阅读以下说明和C++码,将应填入(n)处的字名写在对应栏内。从下列的3道试题(试题五至试题七)中任选1道解答。如果解答的试题数超过1道,则题号小的1道解答有效。[说明] 编写程序,把从键盘上输入的一批整数(以-1作为终止输入的标志)保存到文本文件“a: xxk1. dat”中。(1)include <fstream. h >include < stdlib. h >void main ( ) {(2)if ( ! four) {cerr < <“文件没有找开!” < <end1;exit (1);}int
题目
阅读以下说明和C++码,将应填入(n)处的字名写在对应栏内。
从下列的3道试题(试题五至试题七)中任选1道解答。
如果解答的试题数超过1道,则题号小的1道解答有效。
[说明] 编写程序,把从键盘上输入的一批整数(以-1作为终止输入的标志)保存到文本文件“a: xxk1. dat”中。
(1)
include <fstream. h >
include < stdlib. h >
void main ( ) {
(2)
if ( ! four) {
cerr < <“文件没有找开!” < <end1;
exit (1);
}
int x;
cin > >x;
while((3)){
(4)
cin> >x;
}
(5)
}
相似考题
更多“阅读以下说明和C++码,将应填入(n)处的字名写在对应栏内。 从下列的3道试题(试题五至试题七)中任选 ”相关问题
-
第1题:
●试题一
阅读下列说明和流程图,将应填入(n)的字句写在答题纸的对应栏内。
【说明】
下列流程图(如图4所示)用泰勒(Taylor)展开式
sinx=x-x3/3!+x5/5!-x7/7!+…+(-1)n×x 2n+1/(2n+1)!+…
【流程图】
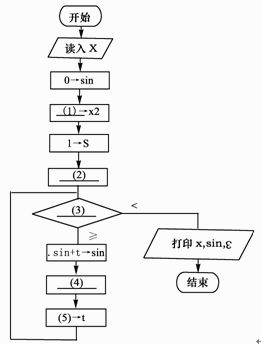
图4
计算并打印sinx的近似值。其中用ε(>0)表示误差要求。
正确答案:
●试题一【答案】(1)x*x(2)x->t(3)|t|∶ε(4)s+2->s(5)(-1)*t*x2/(s*(s-1))【解析】该题的关键是搞清楚几个变量的含义。很显然变量t是用来保存多项式各项的值,变量s和变量x2的作用是什么呢?从流程图的功能上看,需要计算1!、3!、5!,……,又从变量s的初值置为1可知,变量s主要用来计算这此数的阶乘的,但没有其他变量用于整数自增,这样就以判断s用来存储奇数的,即s值依次为1、3、5,……。但x2的功能还不明确,现在可以不用管它。(2)空的作用是给t赋初值,即给它多项式的第一项,因此应填写"x->t"。(3)空处需填写循环条件,显然当t的绝对值小于ε(>0)就表示已经达到误差要求,因此(3)空应填入"|t|∶ε"。由变量s的功能可知,(4)空应当实现变量s的增加,因此(4)空应填入"s+2->s"。(5)空应当是求多项式下一项的值,根据多项式连续两项的关系可知,当前一项为t时,后一项的值为(-1)*t*x*x/(s*(s-1))。但这样的话,每次循环都需要计算一次x*x,计算效率受到影响,联想到变量x2还没用,这时就可以判断x2就是用来存储x*x的值,使得每次循环者少进行一次乘法运算。因此(1)空处应填入"x*x",(5)空处应填入"(-1)*t*x2/(s*(s-1))"。 -
第2题:
试题三(共 15 分)
阅读以下说明和 C 程序,将应填入 (n) 处的字句写在答题纸的对应栏内。
 正确答案:
正确答案:
-
第3题:
阅读下列说明和?C++代码,将应填入(n)处的字句写在答题纸的对应栏内。
【说明】
阅读下列说明和?Java代码,将应填入?(n)?处的字句写在答题纸的对应栏内。
【说明】
某快餐厅主要制作并出售儿童套餐,一般包括主餐(各类比萨)、饮料和玩具,其餐品种
类可能不同,但其制作过程相同。前台服务员?(Waiter)?调度厨师制作套餐。现采用生成器?(Builder)?模式实现制作过程,得到如图?6-1?所示的类图。
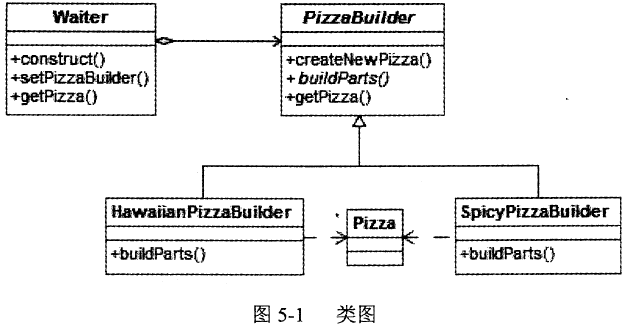


