●试题五阅读下列程序说明,将应填入(n)处的字句写在答卷纸的对应栏内。【程序说明】对于一个公司的雇员来说,无非有3种:普通雇员、管理人员和主管。这些雇员有共同的数据:名字、每小时的工资,也有一些共同的操作:数据成员初始化、读雇员的数据成员及计算雇员的工资。但是,他们也有不同。例如,管理人员除有这些共同的特征外,有可能付固定薪水,主管除有管理人员的共同特征外,还有其他物质奖励等。3种雇员中,管理人员可以看作普通雇员的一种,而主管又可以看作管理人员的一种。我们很容易想到使用类继承来实现这个问题:普通雇员作为基
题目
●试题五
阅读下列程序说明,将应填入(n)处的字句写在答卷纸的对应栏内。
【程序说明】
对于一个公司的雇员来说,无非有3种:普通雇员、管理人员和主管。这些雇员有共同的数据:名字、每小时的工资,也有一些共同的操作:数据成员初始化、读雇员的数据成员及计算雇员的工资。但是,他们也有不同。例如,管理人员除有这些共同的特征外,有可能付固定薪水,主管除有管理人员的共同特征外,还有其他物质奖励等。3种雇员中,管理人员可以看作普通雇员的一种,而主管又可以看作管理人员的一种。我们很容易想到使用类继承来实现这个问题:普通雇员作为基类,管理人员类从普通雇员类中派生,而主管人员类又从管理人员类中派生。
下面的程序1完成上述各个类的定义,并建立了3个雇员(一个普通雇员、一个管理人员和一个主管)的档案,并打印出各自的工资表。将"程序1"中的成员函数定义为内联函数,pay成员函数定义为虚函数,重新完成上述要求。
【程序1】
//普通雇员类
class Employee
{
public:
Employee(char*theName,float thePayRate);
char*getName()const;
float getPayRate()const;
float pay(float hoursWorked)const;
protected:
char*name;//雇员名称
float payRate;//薪水等级
};
Employee::Employee(char*theName,float thePayRate)
{
name=theName;
payRate=thePayRate;
}
char*Employee::getName() const
{
return name;
}
float Employee::getPayRate()const
{
return payRate;
}
float Employee::pay(float hoursWorked)const
{
return hoursWorked*payRate;
}
//管理人员类
class Manager∶public Employee
{
public:
//isSalaried付薪方式:true付薪固定工资,false按小时付薪
Manager(char*theName,float thePayRate,bool isSalaried);
bool getSalaried()const;
float pay(float hoursWorked)const;
protected:
bool salaried;
};
Manager::Manager(char*theName,float thePayRate,bool isSalaried)
∶Employee(theName,thePayRate)
{
salaried=isSalaried;
}
bool Manager::getSalaried() const
{
return salaried;
}
float Manager::pay(float hoursWorked)const
{
if(salaried)
return payRate;
/*else*/
return Employee::pay(hoursWorked);
}
//主管人员类
class Supervisor:public Employee
{
public:
Supervisor(char*theName,float thePayRate,float theBouns):
Employee(theName,thePayRate, (1) ),bouns(theBouns){}
float getBouns()const{return bouns;}
float pay(float hoursWorked)const
return (2) ;
}
protected:
float bouns;
}
#include"iostream.h"
void main()
{
Employee e("Jack",50.00);
Manager m("Tom",8000.00,true);
Supervior s("Tanya",8000.00,8000.00);
cout<<"Name:"<<e.getName()<<endl;
cout<<"Pay:"<<e.pay(80)<<endl;//设每月工作80小时
cout<<"Name:"<<m.getName()<<endl;
cout<<"Pay:"<<m.pay (40) <<endl;
