(b) Explain how the non-payment of contributions and the change in the pension benefits should be treated inthe financial statements of Savage for the year ended 31 October 2005. (4 marks)
题目
(b) Explain how the non-payment of contributions and the change in the pension benefits should be treated in
the financial statements of Savage for the year ended 31 October 2005. (4 marks)
相似考题
参考答案和解析
(b) The contributions payable by Savage to the trustees will not count as an asset for the purposes of the valuation of the fund.
IAS19 (paragraph 103) states that plan assets should not include unpaid contributions due from the reporting entity to the
fund. Thus in the financial statements of Savage the contributions would be shown as an amount payable to the trustees
and there may be legal repercussions if the amount is not paid within a short period of time. Following the introduction of
changes to a defined benefit plan, a company should recognise immediately past service costs where the benefit has vested.
In the case where the benefits have not vested then the past service costs will be recognised as an expense over the averageperiod until the benefits vest. The company will therefore recognise $125 million at 1 November 2004.
更多“(b) Explain how the non-payment of contributions and the change in the pension benefits should be treated inthe financial statements of Savage for the year ended 31 October 2005. (4 marks)”相关问题
-
第1题:
(b) a discussion (with suitable calculations) as to how the directors’ share options would be accounted for in the
financial statements for the year ended 31 May 2005 including the adjustment to opening balances;
(9 marks)
正确答案:(b) Accounting in the financial statements for the year ended 31 May 2005
IFRS2 requires an expense to be recognised for the share options granted to the directors with a corresponding amount shown
in equity. Where options do not vest immediately but only after a period of service, then there is a presumption that the
services will be rendered over the ‘vesting period’. The fair value of the services rendered will be measured by reference to
the fair value of the equity instruments at the date that the equity instruments were granted. Fair value should be based on
market prices. The treatment of vesting conditions depends on whether or not the conditions relate to the market price of the
instruments. Market conditions are effectively taken into account in determining the fair value of the instruments and therefore
can be ignored for the purposes of estimating the number of equity instruments that will vest. For other conditions such as
remaining in the employment of the company, the calculations are carried out based on the best estimate of the number of
instruments that will vest. The estimate is revised when subsequent information is available.
The share options granted to J. Van Heflin on 1 June 2002 were before the date set in IFRS2 for accounting for such options
(7 November 2002). Therefore, no expense calculation is required. (Note: candidates calculating the expense for the latter
share options would be given credit if they stated that the company could apply IFRS2 to other options in certaincircumstances.) The remaining options are valued as follows:
-
第2题:
(iv) Tyre recently undertook a sales campaign whereby customers can obtain free car accessories, by presenting a
coupon, which has been included in an advertisement in a national newspaper, on the purchase of a vehicle.
The offer is valid for a limited time period from 1 January 2006 until 31 July 2006. The management are unsure
as to how to treat this offer in the financial statements for the year ended 31 May 2006.
(5 marks)
Required:
Advise the directors of Tyre on how to treat the above items in the financial statements for the year ended
31 May 2006.
(The mark allocation is shown against each of the above items)
正确答案:
(iv) Car accessories
An obligation should not be recognised for the coupons and no provision created under IAS37 ‘Provisions, Contingent
Liabilities and Contingent Assets’. A provision should only be recognised where there is an obligating event. There has to be
a present obligation (legal or constructive), the probability of an outflow of resources and the ability to make a reliable estimate
of the amount of the obligation. These conditions do not seem to have been met. Until the vehicle is purchased the
accessories cannot be obtained. That is the point at which the present obligation arises, the outflow of resources occurs and
an estimate of the amount of the obligation can be made. When the car is purchased, the accessories become part of the
cost of the sale. The revenue recognised will be the amount received from the customer (the sales price). The revenue will
not be grossed up to include the value of the accessories. -
第3题:
(c) Wader is reviewing the accounting treatment of its buildings. The company uses the ‘revaluation model’ for its
buildings. The buildings had originally cost $10 million on 1 June 2005 and had a useful economic life of
20 years. They are being depreciated on a straight line basis to a nil residual value. The buildings were revalued
downwards on 31 May 2006 to $8 million which was the buildings’ recoverable amount. At 31 May 2007 the
value of the buildings had risen to $11 million which is to be included in the financial statements. The company
is unsure how to treat the above events. (7 marks)
Required:
Discuss the accounting treatments of the above items in the financial statements for the year ended 31 May
2007.
Note: a discount rate of 5% should be used where necessary. Candidates should show suitable calculations where
necessary.
正确答案: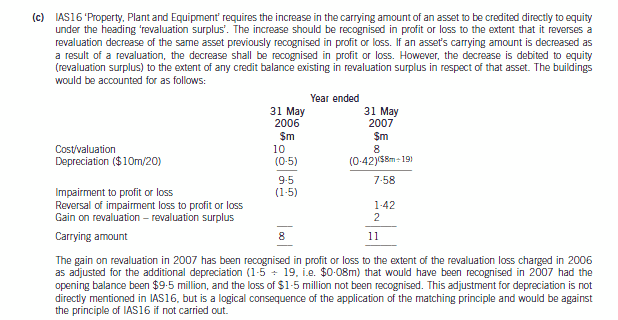
-
第4题:
(b) Router has a number of film studios and office buildings. The office buildings are in prestigious areas whereas
the film studios are located in ‘out of town’ locations. The management of Router wish to apply the ‘revaluation
model’ to the office buildings and the ‘cost model’ to the film studios in the year ended 31 May 2007. At present
both types of buildings are valued using the ‘revaluation model’. One of the film studios has been converted to a
theme park. In this case only, the land and buildings on the park are leased on a single lease from a third party.
The lease term was 30 years in 1990. The lease of the land and buildings was classified as a finance lease even
though the financial statements purport to comply with IAS 17 ‘Leases’.
The terms of the lease were changed on 31 May 2007. Router is now going to terminate the lease early in 2015
in exchange for a payment of $10 million on 31 May 2007 and a reduction in the monthly lease payments.
Router intends to move from the site in 2015. The revised lease terms have not resulted in a change of
classification of the lease in the financial statements of Router. (10 marks)
Required:
Discuss how the above items should be dealt with in the group financial statements of Router for the year ended
31 May 2007.
正确答案:
(b) IAS16 ‘Property, Plant and Equipment’ permits assets to be revalued on a class by class basis. The different characteristics
of the buildings allow them to be classified separately. Different measurement models can, therefore, be used for the office
buildings and the film studios. However, IAS8 ‘Accounting policies, changes in accounting estimates and errors’ says that
once an entity has decided on its accounting policies, it should apply them consistently from period to period and across all
relevant transactions. An entity can change its accounting policies but only in specific circumstances. These circumstances
are:
(a) where there is a new accounting standard or interpretation or changes to an accounting standard
(b) where the change results in the financial statements providing reliable and more relevant information about the effects
of transactions, other events or conditions on the entity’s financial position, financial performance, or cash flows
Voluntary changes in accounting policies are quite uncommon but may occur when an accounting policy is no longer
appropriate. Router will have to ensure that the change in accounting policy meets the criteria in IAS8. Additionally,
depreciated historical cost will have to be calculated for the film studios at the commencement of the period and the opening
balance on the revaluation reserve and any other affected component of equity adjusted. The comparative amounts for each
prior period should be presented as if the new accounting policy had always been applied. There are limits on retrospective
application on the grounds of impracticability.
It is surprising that the lease of the land is considered to be a finance lease under IAS17 ‘Leases’. Land is considered to have
an indefinite life and should, therefore normally be classified as an operating lease unless ownership passes to the lessee
during the lease term. The lease of the land should be separated out from the lease and treated individually. The value of the
land so determined would be taken off the balance sheet in terms of the liability and asset and the lease payments treated
as rentals in the income statement. A prior period adjustment should also be made. The buildings would continue to be
treated as property, plant and equipment (PPE) and the carrying amount not adjusted. However, the remaining useful life of
the building should be revised to reflect the shorter lease term. This will result in the carrying amount being depreciated over
the shorter period. This change to the depreciation policy is applied prospectively not retrospectively.
The lease liability must be assessed for derecognition under IAS39 ‘Financial Instruments: Recognition and Measurement’,
because of the revision of the lease terms, in order to determine whether the new terms are substantially different from the
old. The purpose of this is to determine whether the change in terms is a modification or an extinguishment. The change
seems to constitute a ‘modification’ because there is little change to the terms. The lease liability is, therefore, amended by
deducting the one off payment ($10 million) from the carrying amount (after adjustment for the lease of land) together with
any transaction costs. The lease liability is then remeasured to the present value of the revised future cash flows, discounted
using the original effective interest rate. Any adjustment made in remeasuring the lease liability will be taken to the income
statement.
