of the new subsidiary’ is too vague; the Hopper Group may have purchased a number of subsidiaries which this phrase could relate to. It is important that the auditor provides adequate description of the event and in these circumstances it would be appropriate to name the subsidiary referred to.
The auditor has not quantified the amount of the contingent element of the consideration. For the users to understand the potential implications of any necessary adjustments, they need to know how much the contingent consideration will be if it becomes payable. It is a requirement of ISA 705 that the auditor quantifies the financial effects of any misstatements, unless it is impracticable to do so.
In addition to the above point, the auditor should provide more description of the financial effects of the misstatement, including full quantification of the effect of the required adjustment to the assets, liabilities, incomes, revenues and equity of the Hopper Group.
The auditor should identify the note to the financial statements relevant to the contingent liability disclosure rather than just stating ‘in the note’. This will improve the understandability and usefulness of the contents of the audit report.
The use of the term ‘we do not feel that the treatment is correct’ is too vague and not professional. While there may be some interpretation necessary when trying to apply financial reporting standards to unique circumstances, the expression used is ambiguous and may be interpreted as some form. of disclaimer by the auditor with regard to the correct accounting treatment. The auditor should clearly explain how the treatment applied in the financial statements has departed from the requirements of the relevant standard.
Tutorial note: As an illustration to the above point, an appropriate wording would be: ‘Management has not recognised the acquisition-date fair value of contingent consideration as part of the consideration transferred in exchange for the acquiree, which constitutes a departure from International Financial Reporting Standards.’
The ambiguity is compounded by the use of the phrase ‘if this is the case, it would be appropriate to adjust the goodwill’. This once again suggests that the correct treatment is uncertain and perhaps open to interpretation.
If the auditor wishes to refer to a specific accounting standard they should refer to its full title. Therefore instead of referring to ‘the relevant standard’ they should refer to International Financial Reporting Standard 3 Business Combinations.
The opinion paragraph requires an appropriate heading. In this case the auditors have issued an adverse opinion and the paragraph should be headed ‘Adverse Opinion’.
As with the basis paragraph, the opinion paragraph lacks authority; suggesting that the required adjustments ‘may’ materially affect the financial statements implies that there is a degree of uncertainty. This is not the case; the amount of the contingent consideration will be disclosed in the relevant purchase agreement, so the auditor should be able to determine whether the required adjustments are material or not. Regardless, the sentence discussing whether the balance is material or not is not required in the audit report as to warrant inclusion in the report the matter must be considered material. The disclosure of the nature and financial effect of the misstatement in the basis paragraph is sufficient.
Finally, the emphasis of matter paragraph should not be included in the audit report. An emphasis of matter paragraph is only used to draw attention to an uncertainty/matter of fundamental importance which is correctly accounted for and disclosed in the financial statements. An emphasis of matter is not required in this case for the following reasons:
– Emphasis of matter is only required to highlight matters which the auditor believes are fundamental to the users’ understanding of the business. An example may be where a contingent liability exists which is so significant it could lead to the closure of the reporting entity. That is not the case with the Hopper Group; the contingent liability does not appear to be fundamental.
– Emphasis of matter is only used for matters where the auditor has obtained sufficient appropriate evidence that the matter is not materially misstated in the financial statements. If the financial statements are materially misstated, in this regard the matter would be fully disclosed by the auditor in the basis of qualified/adverse opinion paragraph and no emphasis of matter is necessary.
(b) Communication from the component auditor
The qualified opinion due to insufficient evidence may be a significant matter for the Hopper Group audit. While the possible adjustments relating to the current year may not be material to the Hopper Group, the inability to obtain sufficient appropriate evidence with regard to a material matter in Seurat Sweeteners Co’s financial statements may indicate a control deficiency which the auditor was not aware of at the planning stage and it could indicate potential problems with regard to the integrity of management, which could also indicate a potential fraud. It could also indicate an unwillingness of management to provide information, which could create problems for future audits, particularly if research and development costs increase in future years. If the group auditor suspects that any of these possibilities are true, they may need to reconsider their risk assessment and whether the audit procedures performed are still appropriate.
If the detail provided in the communication from the component auditor is insufficient, the group auditor should first discuss the matter with the component auditor to see whether any further information can be provided. The group auditor can request further working papers from the component auditor if this is necessary. However, if Seurat Sweeteners has not been able to provide sufficient appropriate evidence, it is unlikely that this will be effective.