cout<<"Name:"<<s.getName()<<endl;
cout<<"Pay:"<<s.pay (40) <<endl;//参数40在这里不起作用
}
【程序2】
#include"employee.h"
//普通雇员类
class Employee
{
public:
//构造函数
Employee(string theName,float thePayRate):
name(theName),payRate(thePayRate){}
//取雇员姓名
string getName() const{returnname;}
//取雇员薪水等级
float getPayRate()const{return payRate;}
//计算雇员薪水
virtual float pay(float hoursWorked)const{return (3) ;}
protected:
string name;//雇员名称
float payRate;//薪水等级
};
//管理人员类
//继承普通雇员类
class Manager:public Employee
{
public:
//构造函数
//isSalaried标识管理人员类的付薪方式
//true 按阶段付薪(固定工资)
//false按小时付薪
Manager(string theName,float thePayRate,bool isSalaried):
Employee(theName,thePayRate),salaried(isSalaried){}
//取付薪方式
bool getSalaried()const{return salaried;}
//计算薪水
virtual float pay(float (4) )const;
protected:
bool salaried;
};
float Manager::pay(float hoursWorked)const
{
if(salaried)//固定付薪方式
return payRate;
else//按小时付薪
return (5) ; }
//主管人员类
class Supervisor: (6)
{
public:
//构造函数
Supervisor(string theName,float thePayRate,float theBouns):
Manager(theName,thePayRate,true),bouns(theBouns){}
//取奖金数额
float getBouns()const{return bouns;}
//计算薪水
virtual float pay(float hoursWorked)const
{
retum payRate+bouns;
}
(7)
float bouns;
}
#include"employee.h"
#include"iostream.h"
void main()
{
(8) *ep[3];ep[0]=new Employee("Jack","50.00");
ep[1]=new Manager("Tom","8000.00",true);
ep[2]=new Supervior("Tanya","8000.00","8000.00");
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
cout<<"Name:"<< (9) <<endl;
cout<<"Pay:"<< (10) <<endl;//设每月工作80小时
}
}
相似考题
更多“●试题五 阅读下列程序说明,将应填入(n)处的字句写在答卷纸的对应栏内。 【程序说明】 对于一个公 ”相关问题
-
第1题:
阅读下列程序说明和C++程序,把应填入其中(n)处的字句,写在对应栏内。
【说明】
阅读下面几段C++程序回答相应问题。
比较下面两段程序的优缺点。
①for (i=0; i<N; i++ )
{
if (condition)
//DoSomething
…
else
//DoOtherthing
…
}
②if (condition) {
for (i =0; i<N; i++ )
//DoSomething
}else {
for (i=0; i <N; i++ )
//DoOtherthing
…
}
正确答案:程序1优点:程序简洁;缺点:多执行了N-1次逻辑判断并且程序无法循环“流水”作业使得编译器无法对循环进行优化处理降低了效率。 程序2优点:循环的效率高;缺点:程序不简洁。
程序1优点:程序简洁;缺点:多执行了N-1次逻辑判断,并且程序无法循环“流水”作业,使得编译器无法对循环进行优化处理,降低了效率。 程序2优点:循环的效率高;缺点:程序不简洁。 -
第2题:
●试题二
阅读下列函数说明和C代码,将应填入(n)处的字句写在答题纸的对应栏内。
【说明】
该程序运行后,输出下面的数字金字塔

【程序】
include<stdio.h>
main ()
{char max,next;
int i;
for(max=′1′;max<=′9′;max++)
{for(i=1;i<=20- (1) ;++i)