-
第5题:
(d) Additionally Router purchased 60% of the ordinary shares of a radio station, Playtime, a public limited company,
on 31 May 2007. The remaining 40% of the ordinary shares are owned by a competitor company who owns a
substantial number of warrants issued by Playtime which are currently exercisable. If these warrants are
exercised, they will result in Router only owning 35% of the voting shares of Playtime. (4 marks)
Required:
Discuss how the above items should be dealt with in the group financial statements of Router for the year ended
31 May 2007.
正确答案:(d) IAS27 paragraph 14, ‘Consolidated and Separate Financial Statements’, states that warrants that have the potential to give
the holder voting power or reduce another party’s voting power over the financial and operating policies of the issuer should
be considered when existence of control is assessed. The warrants held by the competitor company, if exercised, would grant
that company control over Playtime. One party only can control Playtime and, therefore, the competitor company should
consolidate Playtime. In coming to this decision all the facts and circumstances that affect potential voting rights (except the
intention of management and the financial ability to exercise or convert) should be considered. It seems, however, that there
is a prima facie case for not consolidating Playtime but accounting for it under IAS28 or IAS39.
-
第6题:
(b) Discuss the relative costs to the preparer and benefits to the users of financial statements of increased
disclosure of information in financial statements. (14 marks)
Quality of discussion and reasoning. (2 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Increased information disclosure benefits users by reducing the likelihood that they will misallocate their capital. This is
obviously a direct benefit to individual users of corporate reports. The disclosure reduces the risk of misallocation of capital
by enabling users to improve their assessments of a company’s prospects. This creates three important results.
(i) Users use information disclosed to increase their investment returns and by definition support the most profitable
companies which are likely to be those that contribute most to economic growth. Thus, an important benefit of
information disclosure is that it improves the effectiveness of the investment process.
(ii) The second result lies in the effect on the liquidity of the capital markets. A more liquid market assists the effective
allocation of capital by allowing users to reallocate their capital quickly. The degree of information asymmetry between
the buyer and seller and the degree of uncertainty of the buyer and the seller will affect the liquidity of the market as
lower asymmetry and less uncertainty will increase the number of transactions and make the market more liquid.
Disclosure will affect uncertainty and information asymmetry.
(iii) Information disclosure helps users understand the risk of a prospective investment. Without any information, the user
has no way of assessing a company’s prospects. Information disclosure helps investors predict a company’s prospects.
Getting a better understanding of the true risk could lower the price of capital for the company. It is difficult to prove
however that the average cost of capital is lowered by information disclosure, even though it is logically and practically
impossible to assess a company’s risk without relevant information. Lower capital costs promote investment, which can
stimulate productivity and economic growth.
However although increased information can benefit users, there are problems of understandability and information overload.
Information disclosure provides a degree of protection to users. The benefit is fairness to users and is part of corporate
accountability to society as a whole.
The main costs to the preparer of financial statements are as follows:
(i) the cost of developing and disseminating information,
(ii) the cost of possible litigation attributable to information disclosure,
(iii) the cost of competitive disadvantage attributable to disclosure.
The costs of developing and disseminating the information include those of gathering, creating and auditing the information.
Additional costs to the preparers include training costs, changes to systems (for example on moving to IFRS), and the more
complex and the greater the information provided, the more it will cost the company.
Although litigation costs are known to arise from information disclosure, it does not follow that all information disclosure leads
to litigation costs. Cases can arise from insufficient disclosure and misleading disclosure. Only the latter is normally prompted
by the presentation of information disclosure. Fuller disclosure could lead to lower costs of litigation as the stock market would
have more realistic expectations of the company’s prospects and the discrepancy between the valuation implicit in the market
price and the valuation based on a company’s financial statements would be lower. However, litigation costs do not
necessarily increase with the extent of the disclosure. Increased disclosure could reduce litigation costs.
Disclosure could weaken a company’s ability to generate future cash flows by aiding its competitors. The effect of disclosure
on competitiveness involves benefits as well as costs. Competitive disadvantage could be created if disclosure is made relating
to strategies, plans, (for example, planned product development, new market targeting) or information about operations (for
example, production-cost figures). There is a significant difference between the purpose of disclosure to users and
competitors. The purpose of disclosure to users is to help them to estimate the amount, timing, and certainty of future cash
flows. Competitors are not trying to predict a company’s future cash flows, and information of use in that context is not
necessarily of use in obtaining competitive advantage. Overlap between information designed to meet users’ needs and
information designed to further the purposes of a competitor is often coincidental. Every company that could suffer competitive
disadvantage from disclosure could gain competitive advantage from comparable disclosure by competitors. Published figures
are often aggregated with little use to competitors.
Companies bargain with suppliers and with customers, and information disclosure could give those parties an advantage in
negotiations. In such cases, the advantage would be a cost for the disclosing entity. However, the cost would be offset
whenever information disclosure was presented by both parties, each would receive an advantage and a disadvantage.
There are other criteria to consider such as whether the information to be disclosed is about the company. This is both a
benefit and a cost criterion. Users of corporate reports need company-specific data, and it is typically more costly to obtain
and present information about matters external to the company. Additionally, consideration must be given as to whether the
company is the best source for the information. It could be inefficient for a company to obtain or develop data that other, more
expert parties could develop and present or do develop at present.
There are many benefits to information disclosure and users have unmet information needs. It cannot be known with any
certainty what the optimal disclosure level is for companies. Some companies through voluntary disclosure may have
achieved their optimal level. There are no quantitative measures of how levels of disclosure stand with respect to optimal
levels. Standard setters have to make such estimates as best they can, guided by prudence, and by what evidence of benefits
and costs they can obtain. -
第7题:
(ii) Explain how the inclusion of rental income in Coral’s UK income tax computation could affect the
income tax due on her dividend income. (2 marks)
You are not required to prepare calculations for part (b) of this question.
Note: you should assume that the tax rates and allowances for the tax year 2006/07 and for the financial year to
31 March 2007 will continue to apply for the foreseeable future.
正确答案:
(ii) The effect of taxable rental income on the tax due on Coral’s dividend income
Remitting rental income to the UK may cause some of Coral’s dividend income currently falling within the basic rate
band to fall within the higher rate band. The effect of this would be to increase the tax on the gross dividend income
from 0% (10% less the 10% tax credit) to 221/2% (321/2% less 10%).
Tutorial note
It would be equally acceptable to state that the effective rate of tax on the dividend income would increase from 0%
to 25%. -
第8题:
(c) In October 2004, Volcan commenced the development of a site in a valley of ‘outstanding natural beauty’ on
which to build a retail ‘megastore’ and warehouse in late 2005. Local government planning permission for the
development, which was received in April 2005, requires that three 100-year-old trees within the valley be
preserved and the surrounding valley be restored in 2006. Additions to property, plant and equipment during
the year include $4·4 million for the estimated cost of site restoration. This estimate includes a provision of
$0·4 million for the relocation of the 100-year-old trees.
In March 2005 the trees were chopped down to make way for a car park. A fine of $20,000 per tree was paid
to the local government in May 2005. (7 marks)
Required:
For each of the above issues:
(i) comment on the matters that you should consider; and
(ii) state the audit evidence that you should expect to find,
in undertaking your review of the audit working papers and financial statements of Volcan for the year ended
31 March 2005.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three issues.
正确答案:
(c) Site restoration
(i) Matters
■ The provision for site restoration represents nearly 2·5% of total assets and is therefore material if it is not
warranted.
■ The estimated cost of restoring the site is a cost directly attributable to the initial measurement of the tangible fixed
asset to the extent that it is recognised as a provision under IAS 37 ‘Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and
Contingent Assets’ (IAS 16 ‘Property, Plant and Equipment’).
■ A provision should not be recognised for site restoration unless it meets the definition of a liability, i.e:
– a present obligation;
– arising from past events;
– the settlement of which is expected to result in an outflow of resources embodying economic benefits.
■ The provision is overstated by nearly $0·34m since Volcan is not obliged to relocate the trees and de facto has
only an obligation of $60,000 as at 31 March 2005 (being the penalty for having felled them). When considered
in isolation, this overstatement is immaterial (representing only 0·2% of total assets and 3·6% of PBT).
■ It seems that even if there are local government regulations calling for site restoration there is no obligation unless
the penalties for non-compliance are prohibitive (unlike the fines for the trees).
■ It is unlikely that commencement of site development has given rise to a constructive obligation, since past actions
(disregarding the preservation of the trees) must dispel any expectation that Volcan will honour any pledge to
restore the valley.
■ Whether commencing development of the site, and destroying the trees, conflicts with any statement of socioenvironmental
responsibility in the annual report.
(ii) Audit evidence
■ A copy of the planning application and permission granted setting out the penalties for non-compliance.
■ Payment of $60,000 to local government in May 2005 agreed to the bank statement.
■ The present value calculation of the future cash expenditure making up the $4·0m provision.
Tutorial note: Evidence supporting the calculation of $0·4m is irrelevant as there is no liability to be provided for.
■ Agreement that the pre-tax discount rate used reflects current market assessments of the time value of money (as
for (a)).
■ Asset inspection at the site as at 31 March 2005.
■ Any contracts entered into which might confirm or dispute management’s intentions to restore the site. For
example, whether plant hire (bulldozers, etc) covers only the period over which the warehouse will be constructed
– or whether it extends to the period in which the valley would be ‘made good’. -
第9题:
(b) You are the audit manager of Johnston Co, a private company. The draft consolidated financial statements for
the year ended 31 March 2006 show profit before taxation of $10·5 million (2005 – $9·4 million) and total
assets of $55·2 million (2005 – $50·7 million).
Your firm was appointed auditor of Tiltman Co when Johnston Co acquired all the shares of Tiltman Co in March
2006. Tiltman’s draft financial statements for the year ended 31 March 2006 show profit before taxation of
$0·7 million (2005 – $1·7 million) and total assets of $16·1 million (2005 – $16·6 million). The auditor’s
report on the financial statements for the year ended 31 March 2005 was unmodified.
You are currently reviewing two matters that have been left for your attention on the audit working paper files for
the year ended 31 March 2006:
(i) In December 2004 Tiltman installed a new computer system that properly quantified an overvaluation of
inventory amounting to $2·7 million. This is being written off over three years.
(ii) In May 2006, Tiltman’s head office was relocated to Johnston’s premises as part of a restructuring.
Provisions for the resulting redundancies and non-cancellable lease payments amounting to $2·3 million
have been made in the financial statements of Tiltman for the year ended 31 March 2006.
Required:
Identify and comment on the implications of these two matters for your auditor’s reports on the financial
statements of Johnston Co and Tiltman Co for the year ended 31 March 2006. (10 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Tiltman Co
Tiltman’s total assets at 31 March 2006 represent 29% (16·1/55·2 × 100) of Johnston’s total assets. The subsidiary is
therefore material to Johnston’s consolidated financial statements.
Tutorial note: Tiltman’s profit for the year is not relevant as the acquisition took place just before the year end and will
therefore have no impact on the consolidated income statement. Calculations of the effect on consolidated profit before
taxation are therefore inappropriate and will not be awarded marks.
(i) Inventory overvaluation
This should have been written off to the income statement in the year to 31 March 2005 and not spread over three
years (contrary to IAS 2 ‘Inventories’).
At 31 March 2006 inventory is overvalued by $0·9m. This represents all Tiltmans’s profit for the year and 5·6% of
total assets and is material. At 31 March 2005 inventory was materially overvalued by $1·8m ($1·7m reported profit
should have been a $0·1m loss).
Tutorial note: 1/3 of the overvaluation was written off in the prior period (i.e. year to 31 March 2005) instead of $2·7m.
That the prior period’s auditor’s report was unmodified means that the previous auditor concurred with an incorrect
accounting treatment (or otherwise gave an inappropriate audit opinion).
As the matter is material a prior period adjustment is required (IAS 8 ‘Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting
Estimates and Errors’). $1·8m should be written off against opening reserves (i.e. restated as at 1 April 2005).
(ii) Restructuring provision
$2·3m expense has been charged to Tiltman’s profit and loss in arriving at a draft profit of $0·7m. This is very material.
(The provision represents 14·3% of Tiltman’s total assets and is material to the balance sheet date also.)
The provision for redundancies and onerous contracts should not have been made for the year ended 31 March 2006
unless there was a constructive obligation at the balance sheet date (IAS 37 ‘Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and
Contingent Assets’). So, unless the main features of the restructuring plan had been announced to those affected (i.e.
redundancy notifications issued to employees), the provision should be reversed. However, it should then be disclosed
as a non-adjusting post balance sheet event (IAS 10 ‘Events After the Balance Sheet Date’).
Given the short time (less than one month) between acquisition and the balance sheet it is very possible that a
constructive obligation does not arise at the balance sheet date. The relocation in May was only part of a restructuring
(and could be the first evidence that Johnston’s management has started to implement a restructuring plan).
There is a risk that goodwill on consolidation of Tiltman may be overstated in Johnston’s consolidated financial
statements. To avoid the $2·3 expense having a significant effect on post-acquisition profit (which may be negligible
due to the short time between acquisition and year end), Johnston may have recognised it as a liability in the
determination of goodwill on acquisition.
However, the execution of Tiltman’s restructuring plan, though made for the year ended 31 March 2006, was conditional
upon its acquisition by Johnston. It does not therefore represent, immediately before the business combination, a
present obligation of Johnston. Nor is it a contingent liability of Johnston immediately before the combination. Therefore
Johnston cannot recognise a liability for Tiltman’s restructuring plans as part of allocating the cost of the combination
(IFRS 3 ‘Business Combinations’).
Tiltman’s auditor’s report
The following adjustments are required to the financial statements:
■ restructuring provision, $2·3m, eliminated;
■ adequate disclosure of relocation as a non-adjusting post balance sheet event;
■ current period inventory written down by $0·9m;
■ prior period inventory (and reserves) written down by $1·8m.
Profit for the year to 31 March 2006 should be $3·9m ($0·7 + $0·9 + $2·3).
If all these adjustments are made the auditor’s report should be unmodified. Otherwise, the auditor’s report should be
qualified ‘except for’ on grounds of disagreement. If none of the adjustments are made, the qualification should still be
‘except for’ as the matters are not pervasive.
Johnston’s auditor’s report
If Tiltman’s auditor’s report is unmodified (because the required adjustments are made) the auditor’s report of Johnston
should be similarly unmodified. As Tiltman is wholly-owned by Johnston there should be no problem getting the
adjustments made.
If no adjustments were made in Tiltman’s financial statements, adjustments could be made on consolidation, if
necessary, to avoid modification of the auditor’s report on Johnston’s financial statements.
The effect of these adjustments on Tiltman’s net assets is an increase of $1·4m. Goodwill arising on consolidation (if
any) would be reduced by $1·4m. The reduction in consolidated total assets required ($0·9m + $1·4m) is therefore
the same as the reduction in consolidated total liabilities (i.e. $2·3m). $2·3m is material (4·2% consolidated total
assets). If Tiltman’s financial statements are not adjusted and no adjustments are made on consolidation, the
consolidated financial position (balance sheet) should be qualified ‘except for’. The results of operations (i.e. profit for
the period) should be unqualified (if permitted in the jurisdiction in which Johnston reports).
Adjustment in respect of the inventory valuation may not be required as Johnston should have consolidated inventory
at fair value on acquisition. In this case, consolidated total liabilities should be reduced by $2·3m and goodwill arising
on consolidation (if any) reduced by $2·3m.
Tutorial note: The effect of any possible goodwill impairment has been ignored as the subsidiary has only just been
acquired and the balance sheet date is very close to the date of acquisition. -
第10题:
(ii) Briefly explain the implications of Parr & Co’s audit opinion for your audit opinion on the consolidated
financial statements of Cleeves Co for the year ended 30 September 2006. (3 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) Implications for audit opinion on consolidated financial statements of Cleeves
■ If the potential adjustments to non-current asset carrying amounts and loss are not material to the consolidated
financial statements there will be no implication. However, as Howard is material to Cleeves and the modification
appears to be ‘so material’ (giving rise to adverse opinion) this seems unlikely.
Tutorial note: The question clearly states that Howard is material to Cleeves, thus there is no call for speculation
on this.
■ As Howard is wholly-owned the management of Cleeves must be able to request that Howard’s financial statements
are adjusted to reflect the impairment of the assets. The auditor’s report on Cleeves will then be unmodified
(assuming that any impairment of the investment in Howard is properly accounted for in the separate financial
statements of Cleeves).
■ If the impairment losses are not recognised in Howard’s financial statements they can nevertheless be adjusted on
consolidation of Cleeves and its subsidiaries (by writing down assets to recoverable amounts). The audit opinion
on Cleeves should then be unmodified in this respect.
■ If there is no adjustment of Howard’s asset values (either in Howard’s financial statements or on consolidation) it
is most likely that the audit opinion on Cleeves’s consolidated financial statements would be ‘except for’. (It should
not be adverse as it is doubtful whether even the opinion on Howard’s financial statements should be adverse.)
Tutorial note: There is currently no requirement in ISA 600 to disclose that components have been audited by another
auditor unless the principal auditor is permitted to base their opinion solely upon the report of another auditor. -
第11题:
(ii) On 1 July 2006 Petrie introduced a 10-year warranty on all sales of its entire range of stainless steel
cookware. Sales of stainless steel cookware for the year ended 31 March 2007 totalled $18·2 million. The
notes to the financial statements disclose the following:
‘Since 1 July 2006, the company’s stainless steel cookware is guaranteed to be free from defects in
materials and workmanship under normal household use within a 10-year guarantee period. No provision
has been recognised as the amount of the obligation cannot be measured with sufficient reliability.’
(4 marks)
Your auditor’s report on the financial statements for the year ended 31 March 2006 was unmodified.
Required:
Identify and comment on the implications of these two matters for your auditor’s report on the financial
statements of Petrie Co for the year ended 31 March 2007.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the matters above.
正确答案:
(ii) 10-year guarantee
$18·2 million stainless steel cookware sales amount to 43·1% of revenue and are therefore material. However, the
guarantee was only introduced three months into the year, say in respect of $13·6 million (3/4 × 18·2 million) i.e.
approximately 32% of revenue.
The draft note disclosure could indicate that Petrie’s management believes that Petrie has a legal obligation in respect
of the guarantee, that is not remote and likely to be material (otherwise no disclosure would have been required).
A best estimate of the obligation amounting to 5% profit before tax (or more) is likely to be considered material, i.e.
$90,000 (or more). Therefore, if it is probable that 0·66% of sales made under guarantee will be returned for refund,
this would require a warranty provision that would be material.
Tutorial note: The return of 2/3% of sales over a 10-year period may well be probable.
Clearly there is a present obligation as a result of a past obligating event for sales made during the nine months to
31 March 2007. Although the likelihood of outflow under the guarantee is likely to be insignificant (even remote) it is
probable that some outflow will be needed to settle the class of such obligations.
The note in the financial statements is disclosing this matter as a contingent liability. This term encompasses liabilities
that do not meet the recognition criteria (e.g. of reliable measurement in accordance with IAS 37 Provisions, Contingent
Liabilities and Contingent Assets).
However, it is extremely rare that no reliable estimate can be made (IAS 37) – the use of estimates being essential to
the preparation of financial statements. Petrie’s management must make a best estimate of the cost of refunds/repairs
under guarantee taking into account, for example:
■ the proportion of sales during the nine months to 31 March 2007 that have been returned under guarantee at the
balance sheet date (and in the post balance sheet event period);
■ the average age of cookware showing a defect;
■ the expected cost of a replacement item (as a refund of replacement is more likely than a repair, say).
If management do not make a provision for the best estimate of the obligation the audit opinion should be qualified
‘except for’ non-compliance with IAS 37 (no provision made). The disclosure made in the note to the financial
statements, however detailed, is not a substitute for making the provision.
Tutorial note: No marks will be awarded for suggesting that an emphasis of matter of paragraph would be appropriate
(drawing attention to the matter more fully explained in the note).
Management’s claim that the obligation cannot be measured with sufficient reliability does not give rise to a limitation
on scope on the audit. The auditor has sufficient evidence of the non-compliance with IAS 37 and disagrees with it. -
第12题:
(b) (i) Explain the matters you should consider, and the evidence you would expect to find in respect of the
carrying value of the cost of investment of Dylan Co in the financial statements of Rosie Co; and
(7 marks)
正确答案:
(b) (i) Cost of investment on acquisition of Dylan Co
Matters to consider
According to the schedule provided by the client, the cost of investment comprises three elements. One matter to
consider is whether the cost of investment is complete.
It appears that no legal or professional fees have been included in the cost of investment (unless included within the
heading ‘cash consideration’). Directly attributable costs should be included per IFRS 3 Business Combinations, and
there is a risk that these costs may be expensed in error, leading to understatement of the investment.
The cash consideration of $2·5 million is the least problematical component. The only matter to consider is whether the
cash has actually been paid. Given that Dylan Co was acquired in the last month of the financial year it is possible that
the amount had not been paid before the year end, in which case the amount should be recognised as a current liability
on the statement of financial position (balance sheet). However, this seems unlikely given that normally control of an
acquired company only passes to the acquirer on cash payment.
IFRS 3 states that the cost of investment should be recognised at fair value, which means that deferred consideration
should be discounted to present value at the date of acquisition. If the consideration payable on 31 January 2009 has
not been discounted, the cost of investment, and the corresponding liability, will be overstated. It is possible that the
impact of discounting the $1·5 million payable one year after acquisition would be immaterial to the financial
statements, in which case it would be acceptable to leave the consideration at face value within the cost of investment.
Contingent consideration should be accrued if it is probable to be paid. Here the amount is payable if revenue growth
targets are achieved over the next four years. The auditor must therefore assess the probability of the targets being
achieved, using forecasts and projections of Maxwell Co’s revenue. Such information is inherently subjective, and could
have been manipulated, if prepared by the vendor of Maxwell Co, in order to secure the deal and maximise
consideration. Here it will be crucial to be sceptical when reviewing the forecasts, and the assumptions underlying the
data. The management of Rosie Co should have reached their own opinion on the probability of paying the contingent
consideration, but they may have relied heavily on information provided at the time of the acquisition.
Audit evidence
– Agreement of the monetary value and payment dates of the consideration per the client schedule to legal
documentation signed by vendor and acquirer.
– Agreement of $2·5 million paid to Rosie Co’s bank statement and cash book prior to year end. If payment occurs
after year end confirm that a current liability is recognised on the individual company and consolidated statement
of financial position (balance sheet).
– Board minutes approving the payment.
– Recomputation of discounting calculations applied to deferred and contingent consideration.
– Agreement that the discount rate used is pre-tax, and reflects current market assessment of the time value of money
(e.g. by comparison to Rosie Co’s weighted average cost of capital).
– Revenue and profit projections for the period until January 2012, checked for arithmetic accuracy.
– A review of assumptions used in the projections, and agreement that the assumptions are comparable with the
auditor’s understanding of Dylan Co’s business.
Tutorial note: As the scenario states that Chien & Co has audited Dylan Co for several years, it is reasonable to rely on
their cumulative knowledge and understanding of the business in auditing the revenue projections. -
第13题:
(b) Misson has purchased goods from a foreign supplier for 8 million euros on 31 July 2006. At 31 October 2006,
the trade payable was still outstanding and the goods were still held by Misson. Similarly Misson has sold goods
to a foreign customer for 4 million euros on 31 July 2006 and it received payment for the goods in euros on
31 October 2006. Additionally Misson had purchased an investment property on 1 November 2005 for
28 million euros. At 31 October 2006, the investment property had a fair value of 24 million euros. The company
uses the fair value model in accounting for investment properties.
Misson would like advice on how to treat these transactions in the financial statements for the year ended 31
October 2006. (7 marks)
Required:
Discuss the accounting treatment of the above transactions in accordance with the advice required by the
directors.
(Candidates should show detailed workings as well as a discussion of the accounting treatment used.)
正确答案:
(b) Inventory, Goods sold and Investment property
The inventory and trade payable initially would be recorded at 8 million euros ÷ 1·6, i.e. $5 million. At the year end, the
amount payable is still outstanding and is retranslated at 1 dollar = 1·3 euros, i.e. $6·2 million. An exchange loss of
$(6·2 – 5) million, i.e. $1·2 million would be reported in profit or loss. The inventory would be recorded at $5 million at the
year end unless it is impaired in value.
The sale of goods would be recorded at 4 million euros ÷ 1·6, i.e. $2·5 million as a sale and as a trade receivable. Payment
is received on 31 October 2006 in euros and the actual value of euros received will be 4 million euros ÷ 1·3,
i.e. $3·1 million.
Thus a gain on exchange of $0·6 million will be reported in profit or loss.
The investment property should be recognised on 1 November 2005 at 28 million euros ÷ 1·4, i.e. $20 million. At
31 October 2006, the property should be recognised at 24 million euros ÷ 1·3, i.e. $18·5 million. The decrease in fair value
should be recognised in profit and loss as a loss on investment property. The property is a non-monetary asset and any foreign
currency element is not recognised separately. When a gain or loss on a non-monetary item is recognised in profit or loss,
any exchange component of that gain or loss is also recognised in profit or loss. If any gain or loss is recognised in equity ona non-monetary asset, any exchange gain is also recognised in equity. -
第14题:
(b) Describe with suitable calculations how the goodwill arising on the acquisition of Briars will be dealt with in
the group financial statements and how the loan to Briars should be treated in the financial statements of
Briars for the year ended 31 May 2006. (9 marks)
正确答案:(b) IAS21 ‘The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates’ requires goodwill arising on the acquisition of a foreign operation
and fair value adjustments to acquired assets and liabilities to be treated as belonging to the foreign operation. They should
be expressed in the functional currency of the foreign operation and translated at the closing rate at each balance sheet date.
Effectively goodwill is treated as a foreign currency asset which is retranslated at the closing rate. In this case the goodwillarising on the acquisition of Briars would be treated as follows:
At 31 May 2006, the goodwill will be retranslated at 2·5 euros to the dollar to give a figure of $4·4 million. Therefore this
will be the figure for goodwill in the balance sheet and an exchange loss of $1·4 million recorded in equity (translation
reserve). The impairment of goodwill will be expensed in profit or loss to the value of $1·2 million. (The closing rate has been
used to translate the impairment; however, there may be an argument for using the average rate.)
The loan to Briars will effectively be classed as a financial liability measured at amortised cost. It is the default category for
financial liabilities that do not meet the definition of financial liabilities at fair value through profit or loss. For most entities,
most financial liabilities will fall into this category. When a financial liability is recognised initially in the balance sheet, the
liability is measured at fair value. Fair value is the amount for which a liability can be settled, between knowledgeable, willing
parties in an arm’s length transaction. In other words, fair value is an actual or estimated transaction price on the reporting
date for a transaction taking place between unrelated parties that have adequate information about the asset or liability being
measured.
Since fair value is a market transaction price, on initial recognition fair value generally is assumed to equal the amount of
consideration paid or received for the financial asset or financial liability. Accordingly, IAS39 specifies that the best evidence
of the fair value of a financial instrument at initial recognition generally is the transaction price. However for longer-term
receivables or payables that do not pay interest or pay a below-market interest, IAS39 does require measurement initially at
the present value of the cash flows to be received or paid.
Thus in Briars financial statements the following entries will be made: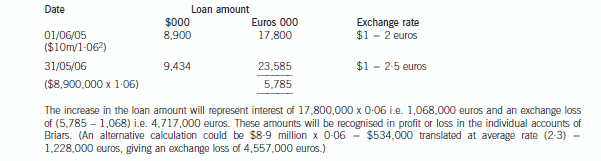
-
第15题:
4 (a) Router, a public limited company operates in the entertainment industry. It recently agreed with a television
company to make a film which will be broadcast on the television company’s network. The fee agreed for the
film was $5 million with a further $100,000 to be paid every time the film is shown on the television company’s
channels. It is hoped that it will be shown on four occasions. The film was completed at a cost of $4 million and
delivered to the television company on 1 April 2007. The television company paid the fee of $5 million on
30 April 2007 but indicated that the film needed substantial editing before they were prepared to broadcast it,
the costs of which would be deducted from any future payments to Router. The directors of Router wish to
recognise the anticipated future income of $400,000 in the financial statements for the year ended 31 May
2007. (5 marks)
Required:
Discuss how the above items should be dealt with in the group financial statements of Router for the year ended
31 May 2007.
正确答案:
(a) Under IAS18 ‘Revenue’, revenue on a service contract is recognised when the outcome of the transaction can be measured
reliably. For revenue arising from the rendering of services, provided that all of the following criteria are met, revenue should
be recognised by reference to the stage of completion of the transaction at the balance sheet date (the percentage-ofcompletion
method) (IAS18 para 20):
(a) the amount of revenue can be measured reliably;
(b) it is probable that the economic benefits will flow to the seller;
(c) the stage of completion at the balance sheet date can be measured reliably; and
(d) the costs incurred, or to be incurred, in respect of the transaction can be measured reliably.
When the above criteria are not met, revenue arising from the rendering of services should be recognised only to the extent
of the expenses recognised that are recoverable. Because the only revenue which can be measured reliably is the fee for
making the film ($5 million), this should therefore be recognised as revenue in the year to 31 May 2007 and matched against
the cost of the film of $4 million. Only when the television company shows the film should any further amounts of $100,000
be recognised as there is an outstanding ‘performance’ condition in the form. of the editing that needs to take place before the
television company will broadcast the film. The costs of the film should not be carried forward and matched against
anticipated future income unless they can be deemed to be an intangible asset under IAS 38 ‘Intangible Assets’. Additionally,
when assessing revenue to be recognised in future years, the costs of the editing and Router’s liability for these costs should
be assessed.
-
第16题:
(c) At 1 June 2006, Router held a 25% shareholding in a film distribution company, Wireless, a public limited
company. On 1 January 2007, Router sold a 15% holding in Wireless thus reducing its investment to a 10%
holding. Router no longer exercises significant influence over Wireless. Before the sale of the shares the net asset
value of Wireless on 1 January 2007 was $200 million and goodwill relating to the acquisition of Wireless was
$5 million. Router received $40 million for its sale of the 15% holding in Wireless. At 1 January 2007, the fair
value of the remaining investment in Wireless was $23 million and at 31 May 2007 the fair value was
$26 million. (6 marks)
Required:
Discuss how the above items should be dealt with in the group financial statements of Router for the year ended
31 May 2007.Required:
Discuss how the above items should be dealt with in the group financial statements of Router for the year ended
31 May 2007.
正确答案:
(c) The investment in Wireless is currently accounted for using the equity method of accounting under IAS28 ‘Investments in
Associates’. On the sale of a 15% holding, the investment in Wireless will be accounted for in accordance with IAS39. Router
should recognise a gain on the sale of the holding in Wireless of $7 million (Working 1). The gain comprises the following:
(i) the difference between the sale proceeds and the proportion of the net assets sold and
(ii) the goodwill disposed of.
The total gain is shown in the income statement.
The remaining 10 per cent investment will be classified as an ‘available for sale’ financial asset or at ‘fair value through profit
or loss’ financial asset. Changes in fair value for these categories are reported in equity or in the income statement respectively.
At 1 January 2007, the investment will be recorded at fair value and a gain of $1 million $(23 – 22) recorded. At 31 May
2007 a further gain of $(26 – 23) million, i.e. $3 million will be recorded. In order for the investment to be categorised as
at fair value through profit or loss, certain conditions have to be fulfilled. An entity may use this designation when doing so
results in more relevant information by eliminating or significantly reducing a measurement or recognition inconsistency (an
‘accounting mismatch’) or where a group of financial assets and/or financial liabilities is managed and its performance is
evaluated on a fair value basis, in accordance with a documented risk management or investment strategy, and information
about the assets and/ or liabilities is provided internally to the entity’s key management personnel.
-
第17题:
(b) One of the hotels owned by Norman is a hotel complex which includes a theme park, a casino and a golf course,
as well as a hotel. The theme park, casino, and hotel were sold in the year ended 31 May 2008 to Conquest, a
public limited company, for $200 million but the sale agreement stated that Norman would continue to operate
and manage the three businesses for their remaining useful life of 15 years. The residual interest in the business
reverts back to Norman after the 15 year period. Norman would receive 75% of the net profit of the businesses
as operator fees and Conquest would receive the remaining 25%. Norman has guaranteed to Conquest that the
net minimum profit paid to Conquest would not be less than $15 million. (4 marks)
Norman has recently started issuing vouchers to customers when they stay in its hotels. The vouchers entitle the
customers to a $30 discount on a subsequent room booking within three months of their stay. Historical
experience has shown that only one in five vouchers are redeemed by the customer. At the company’s year end
of 31 May 2008, it is estimated that there are vouchers worth $20 million which are eligible for discount. The
income from room sales for the year is $300 million and Norman is unsure how to report the income from room
sales in the financial statements. (4 marks)
Norman has obtained a significant amount of grant income for the development of hotels in Europe. The grants
have been received from government bodies and relate to the size of the hotel which has been built by the grant
assistance. The intention of the grant income was to create jobs in areas where there was significant
unemployment. The grants received of $70 million will have to be repaid if the cost of building the hotels is less
than $500 million. (4 marks)
Appropriateness and quality of discussion (2 marks)
Required:
Discuss how the above income would be treated in the financial statements of Norman for the year ended
31 May 2008.
正确答案:
(b) Property is sometimes sold with a degree of continuing involvement by the seller so that the risks and rewards of ownership
have not been transferred. The nature and extent of the buyer’s involvement will determine how the transaction is accounted
for. The substance of the transaction is determined by looking at the transaction as a whole and IAS18 ‘Revenue’ requires
this by stating that where two or more transactions are linked, they should be treated as a single transaction in order to
understand the commercial effect (IAS18 paragraph 13). In the case of the sale of the hotel, theme park and casino, Norman
should not recognise a sale as the company continues to enjoy substantially all of the risks and rewards of the businesses,
and still operates and manages them. Additionally the residual interest in the business reverts back to Norman. Also Norman
has guaranteed the income level for the purchaser as the minimum payment to Conquest will be $15 million a year. The
transaction is in substance a financing arrangement and the proceeds should be treated as a loan and the payment of profits
as interest.
The principles of IAS18 and IFRIC13 ‘Customer Loyalty Programmes’ require that revenue in respect of each separate
component of a transaction is measured at its fair value. Where vouchers are issued as part of a sales transaction and are
redeemable against future purchases, revenue should be reported at the amount of the consideration received/receivable less
the voucher’s fair value. In substance, the customer is purchasing both goods or services and a voucher. The fair value of the
voucher is determined by reference to the value to the holder and not the cost to the issuer. Factors to be taken into account
when estimating the fair value, would be the discount the customer obtains, the percentage of vouchers that would be
redeemed, and the time value of money. As only one in five vouchers are redeemed, then effectively the hotel has sold goods
worth ($300 + $4) million, i.e. $304 million for a consideration of $300 million. Thus allocating the discount between the
two elements would mean that (300 ÷ 304 x $300m) i.e. $296·1 million will be allocated to the room sales and the balance
of $3·9 million to the vouchers. The deferred portion of the proceeds is only recognised when the obligations are fulfilled.
The recognition of government grants is covered by IAS20 ‘Accounting for government grants and disclosure of government
assistance’. The accruals concept is used by the standard to match the grant received with the related costs. The relationship
between the grant and the related expenditure is the key to establishing the accounting treatment. Grants should not be
recognised until there is reasonable assurance that the company can comply with the conditions relating to their receipt and
the grant will be received. Provision should be made if it appears that the grant may have to be repaid.
There may be difficulties of matching costs and revenues when the terms of the grant do not specify precisely the expense
towards which the grant contributes. In this case the grant appears to relate to both the building of hotels and the creation of
employment. However, if the grant was related to revenue expenditure, then the terms would have been related to payroll or
a fixed amount per job created. Hence it would appear that the grant is capital based and should be matched against the
depreciation of the hotels by using a deferred income approach or deducting the grant from the carrying value of the asset
(IAS20). Additionally the grant is only to be repaid if the cost of the hotel is less than $500 million which itself would seem
to indicate that the grant is capital based. If the company feels that the cost will not reach $500 million, a provision should
be made for the estimated liability if the grant has been recognised. -
第18题:
(b) Explain why making sales of Sabals in North America will have no effect on Nikau Ltd’s ability to recover its
input tax. (3 marks)
Notes: – you should assume that the corporation tax rates and allowances for the financial year to 31 March 2007
will continue to apply for the foreseeable future.
– you should ignore indexation allowance.
正确答案:
(b) Recoverability of input tax
Sales by Nikau Ltd of its existing products are subject to UK VAT at 17·5% because it is selling to domestic customers who
will not be registered for VAT. Accordingly, at present, Nikau Ltd can recover all of its input tax.
Sales to customers in North America will be zero rated because the goods are being exported from the EU. Zero rated supplies
are classified as taxable for the purposes of VAT and therefore Nikau Ltd will continue to be able to recover all of its input tax. -
第19题:
(b) Using the information provided, state the financial statement risks arising and justify an appropriate audit
approach for Indigo Co for the year ending 31 December 2005. (14 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Financial statement risks
Assets
■ There is a very high risk that inventory could be materially overstated in the balance sheet (thereby overstating profit)
because:
? there is a high volume of metals (hence material);
? valuable metals are made more portable;
? subsidy gives an incentive to overstate purchases (and hence inventory);
? inventory may not exist due to lack of physical controls (e.g. aluminium can blow away);
? scrap metal in the stockyard may have zero net realisable value (e.g. iron is rusty and slow-moving);
? quantities per counts not attended by an auditor have increased by a third.
■ Inventory could be otherwise misstated (over or under) due to:
? the weighbridge being inaccurate;
? metal qualities being estimated;
? different metals being mixed up; and
? the lack of an independent expert to identify/measure/value metals.
■ Tangible non-current assets are understated as the parts of the furnaces that require replacement (the linings) are not
capitalised (and depreciated) as separate items but treated as repairs/maintenance/renewals and expensed.
■ Cash may be understated due to incomplete recording of sales.
■ Recorded cash will be overstated if it does not exist (e.g. if it has been stolen).
■ Trade receivables may be understated if cash receipts from credit customers have been misappropriated.
Liabilities
■ The provision for the replacement of the furnace linings is overstated by the amount provided in the current and previous
year (i.e. in its entirety).
Tutorial note: Last replacement was two years ago.
Income statement
■ Revenue will be understated in respect of unrecorded cash sales of salvaged metals and ‘clinker’.
■ Scrap metal purchases (for cash) are at risk of overstatement:
? to inflate the 15% subsidy;
? to conceal misappropriated cash.
■ The income subsidy will be overstated if quantities purchased are overstated and/or overvalued (on the quarterly returns)
to obtain the amount of the subsidy.
■ Cash receipts/payments that were recorded only in the cash book in November are at risk of being unrecorded (in the
absence of cash book postings for November), especially if they are of a ‘one-off’ nature.
Tutorial note: Cash purchases of scrap and sales of salvaged metal should be recorded elsewhere (i.e. in the manual
inventory records). However, a one-off expense (of a capital or revenue nature) could be omitted in the absence of
another record.
■ Expenditure is overstated in respect of the 25% provision for replacing the furnace linings. However, as depreciation
will be similarly understated (as the furnace linings have not been capitalised) there is no risk of material misstatement
to the income statement overall.
Disclosure risk
■ A going concern (‘failure’) risk may arise through the loss of:
? sales revenue (e.g. through misappropriation of salvaged metals and/or cash);
? the subsidy (e.g. if returns are prepared fraudulently);
? cash (e.g. if material amounts stolen).
Any significant doubts about going concern must be suitably disclosed in the notes to the financial statements.
Disclosure risk arises if the requirements of IAS 1 ‘Presentation of Financial Statements’ are not met.
■ Disclosure risk arises if contingent liabilities in connection with the dumping of ‘clinker’ (e.g. for fines and penalties) are
not adequately disclosed in accordance with IAS 37 ‘Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets’.
Appropriate audit approach
Tutorial note: In explaining why AN audit approach is appropriate for Indigo it can be relevant to comment on the
unsuitability of other approaches.
■ A risk-based approach is suitable because:
? inherent risk is high at the entity and financial assertion levels;
? material errors are likely to arise in inventory where a high degree of subjectivity will be involved (regarding quality
of metals, quantities, net realisable value, etc);
? it directs the audit effort to inventory, purchases, income (sales and subsidy) and other risk areas (e.g. contingent
liabilities).
■ A systems-based/compliance approach is not suited to the risk areas identified because controls are lacking/ineffective
(e.g. over inventory and cash). Also, as the audit appointment was not more than three months ago and no interim
audit has been conducted (and the balance sheet date is only three weeks away) testing controls is likely to be less
efficient than a substantive approach.
■ A detailed substantive/balance sheet approach would be suitable to direct audit effort to the appropriate valuation of
assets (and liabilities) existing at balance sheet date. Principal audit work would include:
? attendance at a full physical inventory count at 31 December 2005;
? verifying cash at bank (through bank confirmation and reconciliation) and in hand (through physical count);
? confirming the accuracy of the quarterly returns to the local authority.
■ A cyclical approach/directional testing is unlikely to be suitable as cycles are incomplete. For example the purchases
cycle for metals is ‘purchase/cash’ rather than ‘purchase/payable/cash’ and there is no independent third party evidence
to compensate for that which would be available if there were trade payables (i.e. suppliers’ statements). Also the cycles
are inextricably inter-related to cash and inventory – amounts of which are subject to high inherent risk.
■ Analytical procedures may be of limited use for substantive purposes. Factors restricting the use of substantive analytical
procedures include:
? fluctuating margins (e.g. as many factors will influence the price at which scrap is purchased and subsequently
sold, when salvaged, sometime later);
? a lack of reliable/historic information on which to make comparisons. -
第20题:
(b) You are an audit manager with specific responsibility for reviewing other information in documents containing
audited financial statements before your firm’s auditor’s report is signed. The financial statements of Hegas, a
privately-owned civil engineering company, show total assets of $120 million, revenue of $261 million, and profit
before tax of $9·2 million for the year ended 31 March 2005. Your review of the Annual Report has revealed
the following:
(i) The statement of changes in equity includes $4·5 million under a separate heading of ‘miscellaneous item’
which is described as ‘other difference not recognized in income’. There is no further reference to this
amount or ‘other difference’ elsewhere in the financial statements. However, the Management Report, which
is required by statute, is not audited. It discloses that ‘changes in shareholders’ equity not recognized in
income includes $4·5 million arising on the revaluation of investment properties’.
The notes to the financial statements state that the company has implemented IAS 40 ‘Investment Property’
for the first time in the year to 31 March 2005 and also that ‘the adoption of this standard did not have a
significant impact on Hegas’s financial position or its results of operations during 2005’.
(ii) The chairman’s statement asserts ‘Hegas has now achieved a position as one of the world’s largest
generators of hydro-electricity, with a dedicated commitment to accountable ethical professionalism’. Audit
working papers show that 14% of revenue was derived from hydro-electricity (2004: 12%). Publicly
available information shows that there are seven international suppliers of hydro-electricity in Africa alone,
which are all at least three times the size of Hegas in terms of both annual turnover and population supplied.
Required:
Identify and comment on the implications of the above matters for the auditor’s report on the financial
statements of Hegas for the year ended 31 March 2005. (10 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Implications for the auditor’s report
(i) Management Report
■ $4·5 million represents 3·75% of total assets, 1·7% of revenue and 48·9% profit before tax. As this is material
by any criteria (exceeding all of 2% of total assets, 1/2% revenue and 5% PBT), the specific disclosure requirements
of IASs need to be met (IAS 1 ‘Presentation of Financial Statements’).
■ The Management Report discloses the amount and the reason for a material change in equity whereas the financial
statements do not show the reason for the change and suggest that it is immaterial. As the increase in equity
attributable to this adjustment is nearly half as much as that attributable to PBT there is a material inconsistency
between the Management Report and the audited financial statements.
■ Amendment to the Management Report is not required.
Tutorial note: Marks will be awarded for arguing, alternatively, that the Management Report disclosure needs to
be amended to clarify that the revaluation arises from the first time implementation.
■ Amendment to the financial statements is required because the disclosure is:
– incorrect – as, on first adoption of IAS 40, the fair value adjustment should be against the opening balance
of retained earnings; and
– inadequate – because it is being ‘supplemented’ by additional disclosure in a document which is not within
the scope of the audit of financial statements.
■ Whilst it is true that the adoption of IAS 40 did not have a significant impact on results of operations, Hegas’s
financial position has increased by nearly 4% in respect of the revaluation (to fair value) of just one asset category
(investment properties). As this is significant, the statement in the notes should be redrafted.
■ If the financial statements are not amended, the auditor’s report should be qualified ‘except for’ on grounds of
disagreement (non-compliance with IAS 40) as the matter is material but not pervasive. Additional disclosure
should also be given (e.g. that the ‘other difference’ is a fair value adjustment).
■ However, it is likely that when faced with the prospect of a qualified auditor’s report Hegas’s management will
rectify the financial statements so that an unmodified auditor’s report can be issued.
Tutorial note: Marks will be awarded for other relevant points e.g. citing IAS 8 ‘Accounting Policies, Changes in
Accounting Estimates and Errors’.
(ii) Chairman’s statement
Tutorial note: Hegas is privately-owned therefore IAS 14 ‘Segment Reporting’ does not apply and the proportion of
revenue attributable to hydro-electricity will not be required to be disclosed in the financial statements. However, credit
will be awarded for discussing the implications for the auditor’s report if it is regarded as a material inconsistency on
the assumption that segment revenue (or similar) is reported in the financial statements.
■ The assertion in the chairman’s statement, which does not fall within the scope of the audit of the financial
statements, claims two things, namely that the company:
(1) is ‘one of the world’s largest generators of hydro-electricity’; and
(2) has ‘a dedicated commitment to accountable ethical professionalism’.
■ To the extent that this information does not relate to matters disclosed in the financial statements it may give rise
to a material misstatement of fact. In particular, the first statement presents a misleading impression of the
company’s size. In misleading a user of the financial statements with this statement, the second statement is not
true (as it is not ethical or professional to mislead the reader and potentially undermine the credibility of the
financial statements).
■ The first statement is a material misstatement of fact because, for example:
– the company is privately-owned, and publicly-owned international/multi-nationals are larger;
– the company’s main activity is civil engineering not electricity generation (only 14% of revenue is derived from
HEP);
– as the company ranks at best eighth against African companies alone it ranks much lower globally.
■ Hegas should be asked to reconsider the wording of the chairman’s statement (i.e. removing these assertions) and
consult, as necessary, the company’s legal advisor.
■ If the statement is not changed there will be no grounds for qualification of the opinion on the audited financial
statements. The audit firm should therefore take legal advice on how the matter should be reported.
■ However, an emphasis of matter paragraph may be used to report on matters other than those affecting the audited
financial statements. For example, to explain the misstatement of fact if management refuses to make the
amendment.
Tutorial note: Marks will also be awarded for relevant comments about the chairman’s statement being perceived by
many readers to be subject to audit and therefore that the unfounded statement might undermine the credibility of the
financial statements. Shareholders tend to rely on the chairman’s statement, even though it is not regulated or audited,
because modern financial statements are so complex. -
第21题:
(b) Seymour offers health-related information services through a wholly-owned subsidiary, Aragon Co. Goodwill of
$1·8 million recognised on the purchase of Aragon in October 2004 is not amortised but included at cost in the
consolidated balance sheet. At 30 September 2006 Seymour’s investment in Aragon is shown at cost,
$4·5 million, in its separate financial statements.
Aragon’s draft financial statements for the year ended 30 September 2006 show a loss before taxation of
$0·6 million (2005 – $0·5 million loss) and total assets of $4·9 million (2005 – $5·7 million). The notes to
Aragon’s financial statements disclose that they have been prepared on a going concern basis that assumes that
Seymour will continue to provide financial support. (7 marks)
Required:
For each of the above issues:
(i) comment on the matters that you should consider; and
(ii) state the audit evidence that you should expect to find,
in undertaking your review of the audit working papers and financial statements of Seymour Co for the year ended
30 September 2006.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three issues.
正确答案:
(b) Goodwill
(i) Matters
■ Cost of goodwill, $1·8 million, represents 3·4% consolidated total assets and is therefore material.
Tutorial note: Any assessments of materiality of goodwill against amounts in Aragon’s financial statements are
meaningless since goodwill only exists in the consolidated financial statements of Seymour.
■ It is correct that the goodwill is not being amortised (IFRS 3 Business Combinations). However, it should be tested
at least annually for impairment, by management.
■ Aragon has incurred losses amounting to $1·1 million since it was acquired (two years ago). The write-off of this
amount against goodwill in the consolidated financial statements would be material (being 61% cost of goodwill,
8·3% PBT and 2·1% total assets).
■ The cost of the investment ($4·5 million) in Seymour’s separate financial statements will also be material and
should be tested for impairment.
■ The fair value of net assets acquired was only $2·7 million ($4·5 million less $1·8 million). Therefore the fair
value less costs to sell of Aragon on other than a going concern basis will be less than the carrying amount of the
investment (i.e. the investment is impaired by at least the amount of goodwill recognised on acquisition).
■ In assessing recoverable amount, value in use (rather than fair value less costs to sell) is only relevant if the going
concern assumption is appropriate for Aragon.
■ Supporting Aragon financially may result in Seymour being exposed to actual and/or contingent liabilities that
should be provided for/disclosed in Seymour’s financial statements in accordance with IAS 37 Provisions,
Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets.
(ii) Audit evidence
■ Carrying values of cost of investment and goodwill arising on acquisition to prior year audit working papers and
financial statements.
■ A copy of Aragon’s draft financial statements for the year ended 30 September 2006 showing loss for year.
■ Management’s impairment test of Seymour’s investment in Aragon and of the goodwill arising on consolidation at
30 September 2006. That is a comparison of the present value of the future cash flows expected to be generated
by Aragon (a cash-generating unit) compared with the cost of the investment (in Seymour’s separate financial
statements).
■ Results of any impairment tests on Aragon’s assets extracted from Aragon’s working paper files.
■ Analytical procedures on future cash flows to confirm their reasonableness (e.g. by comparison with cash flows for
the last two years).
■ Bank report for audit purposes for any guarantees supporting Aragon’s loan facilities.
■ A copy of Seymour’s ‘comfort letter’ confirming continuing financial support of Aragon for the foreseeable future. -
第22题:
(b) Explain what effect the acquisition of Di Rollo Co will have on the planning of your audit of the consolidated
financial statements of Murray Co for the year ending 31 March 2008. (10 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Effect of acquisition on planning the audit of Murray’s consolidated financial statements for the year ending 31 March
2008
Group structure
The new group structure must be ascertained to identify all entities that should be consolidated into the Murray group’s
financial statements for the year ending 31 March 2008.
Materiality assessment
Preliminary materiality for the group will be much higher, in monetary terms, than in the prior year. For example, if a % of
total assets is a determinant of the preliminary materiality, it may be increased by 10% (as the fair value of assets acquired,
including goodwill, is $2,373,000 compared with $21·5m in Murray’s consolidated financial statements for the year ended
31 March 2007).
The materiality of each subsidiary should be re-assessed, in terms of the enlarged group as at the planning stage. For
example, any subsidiary that was just material for the year ended 31 March 2007 may no longer be material to the group.
This assessment will identify, for example:
– those entities requiring an audit visit; and
– those entities for which substantive analytical procedures may suffice.
As Di Rollo’s assets are material to the group Ross should plan to inspect the South American operations. The visit may
include a meeting with Di Rollo’s previous auditors to discuss any problems that might affect the balances at acquisition and
a review of the prior year audit working papers, with their permission.
Di Rollo was acquired two months into the financial year therefore its post-acquisition results should be expected to be
material to the consolidated income statement.
Goodwill acquired
The assets and liabilities of Di Rollo at 31 March 2008 will be combined on a line-by-line basis into the consolidated financial
statements of Murray and goodwill arising on acquisition recognised.
Audit work on the fair value of the Di Rollo brand name at acquisition, $600,000, may include a review of a brand valuation
specialist’s working papers and an assessment of the reasonableness of assumptions made.
Significant items of plant are likely to have been independently valued prior to the acquisition. It may be appropriate to plan
to place reliance on the work of expert valuers. The fair value adjustment on plant and equipment is very high (441% of
carrying amount at the date of acquisition). This may suggest that Di Rollo’s depreciation policies are over-prudent (e.g. if
accelerated depreciation allowed for tax purposes is accounted for under local GAAP).
As the amount of goodwill is very material (approximately 50% of the cash consideration) it may be overstated if Murray has
failed to recognise any assets acquired in the purchase of Di Rollo in accordance with IFRS 3 Business Combinations. For
example, Murray may have acquired intangible assets such as customer lists or franchises that should be recognised
separately from goodwill and amortised (rather than tested for impairment).
Subsequent impairment
The audit plan should draw attention to the need to consider whether the Di Rollo brand name and goodwill arising have
suffered impairment as a result of the allegations against Di Rollo’s former chief executive.
Liabilities
Proceedings in the legal claim made by Di Rollo’s former chief executive will need to be reviewed. If the case is not resolved
at 31 March 2008, a contingent liability may require disclosure in the consolidated financial statements, depending on the
materiality of amounts involved. Legal opinion on the likelihood of Di Rollo successfully defending the claim may be sought.
Provision should be made for any actual liabilities, such as legal fees.
Group (related party) transactions and balances
A list of all the companies in the group (including any associates) should be included in group audit instructions to ensure
that intra-group transactions and balances (and any unrealised profits and losses on transactions with associates) are
identified for elimination on consolidation. Any transfer pricing policies (e.g. for clothes manufactured by Di Rollo for Murray
and sales of Di Rollo’s accessories to Murray’s retail stores) must be ascertained and any provisions for unrealised profit
eliminated on consolidation.
It should be confirmed at the planning stage that inter-company transactions are identified as such in the accounting systems
of all companies and that inter-company balances are regularly reconciled. (Problems are likely to arise if new inter-company
balances are not identified/reconciled. In particular, exchange differences are to be expected.)
Other auditors
If Ross plans to use the work of other auditors in South America (rather than send its own staff to undertake the audit of Di
Rollo), group instructions will need to be sent containing:
– proforma statements;
– a list of group and associated companies;
– a statement of group accounting policies (see below);
– the timetable for the preparation of the group accounts (see below);
– a request for copies of management letters;
– an audit work summary questionnaire or checklist;
– contact details (of senior members of Ross’s audit team).
Accounting policies
Di Rollo may have material accounting policies which do not comply with the rest of the Murray group. As auditor to Di Rollo,
Ross will be able to recalculate the effect of any non-compliance with a group accounting policy (that Murray’s management
would be adjusting on consolidation).
Timetable
The timetable for the preparation of Murray’s consolidated financial statements should be agreed with management as soon
as possible. Key dates should be planned for:
– agreement of inter-company balances and transactions;
– submission of proforma statements;
– completion of the consolidation package;
– tax review of group accounts;
– completion of audit fieldwork by other auditors;
– subsequent events review;
– final clearance on accounts of subsidiaries;
– Ross’s final clearance of consolidated financial statements.
Tutorial note: The order of dates is illustrative rather than prescriptive. -
第23题:
(b) You are the manager responsible for the audit of Poppy Co, a manufacturing company with a year ended
31 October 2008. In the last year, several investment properties have been purchased to utilise surplus funds
and to provide rental income. The properties have been revalued at the year end in accordance with IAS 40
Investment Property, they are recognised on the statement of financial position at a fair value of $8 million, and
the total assets of Poppy Co are $160 million at 31 October 2008. An external valuer has been used to provide
the fair value for each property.
Required:
(i) Recommend the enquiries to be made in respect of the external valuer, before placing any reliance on their
work, and explain the reason for the enquiries; (7 marks)
正确答案:
(b) (i) Enquiries in respect of the external valuer
Enquiries would need to be made for two main reasons, firstly to determine the competence, and secondly the objectivity
of the valuer. ISA 620 Using the Work of an Expert contains guidance in this area.
Competence
Enquiries could include:
– Is the valuer a member of a recognised professional body, for example a nationally or internationally recognised
institute of registered surveyors?
– Does the valuer possess any necessary licence to carry out valuations for companies?
– How long has the valuer been a member of the recognised body, or how long has the valuer been licensed under
that body?
– How much experience does the valuer have in providing valuations of the particular type of investment properties
held by Poppy Co?
– Does the valuer have specific experience of evaluating properties for the purpose of including their fair value within
the financial statements?
– Is there any evidence of the reputation of the valuer, e.g. professional references, recommendations from other
companies for which a valuation service has been provided?
– How much experience, if any, does the valuer have with Poppy Co?
Using the above enquiries, the auditor is trying to form. an opinion as to the relevance and reliability of the valuation
provided. ISA 500 Audit Evidence requires that the auditor gathers evidence that is both sufficient and appropriate. The
auditor needs to ensure that the fair values provided by the valuer for inclusion in the financial statements have been
arrived at using appropriate knowledge and skill which should be evidenced by the valuer being a member of a
professional body, and, if necessary, holding a licence under that body.
It is important that the fair values have been arrived at using methods allowed under IAS 40 Investment Property. If any
other valuation method has been used then the value recognised in the statement of financial position may not be in
accordance with financial reporting standards. Thus it is important to understand whether the valuer has experience
specifically in providing valuations that comply with IAS 40, and how many times the valuer has appraised properties
similar to those owned by Poppy Co.
In gauging the reliability of the fair value, the auditor may wish to consider how Poppy Co decided to appoint this
particular valuer, e.g. on the basis of a recommendation or after receiving references from companies for which
valuations had previously been provided.
It will also be important to consider how familiar the valuer is with Poppy Co’s business and environment, as a way to
assess the reliability and appropriateness of any assumptions used in the valuation technique.
Objectivity
Enquiries could include:
– Does the valuer have any financial interest in Poppy Co, e.g. shares held directly or indirectly in the company?
– Does the valuer have any personal relationship with any director or employee of Poppy Co?
– Is the fee paid for the valuation service reasonable and a fair, market based price?
With these enquiries, the auditor is gaining assurance that the valuer will perform. the valuation from an independent
point of view. If the valuer had a financial interest in Poppy Co, there would be incentive to manipulate the valuation in
a way best suited to the financial statements of the company. Equally if the valuer had a personal relationship with a
senior member of staff at Poppy Co, the valuer may feel pressured to give a favourable opinion on the valuation of the
properties.
The level of fee paid is important. It should be commensurate with the market rate paid for this type of valuation. If the
valuer was paid in excess of what might be considered a normal fee, it could indicate that the valuer was encouraged,
or even bribed, to provide a favourable valuation.