If the discussions with the component auditor do not provide satisfactory responses to evaluate the potential impact on the Hopper Group, the group auditor may need to communicate with either the management of Seurat Sweeteners or the Hopper Group to obtain necessary clarification with regard to the matter.
Following these procedures, the group auditor needs to determine whether they have sufficient appropriate evidence to draw reasonable conclusions on the Hopper Group’s financial statements. If they believe the lack of information presents a risk of material misstatement in the group financial statements, they can request that further audit procedures be performed, either by the component auditor or by themselves.
Ultimately the group engagement partner has to evaluate the effect of the inability to obtain sufficient appropriate evidence on the audit opinion of the Hopper Group. The matter relates to research expenses totalling $1·2 million, which represents 0·2% of the profit for the year and 0·03% of the total assets of the Hopper Group. It is therefore not material to the Hopper Group’s financial statements. For this reason no modification to the audit report of the Hopper Group would be required as this does not represent a lack of sufficient appropriate evidence with regard to a matter which is material to the Group financial statements.
Although this may not have an impact on the Hopper Group audit opinion, this may be something the group auditor wishes to bring to the attention of those charged with governance. This would be particularly likely if the group auditor believed that this could indicate some form. of fraud in Seurat Sweeteners Co, a serious deficiency in financial reporting controls or if this could create problems for accepting future audits due to management’s unwillingness to provide access to accounting records.
(c) Quality control procedures prior to issuing the audit report
ISA 220 Quality Control for an Audit of Financial Statements and ISQC 1 Quality Control for Firms that Perform. Audits and Reviews of Historical Financial Information, and Other Assurance and Related Services Agreements require that an engagement quality control reviewer shall be appointed for audits of financial statements of listed entities. The audit engagement partner then discusses significant matters arising during the audit engagement with the engagement quality control reviewer.
The engagement quality control reviewer and the engagement partner should discuss the failure to recognise the contingent consideration and its impact on the auditor’s report. The engagement quality control reviewer must review the financial statements and the proposed auditor’s report, in particular focusing on the conclusions reached in formulating the auditor’s report and consideration of whether the proposed auditor’s opinion is appropriate. The audit documentation relating to the acquisition of Seurat Sweeteners Co will be carefully reviewed, and the reviewer is likely to consider whether procedures performed in relation to these balances were appropriate.
Given the listed status of the Hopper Group, any modification to the auditor’s report will be scrutinised, and the firm must be sure of any decision to modify the report, and the type of modification made. Once the engagement quality control reviewer has considered the necessity of a modification, they should consider whether a qualified or an adverse opinion is appropriate in the circumstances. This is an important issue, given that it requires judgement as to whether the matters would be material or pervasive to the financial statements.
The engagement quality control reviewer should ensure that there is adequate documentation regarding the judgements used in forming the final audit opinion, and that all necessary matters have been brought to the attention of those charged with governance.
The auditor’s report must not be signed and dated until the completion of the engagement quality control review.
Tutorial note: In the case of the Hopper Group’s audit, the lack of evidence in respect of research costs is unlikely to be discussed unless the audit engagement partner believes that the matter could be significant, for example, if they suspected the lack of evidence is being used to cover up a financial statements fraud.
-
第21题:
Your firm has been recommended to us by AMK company, () we have done business for many years.
Awith whom
Bwith who
Cwhom
Dwho
A
略 -
第22题:
Your IT director has decided to allow employees to use their laptops at home as well as in the office. You have deployed the Junos Pulse client to allow access to the offices 802.1X-enabled wired network. Your company also has the Junos Pulse Secure Access Service deployed. You want the Junos Pulse client to automatically launch the appropriate access method depending on each users location. Which three are supported to determine the users location?()
- A、MAC address
- B、DNS server
- C、DHCP server
- D、resolve address
- E、endpoint address
正确答案:B,D,E -
第23题:
You work as an Exchange Administrator for Xxx Inc.The company has a Windows 2008 Active Directorybased network.The network contains an Exchange Server 2010 organization.The CIO has requested you to ensure that all emails with JPEG attachments be filtered so that they are not allowed into the users’ mailboxes.You decide to use the Exchange Management Shell.Which of the following commands will you use to accomplish the task?()
- A、Add-AttachmentFilterEntry -Name *.jpeg -Type ContentType
- B、Add-AttachmentFilterEntry -Name *.exe -Type FileName
- C、Add-AttachmentFilterEntry -Name image/jpeg -Type ContentType
- D、Add-AttachmentFilterEntry -Name image/jpeg -Type FileName
正确答案:C