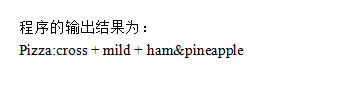 答案:解析:
答案:解析:
-
第4题:
●试题一
阅读下列说明和流程图,将应填入(n)处的语句写在答题纸的对应栏内。
【说明】
下列流程图用于从数组K中找出一切满足:K(I)+K(J)=M的元素对(K(I),K(J))(1≤I≤J≤N)。假定数组K中的N个不同的整数已按从小到大的顺序排列,M是给定的常数。
【流程图】
此流程图1中,比较"K(I)+K(J)∶M"最少执行次数约为 (5) 。

图1
正确答案:
●试题一【答案】(1)(2)<(3)I+l->I(4)J-1->J(5)「N/2」【解析】该算法的思路是:设置了两个变量I和J,初始时分别指向数组K的第一个元素和最后一个元素。如果这两个元素之和等于M时,输出结果,并这两个指针都向中间移动;如果小于M,则将指针I向中间移动(因为数组K已按从小到大的顺序排列);如果大于M,则将指针J向中间移动(因为数组K已按从小到大的顺序排列)。当IJ时,说明所有的元素都搜索完毕,退出循环。根据上面的分析,(1)、(2)空要求填写循环结束条件,显然,(1)空处应填写"",(2)空处应填写"<"。这里主要要注意I=J的情况,当I=J时,说明指两个指针指向同一元素,应当退出循环。(3)空在流程图有两处,一处是当K(I)+K(J)=M时,另一处是当K(I)+K(J)<M时,根据上面分析这两种情况都要将指针I向中间移动,即"I+1->I"。同样的道理,(4)空处应填写"J-1->J"。比较"K(I)+K(J):M"最少执行次数发生在第1元素与第N个元素之和等于M、第2元素与第N-1个元素之和等于M、……,这样每次比较,两种指针都向中间移动,因此最小执行次数约为"N-2"。 -
第5题:
从下列2道试题(试题五至试题六)中任选 1道解答。如果解答的试题数超过1道,则题号小的1道解答有效。
试题五(共15分)
阅读以下说明、图和C++代码,填补C++代码中的空缺(1)~(5),将解答写在答题纸的对应栏内。
【说明】
已知对某几何图形绘制工具进行类建模的结果如图5.1所示,其中Shape为抽象类(应至少包含一个纯虚拟( virtual)函数),表示通用图形,Box表示矩形,Ellipse表示椭圆,Circle表示圆(即特殊的椭圆),Line表示线条。

下面的C++代码用于实现图5-1所给出的设计思路,将其空缺处填充完整并编译运行,输
出结果为:
Ellipse
Circle
Ellipse
C
E
【C++代码】
include <string>
include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Shape{
public:
Shape(const string& name){
m_name= name;
}
~Shape(){}
(1) void paint() = 0;
stringgetName()const {
retumm name;
}
Private:
string m_name;
};
//Box和 Line类的定义与 Ellipse类似,其代码略
classEllipse (2) {
public:
Ellipse(const string& name) : Shape(name){ cout<<"Ellipse" <<endl; }
Voidpaint() { cout<<getName()<<endl;}
};
classCircle (3) {
public:
Circle(const string& name) : Ellipse(name){ cout<<"Circl"<<endl; }
};
class Diagram {
public:
void drawAShap(Shape* shape){ shape->paint(); }
void drawShapes() {
shapes[0] = new Circle("C");
shapes[l] = new Ellipse("E");
for (int i=O;i<2; ++1) {
drawAShap(shapes[i]);
}
}
void close (){ /*删除形状,代码略 */ }
private:
Shape* shapes[2];
};
int main( )
{
Diagram* diagram = (4)
diagram->drawShapes();
diagram->close ();
(5) diagram;
}
正确答案:
试题五分析
本题考查C++语言程序设计的能力,涉及类和抽象类、对象、函数和虚函数的定义和相关操作,以及继承关系。要求考生根据给出的案例和执行过程说明,认真阅读理清程序思路,然后完成题目。
先考查类图整体结构。本题中根据类图定义了类:Diagram、Shape、 Box、 Ellipse、Line和Circle。其中Shape为抽象类,表示通用图形,抽象类中应至少包含一个纯虚拟( virtual)函数。Box表示矩形,Ellipse表示椭圆,Line表示线条,三者都是Shape的子类,继承了Shape类,Circle表示圆(即特殊的椭圆),继承了Ellipse。抽象类Shape的定义中,需要通过使用virtual标识虚函数,void paint()=0;表示paint()是纯虚函数,其定义前必须添加virtual进行表示。类Ellipse为Shape的子类,Circle为Ellipse的子类,需要在代码中体现出继承。另外,在子类的构造函数中,调用父类的构造函数,所以继承的权限为public。其语法为:public后加类名。
类Diagram中没有定义构造函数,编译器生成一个缺省的构造函数,调用是采用new关键字加类名。使用完成之后,通过delete进行释放。
因此空(1)需要表现出paint()函数为纯虚函数,即为virtual;空(2)和空(3)处添力口继承父类,并且权限为public,即为:public Shape和:public Ellipse;空(4)处补充通过使用编译器生成的缺省构造函数创建对象,即new Diagram;空(5)处通过delete释放new创建的对象diagram。
参考答案
(1) virtual
(2):public Shape
(3): public Ellipse
(4) new Diagram
(5) delete