printf(" ");
for(next= (2) ;next<= (3) ;next++)
printf("%c",next);
for(next= (4) ;next>= (5) ;next--)
printf("%c",next);
printf("\n");
}
}
正确答案:
●试题二【答案】(1)(max-′0′)(2)′1′(3)max(4)max-1(5)′1′【解析】该程序共有9行输出,即循环控制变量max的值是从1~9。每行输出分3部分,先用循环for语句输出左边空白,(1)空填"(max-′0′)";再用循环输出从1到max-′0′的显示数字,即(2)空和(3)空分别填1和max;最后输出从max-′1′~1的显示数字,即(4)空和(5)空分别填和max-1和′1′。 -
第3题:
()阅读下列说明和C语言程序,将应填入 (n)处的语句写在答题纸的对应栏内。[说明]下面程序是一个带参数的主函数,其功能是显示在命令行中输入的文本文件内容。[C语言函数]#include"stdio.h"main(argc,argv) int argc; char *argv[]; { (1) ; if((fp=fopen(argv[1],”r’’))== (2) ) { printf(”file not open!\n”);exit(0);} while( (3) ) putchar( (4) ); (5); }
正确答案:()
(1)FILE *fp; (2)NULL (3)!feof(fp) (4)fgetc(fp) (5)fclose(fp)
从程序功能来看,程序中需要用到文件型指针变量中,而主函数体没有定义,所以(1)应该填写的是“FILE *fp;”。接下来的语句是标准的打开只读文本文件的语句,显示的是文件没打开,说明文件名不存在,也就是为“NULL”。接着的while循环语句中有两处空白。前一个空白是控制循环的条件,从程序功能来看,要将文本文件中的所有字符显示出来,这儿当然只能填写“不是文件尾则继续循环”,具体说,需要填写的是“!feof(fp)”。(4)出现在循环体中的语句中,该循环体的功能是从fp指向的文本文件中读取单个字符并显示在屏幕上,此处使用的是putchar函数,该函数的功能是将形参对应的字符显示在屏幕上,所以该处的空白就是要显示的字符,这个字符必须是从文本文件中读取的单个字符,完成这项工作的可以利用fgetc()函数,所以(4)填写的是“fgetc(fp)”。最后一句应当是关闭文件,所以(5)应填fclose(fp)。
-
第4题:
阅读下列程序说明和C程序,将应填入(n)处的字句写在对应栏内。
[函数2.1说明]
下面程序的功能是计算x和y的最小公倍数。
[函数2.1]
main()
{ int m,n,d,r;
seanf("%d %d",&m,&n);
if(m<n) {r=m;m=n;n=r;}
(1);
while (d%n! =0) (2);
printf("%d\n",d);
}
[函数2.2说明]
下述程序接收键盘输入,直到句点“.”时结束。输入的字符被原样输出,但连续的空格输入将转换成一个空格。
[函数2.2]
include <stdio.h>
main()
{ char c,preChar='\0';
c = getchar();
while(c! = '.'){
if((3)) putchar(c);
else if(preChar! =' ') putchar(c);
(4);
c=(5);
}
}
正确答案:(1)d=m (2) d+=m或d=d+m (3) c!=‘’ (4) preChar=c (5) getchar()
(1)d=m (2) d+=m或d=d+m (3) c!=‘’ (4) preChar=c (5) getchar() 解析:(1)下文使用了变量d,因此需在此初始化,由下面循环的条件“d%n!=0”知初值不能是n,因此必为m;
(2)此处while循环生成最小公倍数d,其终止条件是n整除d,因此循环过程中需要保证m整除d并且d尽可能地小,于是d应以m为增量递增;
(3)当输入的字符非空格时,原样输出;
(4)程序中变量preChar用于记录上一次读入的字符,循环过程中应不断更新其值;
(5)接收下一个输入。 -
第5题:
试题三(共 15 分)
阅读以下说明和 C 程序,将应填入 (n) 处的字句写在答题纸的对应栏内。
 正确答案:
正确答案:
-
第6题:
阅读下列说明和?C++代码,将应填入(n)处的字句写在答题纸的对应栏内。
【说明】
阅读下列说明和?Java代码,将应填入?(n)?处的字句写在答题纸的对应栏内。
【说明】
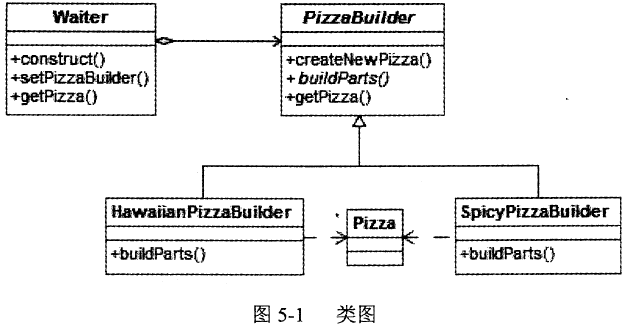
某快餐厅主要制作并出售儿童套餐,一般包括主餐(各类比萨)、饮料和玩具,其餐品种
类可能不同,但其制作过程相同。前台服务员?(Waiter)?调度厨师制作套餐。现采用生成器?(Builder)?模式实现制作过程,得到如图?6-1?所示的类图。


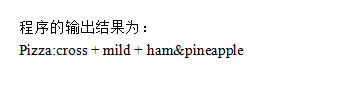 答案:解析:
答案:解析:
